| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Cell theory states that the cell is the fundamental unit of life. However, cells vary significantly in size, shape, structure, and function. At the simplest level of construction, all cells possess a few fundamental components. These include cytoplasm (a gel-like substance composed of water and dissolved chemicals needed for growth), which is contained within a plasma membrane (also called a cell membrane or cytoplasmic membrane); one or more chromosomes, which contain the genetic blueprints of the cell; and ribosomes , organelles used for the production of proteins.
Beyond these basic components, cells can vary greatly between organisms, and even within the same multicellular organism. The two largest categories of cells— prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells —are defined by major differences in several cell structures. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane and generally have a single, circular chromosome located in a nucleoid. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane that contains multiple, rod-shaped chromosomes. Y.-H.M. Chan, W.F. Marshall. “Scaling Properties of Cell and Organelle Size.” Organogenesis 6 no. 2 (2010):88–96.
All plant cells and animal cells are eukaryotic. Some microorganisms are composed of prokaryotic cells, whereas others are composed of eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic microorganisms are classified within the domains Archaea and Bacteria, whereas eukaryotic organisms are classified within the domain Eukarya.
The structures inside a cell are analogous to the organs inside a human body, with unique structures suited to specific functions. Some of the structures found in prokaryotic cells are similar to those found in some eukaryotic cells; others are unique to prokaryotes. Although there are some exceptions, eukaryotic cells tend to be larger than prokaryotic cells. The comparatively larger size of eukaryotic cells dictates the need to compartmentalize various chemical processes within different areas of the cell, using complex membrane-bound organelles. In contrast, prokaryotic cells generally lack membrane-bound organelles; however, they often contain inclusions that compartmentalize their cytoplasm. [link] illustrates structures typically associated with prokaryotic cells. These structures are described in more detail in the next section.
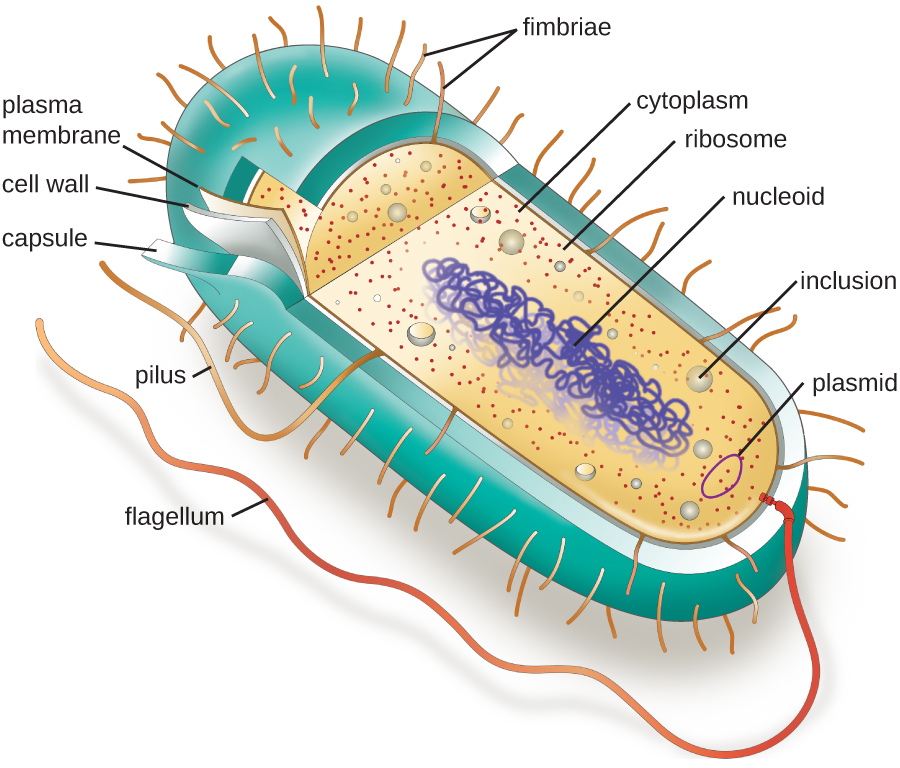
Individual cells of a particular prokaryotic organism are typically similar in shape, or cell morphology . Although thousands of prokaryotic organisms have been identified, only a handful of cell morphologies are commonly seen microscopically. [link] names and illustrates cell morphologies commonly found in prokaryotic cells. In addition to cellular shape, prokaryotic cells of the same species may group together in certain distinctive arrangements depending on the plane of cell division. Some common arrangements are shown in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?