| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
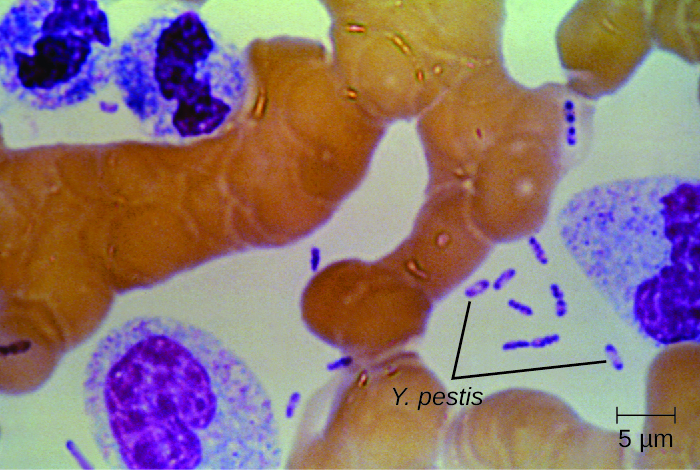
The first recorded pandemic of plague, the Justinian plague , occurred in the sixth century CE. It is thought to have originated in central Africa and spread to the Mediterranean through trade routes. At its peak, more than 5,000 people died per day in Constantinople alone. Ultimately, one-third of that city’s population succumbed to plague. Rosen, William. Justinian’s Flea: Plague, Empire, and the Birth of Europe. Viking Adult; pg 3; ISBN 978-0-670-03855-8. The impact of this outbreak probably contributed to the later fall of Emperor Justinian.
The second major pandemic, dubbed the Black Death , occurred during the 14th century. This time, the infections are thought to have originated somewhere in Asia before being transported to Europe by trade, soldiers, and war refugees. This outbreak killed an estimated one-quarter of the population of Europe (25 million, primarily in major cities). In addition, at least another 25 million are thought to have been killed in Asia and Africa. Benedictow, Ole J. 2004. The Black Death 1346-1353: The Complete History. Woodbridge: Boydell Press. This second pandemic, associated with strain Yersinia pestis biovar Medievalis, cycled for another 300 years in Europe and Great Britain, and was called the Great Plague in the 1660s.
The most recent pandemic occurred in the 1890s with Yersinia pestis biovar Orientalis. This outbreak originated in the Yunnan province of China and spread worldwide through trade. It is at this time that plague made its way to the US. The etiologic agent of plague was discovered by Alexandre Yersin (1863–1943) during this outbreak as well. The overall number of deaths was lower than in prior outbreaks, perhaps because of improved sanitation and medical support. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “Plague: History.” http://www.cdc.gov/plague/history/. Accessed September 15, 2016. Most of the deaths attributed to this final pandemic occurred in India.
Visit this link to see a video describing how similar the genome of the Black Death bacterium is to today’s strains of bubonic plague.
A wide variety of zoonotic febrile diseases (diseases that cause fever) are caused by pathogenic bacteria that require arthropod vectors. These pathogens are either obligate intracellular species of Anaplasma, Bartonella , Ehrlichia, Orientia, and Rickettsia , or spirochetes in the genus Borrelia . Isolation and identification of pathogens in this group are best performed in BSL-3 laboratories because of the low infective dose associated with the diseases.
The zoonotic tickborne disease human granulocytic anaplasmosis (HGA) is caused by the obligate intracellular pathogen Anaplasma phagocytophilum . HGA is endemic primarily in the central and northeastern US and in countries in Europe and Asia.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?