| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The National Center for Biotechnology Information houses a widely used genetic sequence database called GenBank where researchers deposit genetic information for public use. Upon publication of sequence data, researchers upload it to GenBank, giving other researchers access to the information. The collaboration allows researchers to compare newly discovered or unknown sample sequence information with the vast array of sequence data that already exists.

View an animation about 454 sequencing to deepen your understanding of this method.
Javier, an 80-year-old patient with a history of heart disease, recently returned home from the hospital after undergoing an angioplasty procedure to insert a stent into a cardiac artery. To minimize the possibility of infection, Javier was administered intravenous broad-spectrum antibiotics during and shortly after his procedure. He was released four days after the procedure, but a week later, he began to experience mild abdominal cramping and watery diarrhea several times a day. He lost his appetite, became severely dehydrated, and developed a fever. He also noticed blood in his stool. Javier’s wife called the physician, who instructed her to take him to the emergency room immediately.
The hospital staff ran several tests and found that Javier’s kidney creatinine levels were elevated compared with the levels in his blood, indicating that his kidneys were not functioning well. Javier’s symptoms suggested a possible infection with Clostridium difficile , a bacterium that is resistant to many antibiotics. The hospital collected and cultured a stool sample to look for the production of toxins A and B by C. difficile , but the results came back negative. However, the negative results were not enough to rule out a C. difficile infection because culturing of C. difficile and detection of its characteristic toxins can be difficult, particularly in some types of samples. To be safe, they proceeded with a diagnostic nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT). Currently NAATs are the clinical diagnostician’s gold standard for detecting the genetic material of a pathogen. In Javier’s case, qPCR was used to look for the gene encoding C. difficile toxin B ( tcdB ). When the qPCR analysis came back positive, the attending physician concluded that Javier was indeed suffering from a C. difficile infection and immediately prescribed the antibiotic vancomycin , to be administered intravenously. The antibiotic cleared the infection and Javier made a full recovery.
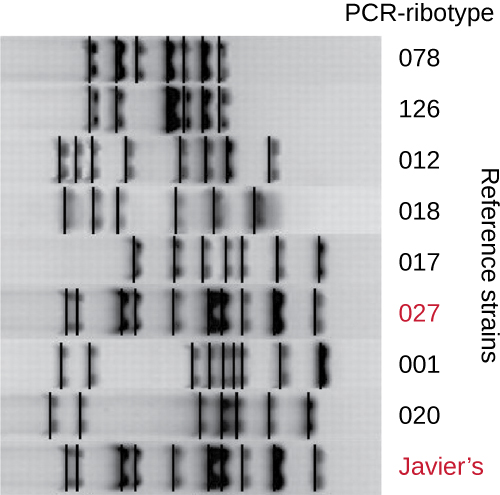
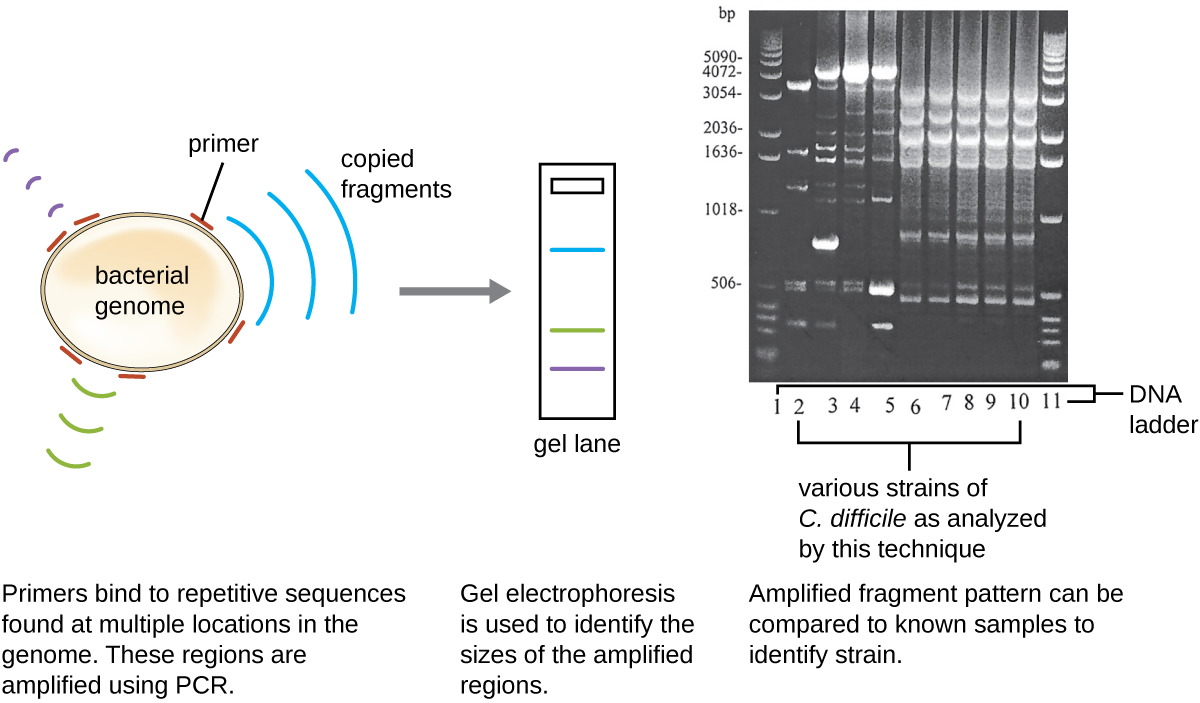
Because infections with C. difficile were becoming widespread in Javier’s community, his sample was further analyzed to see whether the specific strain of C. difficile could be identified. Javier’s stool sample was subjected to ribotyping and repetitive sequence-based PCR (rep-PCR) analysis. In ribotyping, a short sequence of DNA between the 16S rRNA and 23S rRNA genes is amplified and subjected to restriction digestion ( [link] ). This sequence varies between strains of C. difficile , so restriction enzymes will cut in different places. In rep-PCR, DNA primers designed to bind to short sequences commonly found repeated within the C. difficile genome were used for PCR. Following restriction digestion, agarose gel electrophoresis was performed in both types of analysis to examine the banding patterns that resulted from each procedure ( [link] ). Rep-PCR can be used to further subtype various ribotypes, increasing resolution for detecting differences between strains. The ribotype of the strain infecting Javier was found to be ribotype 27, a strain known for its increased virulence, resistance to antibiotics, and increased prevalence in the United States, Canada, Japan, and Europe. Patrizia Spigaglia, Fabrizio Barbanti, Anna Maria Dionisi, and Paola Mastrantonio. “ Clostridium difficile Isolates Resistant to Fluoroquinolones in Italy: Emergence of PCR Ribotype 018.” Journal of Clinical Microbiology 48 no. 8 (2010): 2892–2896.
The __________ blot technique is used to find an RNA fragment within a sample that is complementary to a DNA probe.
northern
The PCR step during which the double-stranded template molecule becomes single-stranded is called _____________.
denaturation
The sequencing method involving the incorporation of ddNTPs is called __________.
Sanger sequencing, dideoxy method, or chain termination method
In agarose gel electrophoresis, DNA will be attracted to the negative electrode.
false
Why is it important that a DNA probe be labeled with a molecular beacon?
When separating proteins strictly by size, why is exposure to SDS first required?
Why must the DNA polymerase used during PCR be heat-stable?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?