| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
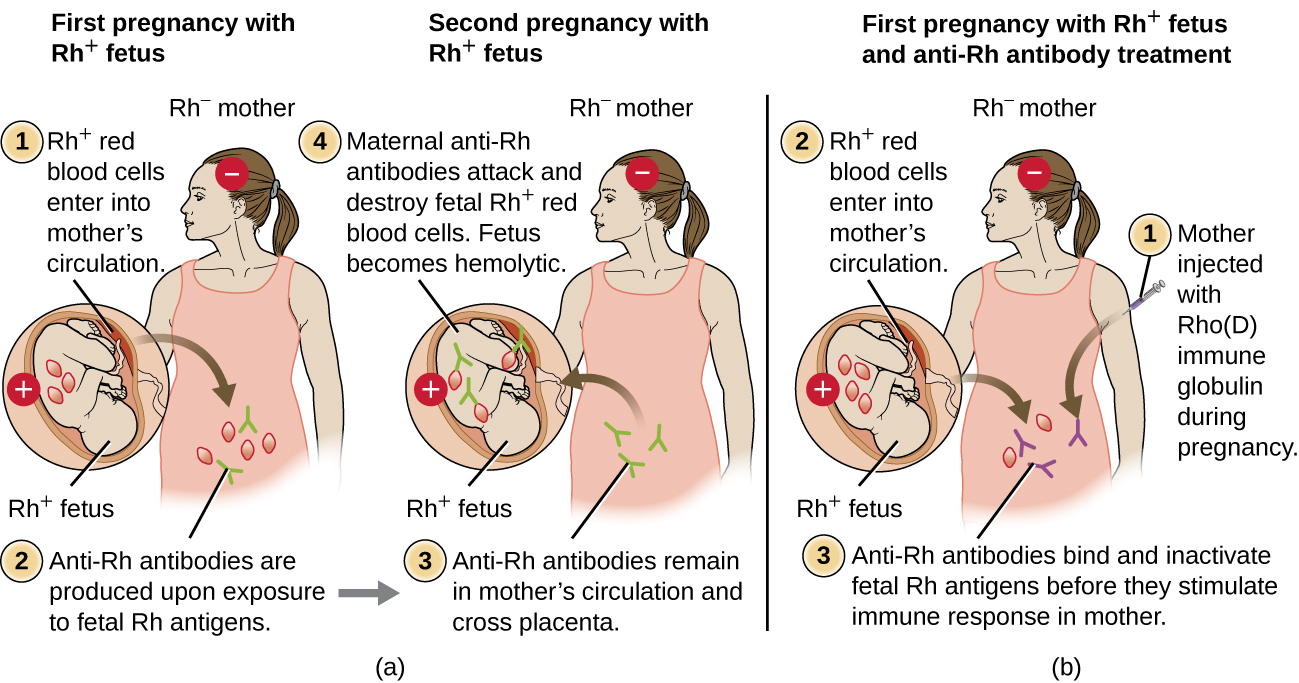
If a subsequent pregnancy with an Rh+ fetus occurs, however, the mother’s second exposure to the Rh factor antigens causes a strong secondary antibody response that produces larger quantities of anti-Rh factor IgG. These antibodies can cross the placenta from mother to fetus and cause HDN, a potentially lethal condition for the baby ( [link] ).
Prior to the development of techniques for diagnosis and prevention, Rh factor incompatibility was the most common cause of HDN, resulting in thousands of infant deaths each year worldwide. G. Reali. “Forty Years of Anti-D Immunoprophylaxis.” Blood Transfusion 5 no. 1 (2007):3–6. For this reason, the Rh factors of prospective parents are regularly screened, and treatments have been developed to prevent HDN caused by Rh incompatibility. To prevent Rh factor-mediated HDN, human Rho(D) immune globulin (e.g., RhoGAM ) is injected intravenously or intramuscularly into the mother during the 28th week of pregnancy and within 72 hours after delivery. Additional doses may be administered after events that may result in transplacental hemorrhage (e.g., umbilical blood sampling, chorionic villus sampling, abdominal trauma, amniocentesis). This treatment is initiated during the first pregnancy with an Rh+ fetus. The anti-Rh antibodies in Rho(D) immune globulin will bind to the Rh factor of any fetal RBCs that gain access to the mother’s bloodstream, preventing these Rh+ cells from activating the mother’s primary antibody response. Without a primary anti-Rh factor antibody response, the next pregnancy with an Rh+ will have minimal risk of HDN. However, the mother will need to be retreated with Rho(D) immune globulin during that pregnancy to prevent a primary anti-Rh antibody response that could threaten subsequent pregnancies.

Use this interactive Blood Typing Game to reinforce your knowledge of blood typing.
Kerry’s primary care physician is not sure why Kerry seems to develop rashes after spending time in the sun, so she orders a urinalysis and basic blood tests. The results reveal that Kerry has proteinuria (abnormal protein levels in the urine), hemoglobinuria (excess hemoglobin in the urine), and a low hematocrit (RBC count). These tests suggest that Kerry is suffering from a mild bout of hemolytic anemia. The physician suspects that the problem might be autoimmune, so she refers Kerry to a rheumatologist for additional testing and diagnosis.
Jump to the next Clinical Focus box. Go back to the previous Clinical Focus box.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?