| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
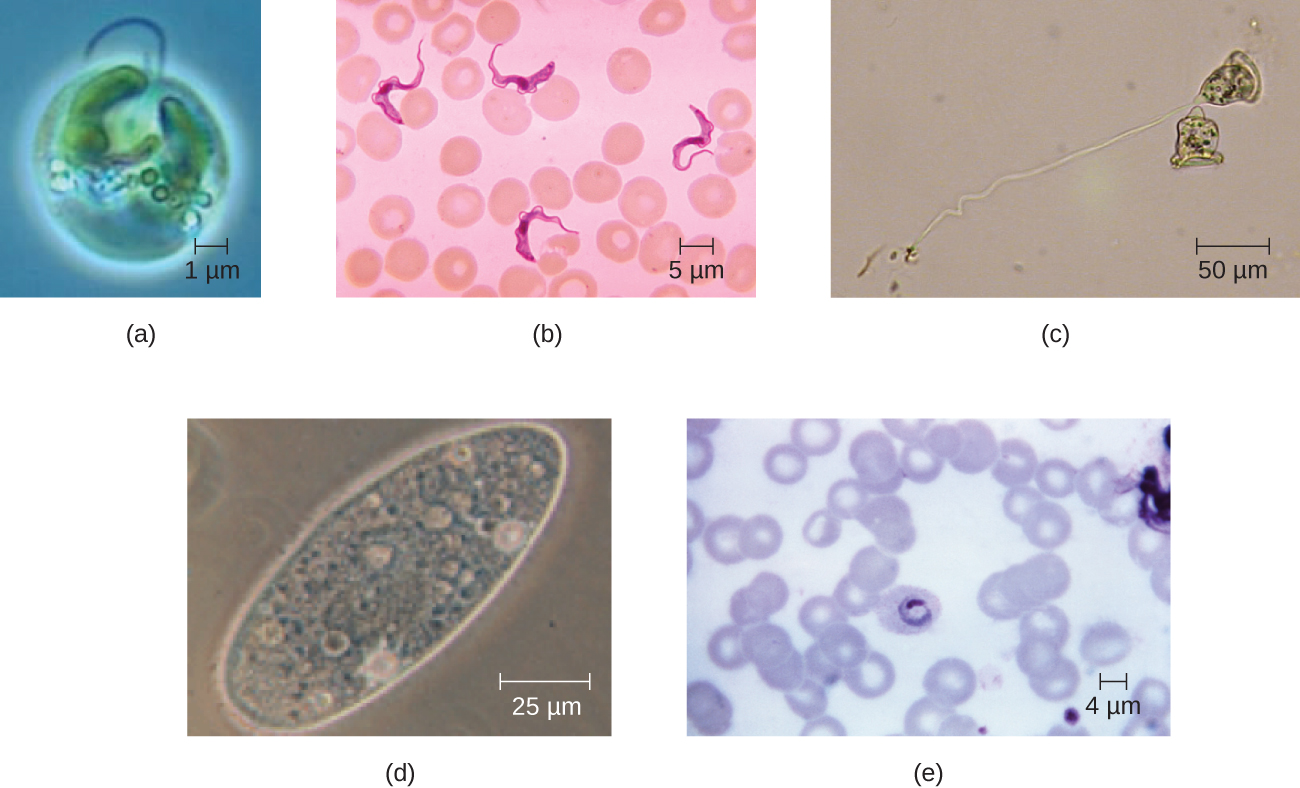
Unlike prokaryotic cells, in which DNA is loosely contained in the nucleoid region, eukaryotic cells possess a nucleus , which is surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane that houses the DNA genome ( [link] ). By containing the cell’s DNA, the nucleus ultimately controls all activities of the cell and also serves an essential role in reproduction and heredity. Eukaryotic cells typically have their DNA organized into multiple linear chromosomes. The DNA within the nucleus is highly organized and condensed to fit inside the nucleus, which is accomplished by wrapping the DNA around proteins called histones.
Although most eukaryotic cells have only one nucleus, exceptions exist. For example, protozoans of the genus Paramecium typically have two complete nuclei: a small nucleus that is used for reproduction (micronucleus) and a large nucleus that directs cellular metabolism (macronucleus). Additionally, some fungi transiently form cells with two nuclei, called heterokaryotic cells, during sexual reproduction. Cells whose nuclei divide, but whose cytoplasm does not, are called coenocytes .
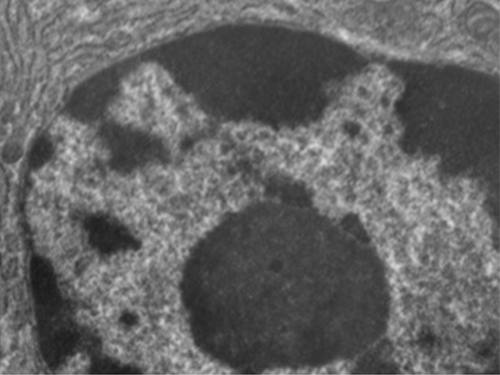
The nucleus is bound by a complex nuclear membrane , often called the nuclear envelope , that consists of two distinct lipid bilayers that are contiguous with each other ( [link] ). Despite these connections between the inner and outer membranes, each membrane contains unique lipids and proteins on its inner and outer surfaces. The nuclear envelope contains nuclear pores, which are large, rosette-shaped protein complexes that control the movement of materials into and out of the nucleus. The overall shape of the nucleus is determined by the nuclear lamina , a meshwork of intermediate filaments found just inside the nuclear envelope membranes. Outside the nucleus, additional intermediate filaments form a looser mesh and serve to anchor the nucleus in position within the cell.
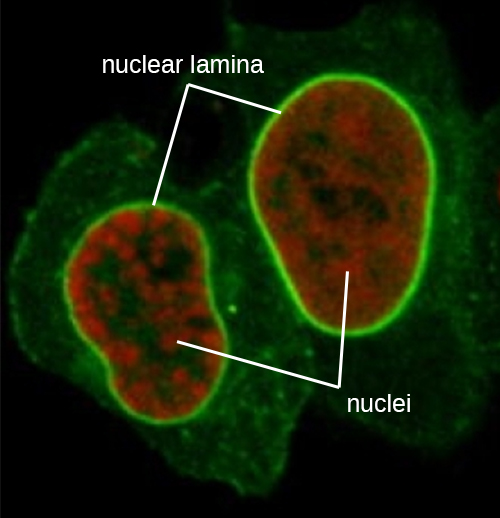
The nucleolus is a dense region within the nucleus where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) biosynthesis occurs. In addition, the nucleolus is also the site where assembly of ribosomes begins. Preribosomal complexes are assembled from rRNA and proteins in the nucleolus; they are then transported out to the cytoplasm, where ribosome assembly is completed ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?