| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
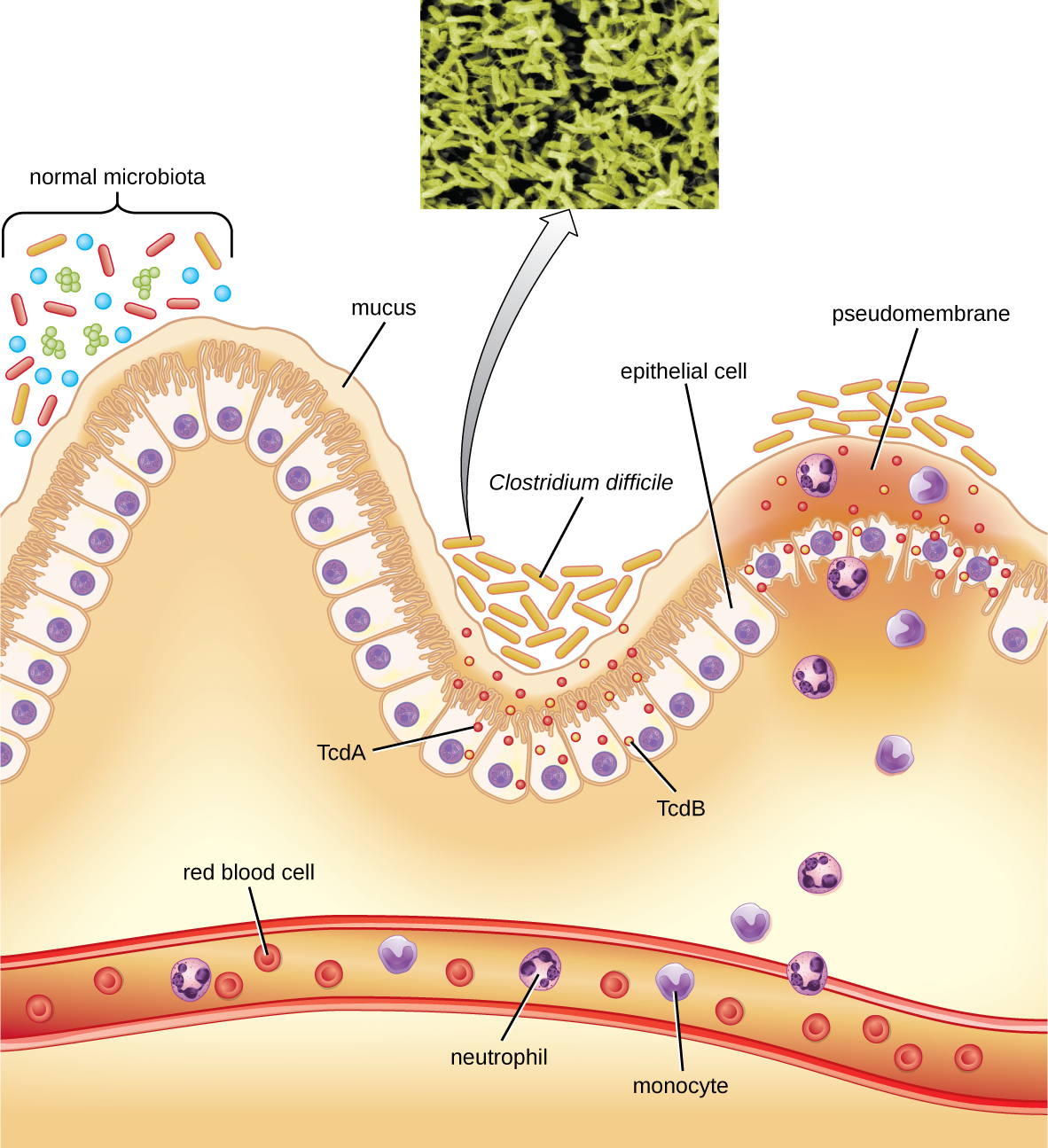
This bacterium produces two toxins, Clostridium difficile toxin A (TcdA) and Clostridium difficile toxin B (TcdB). These toxins inactivate small GTP-binding proteins, resulting in actin condensation and cell rounding, followed by cell death. Infections begin with focal necrosis, then ulceration with exudate, and can progress to pseudomembranous colitis , which involves inflammation of the colon and the development of a pseudomembrane of fibrin containing dead epithelial cells and leukocytes ( [link] ). Watery diarrhea, dehydration, fever, loss of appetite, and abdominal pain can result. Perforation of the colon can occur, leading to septicemia, shock, and death. C. difficile is also associated with necrotizing enterocolitis in premature babies and neutropenic enterocolitis associated with cancer therapies.
Diagnosis is made by considering the patient history (such as exposure to antibiotics), clinical presentation, imaging, endoscopy, lab tests, and other available data. Detecting the toxin in stool samples is used to confirm diagnosis. Although culture is preferred, it is rarely practical in clinical practice because the bacterium is an obligate anaerobe. Nucleic acid amplification tests, including PCR, are considered preferable to ELISA testing for molecular analysis.
The first step of conventional treatment is to stop antibiotic use, and then to provide supportive therapy with electrolyte replacement and fluids. Metronidazole is the preferred treatment if the C. difficile diagnosis has been confirmed. Vancomycin can also be used, but it should be reserved for patients for whom metronidazole was ineffective or who meet other criteria (e.g., under 10 years of age, pregnant, or allergic to metronidazole).
A newer approach to treatment, known as a fecal transplant , focuses on restoring the microbiota of the gut in order to combat the infection. In this procedure, a healthy individual donates a stool sample, which is mixed with saline and transplanted to the recipient via colonoscopy, endoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, or enema. It has been reported that this procedure has greater than 90% success in resolving C. difficile infections. Faith Rohlke and Neil Stollman. “Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Relapsing Clostridium difficile Infection,” Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology 5 (2012) 6: 403–420. doi: 10.1177/1756283X12453637.
Bacillus cereus , commonly found in soil, is a gram-positive endospore-forming bacterium that can sometimes cause foodborne illness. B. cereus endospores can survive cooking and produce enterotoxins in food after it has been heated; illnesses often occur after eating rice and other prepared foods left at room temperature for too long. The signs and symptoms appear within a few hours of ingestion and include nausea, pain, and abdominal cramps. B. cereus produces two toxins: one causing diarrhea, and the other causing vomiting. More severe signs and symptoms can sometimes develop.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?