| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Normal optical microscopes can magnify up to with a theoretical resolution of . The lenses can be quite complicated and are composed of multiple elements to reduce aberrations. Microscope objective lenses are particularly important as they primarily gather light from the specimen. Three parameters describe microscope objectives: the numerical aperture , the magnification , and the working distance. The is related to the light gathering ability of a lens and is obtained using the angle of acceptance formed by the maximum cone of rays focusing on the specimen (see [link] (a)) and is given by
where is the refractive index of the medium between the lens and the specimen and . As the angle of acceptance given by increases, becomes larger and more light is gathered from a smaller focal region giving higher resolution. A objective gives more detail than a objective.
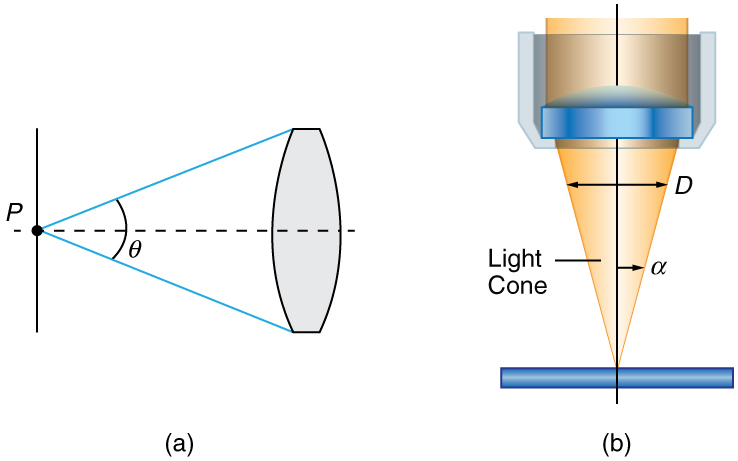
While the numerical aperture can be used to compare resolutions of various objectives, it does not indicate how far the lens could be from the specimen. This is specified by the “working distance,” which is the distance (in mm usually) from the front lens element of the objective to the specimen, or cover glass. The higher the the closer the lens will be to the specimen and the more chances there are of breaking the cover slip and damaging both the specimen and the lens. The focal length of an objective lens is different than the working distance. This is because objective lenses are made of a combination of lenses and the focal length is measured from inside the barrel. The working distance is a parameter that microscopists can use more readily as it is measured from the outermost lens. The working distance decreases as the and magnification both increase.
The term in general is called the -number and is used to denote the light per unit area reaching the image plane. In photography, an image of an object at infinity is formed at the focal point and the -number is given by the ratio of the focal length of the lens and the diameter of the aperture controlling the light into the lens (see [link] (b)). If the acceptance angle is small the of the lens can also be used as given below.
As the -number decreases, the camera is able to gather light from a larger angle, giving wide-angle photography. As usual there is a trade-off. A greater means less light reaches the image plane. A setting of usually allows one to take pictures in bright sunlight as the aperture diameter is small. In optical fibers, light needs to be focused into the fiber. [link] shows the angle used in calculating the of an optical fiber.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for the modern world' conversation and receive update notifications?