| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Explore the Salem Witchcraft Trials to learn more about the prosecution of witchcraft in seventeenth-century New England.
Like their Spanish and French Catholic rivals, English Puritans in America took steps to convert native peoples to their version of Christianity. John Eliot, the leading Puritan missionary in New England, urged natives in Massachusetts to live in “praying towns” established by English authorities for converted Indians, and to adopt the Puritan emphasis on the centrality of the Bible. In keeping with the Protestant emphasis on reading scripture, he translated the Bible into the local Algonquian language and published his work in 1663. Eliot hoped that as a result of his efforts, some of New England’s native inhabitants would become preachers.
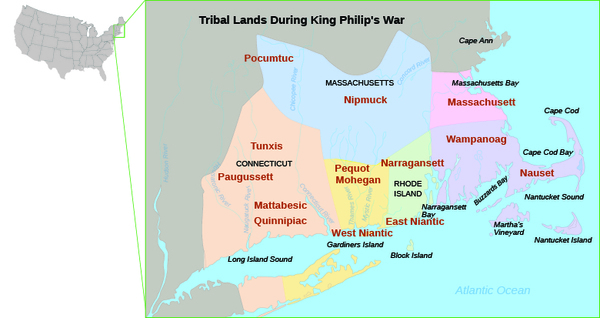
Tensions had existed from the beginning between the Puritans and the native people who controlled southern New England ( [link] ). Relationships deteriorated as the Puritans continued to expand their settlements aggressively and as European ways increasingly disrupted native life. These strains led to King Philip’s War (1675–1676), a massive regional conflict that was nearly successful in pushing the English out of New England.
When the Puritans began to arrive in the 1620s and 1630s, local Algonquian peoples had viewed them as potential allies in the conflicts already simmering between rival native groups. In 1621, the Wampanoag, led by Massasoit, concluded a peace treaty with the Pilgrims at Plymouth. In the 1630s, the Puritans in Massachusetts and Plymouth allied themselves with the Narragansett and Mohegan people against the Pequot, who had recently expanded their claims into southern New England. In May 1637, the Puritans attacked a large group of several hundred Pequot along the Mystic River in Connecticut. To the horror of their native allies, the Puritans massacred all but a handful of the men, women, and children they found.
By the mid-seventeenth century, the Puritans had pushed their way further into the interior of New England, establishing outposts along the Connecticut River Valley. There seemed no end to their expansion. Wampanoag leader Metacom or Metacomet, also known as King Philip among the English, was determined to stop the encroachment. The Wampanoag, along with the Nipmuck, Pocumtuck, and Narragansett, took up the hatchet to drive the English from the land. In the ensuing conflict, called King Philip’s War, native forces succeeded in destroying half of the frontier Puritan towns; however, in the end, the English (aided by Mohegans and Christian Indians) prevailed and sold many captives into slavery in the West Indies. (The severed head of King Philip was publicly displayed in Plymouth.) The war also forever changed the English perception of native peoples; from then on, Puritan writers took great pains to vilify the natives as bloodthirsty savages. A new type of racial hatred became a defining feature of Indian-English relationships in the Northeast.
Mary Rowlandson was a Puritan woman whom Indian tribes captured and imprisoned for several weeks during King Philip’s War. After her release, she wrote The Narrative of the Captivity and the Restoration of Mrs. Mary Rowlandson , which was published in 1682 ( [link] ). The book was an immediate sensation that was reissued in multiple editions for over a century.

But now, the next morning, I must turn my back upon the town, and travel with them into the vast and desolate wilderness, I knew not whither. It is not my tongue, or pen, can express the sorrows of my heart, and bitterness of my spirit that I had at this departure: but God was with me in a wonderful manner, carrying me along, and bearing up my spirit, that it did not quite fail. One of the Indians carried my poor wounded babe upon a horse; it went moaning all along, “I shall die, I shall die.” I went on foot after it, with sorrow that cannot be expressed. At length I took it off the horse, and carried it in my arms till my strength failed, and I fell down with it. Then they set me upon a horse with my wounded child in my lap, and there being no furniture upon the horse’s back, as we were going down a steep hill we both fell over the horse’s head, at which they, like inhumane creatures, laughed, and rejoiced to see it, though I thought we should there have ended our days, as overcome with so many difficulties. But the Lord renewed my strength still, and carried me along, that I might see more of His power; yea, so much that I could never have thought of, had I not experienced it.
What sustains Rowlandson her during her ordeal? How does she characterize her captors? What do you think made her narrative so compelling to readers?
Access the entire text of Mary Rowlandson’s captivity narrative at the Gutenberg Project.
The English came late to colonization of the Americas, establishing stable settlements in the 1600s after several unsuccessful attempts in the 1500s. After Roanoke Colony failed in 1587, the English found more success with the founding of Jamestown in 1607 and Plymouth in 1620. The two colonies were very different in origin. The Virginia Company of London founded Jamestown with the express purpose of making money for its investors, while Puritans founded Plymouth to practice their own brand of Protestantism without interference.
Both colonies battled difficult circumstances, including poor relationships with neighboring Indian tribes. Conflicts flared repeatedly in the Chesapeake Bay tobacco colonies and in New England, where a massive uprising against the English in 1675 to 1676—King Philip’s War—nearly succeeded in driving the intruders back to the sea.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'U.s. history' conversation and receive update notifications?