| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
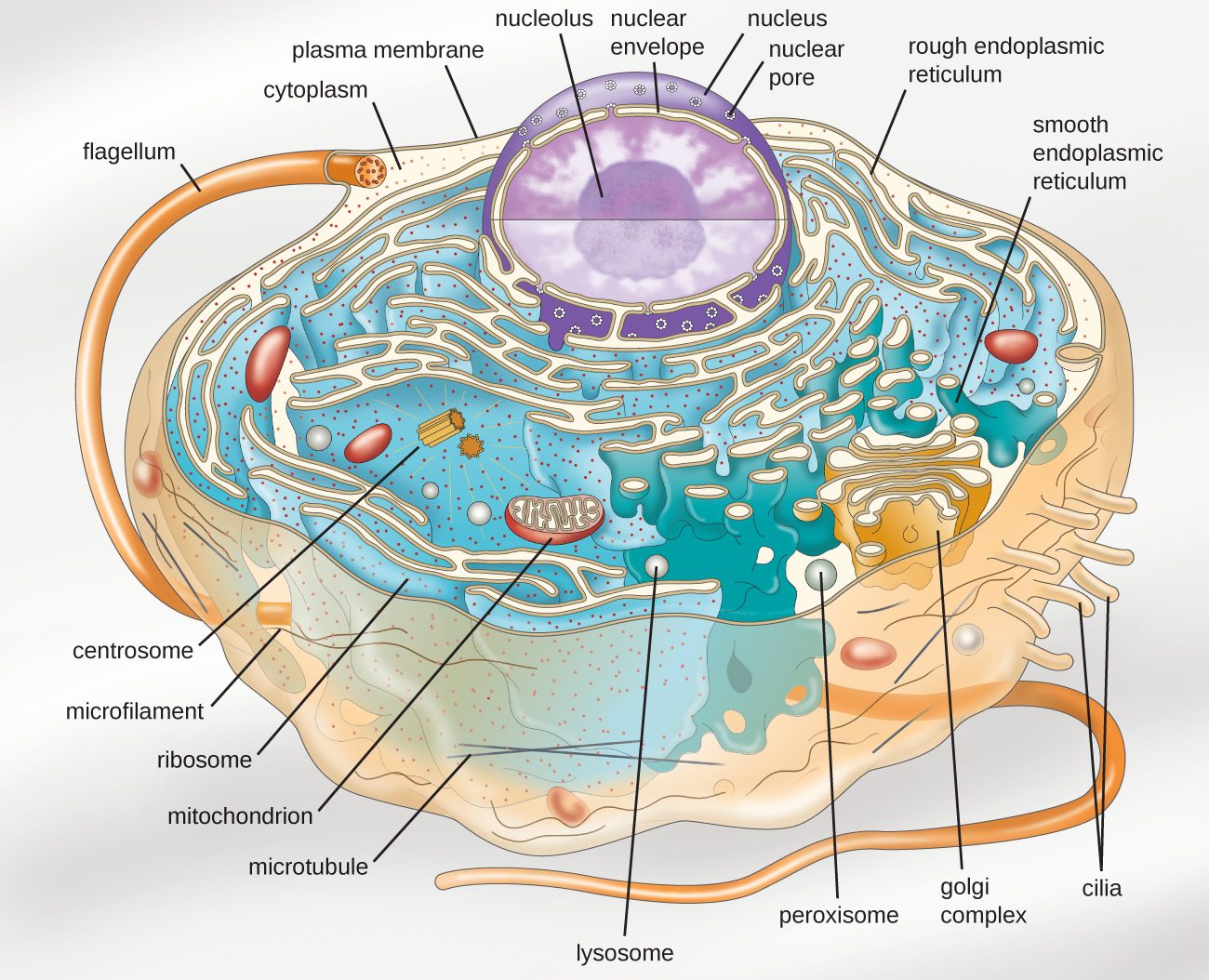
Eukaryotic organisms include protozoans, algae, fungi, plants, and animals. Some eukaryotic cells are independent, single-celled microorganisms, whereas others are part of multicellular organisms. The cells of eukaryotic organisms have several distinguishing characteristics. Above all, eukaryotic cells are defined by the presence of a nucleus surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane. Also, eukaryotic cells are characterized by the presence of membrane-bound organelles in the cytoplasm. Organelles such as mitochondria, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and peroxisomes are held in place by the cytoskeleton , an internal network that supports transport of intracellular components and helps maintain cell shape ( [link] ). The genome of eukaryotic cells is packaged in multiple, rod-shaped chromosomes as opposed to the single, circular-shaped chromosome that characterizes most prokaryotic cells. [link] compares the characteristics of eukaryotic cell structures with those of bacteria and archaea.
| Summary of Cell Structures | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Structure | Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes | |
| Bacteria | Archaea | ||
| Size | ~0.5–1 μM | ~0.5–1 μM | ~5–20 μM |
| Surface area-to-volume ratio | High | High | Low |
| Nucleus | No | No | Yes |
| Genome characteristics |
|
|
|
| Cell division | Binary fission | Binary fission | Mitosis, meiosis |
| Membrane lipid composition |
|
|
|
| Cell wall composition |
|
|
|
| Motility structures | Rigid spiral flagella composed of flagellin | Rigid spiral flagella composed of archaeal flagellins | Flexible flagella and cilia composed of microtubules |
| Membrane-bound organelles | No | No | Yes |
| Endomembrane system | No | No | Yes (ER, Golgi, lysosomes) |
| Ribosomes | 70S | 70S |
|
Eukaryotic cells display a wide variety of different cell morphologies . Possible shapes include spheroid, ovoid, cuboidal, cylindrical, flat, lenticular, fusiform, discoidal, crescent, ring stellate, and polygonal ( [link] ). Some eukaryotic cells are irregular in shape, and some are capable of changing shape. The shape of a particular type of eukaryotic cell may be influenced by factors such as its primary function, the organization of its cytoskeleton, the viscosity of its cytoplasm, the rigidity of its cell membrane or cell wall (if it has one), and the physical pressure exerted on it by the surrounding environment and/or adjoining cells.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?