| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
We can broadly divide the provisions of the Bill of Rights into three categories. The First, Second, Third, and Fourth Amendments protect basic individual freedoms; the Fourth (partly), Fifth, Sixth, Seventh, and Eighth protect people suspected or accused of criminal activity; and the Ninth and Tenth, are consistent with the framers’ view that the Bill of Rights is not necessarily an exhaustive list of all the rights people have and guarantees a role for state as well as federal government ( [link] ).
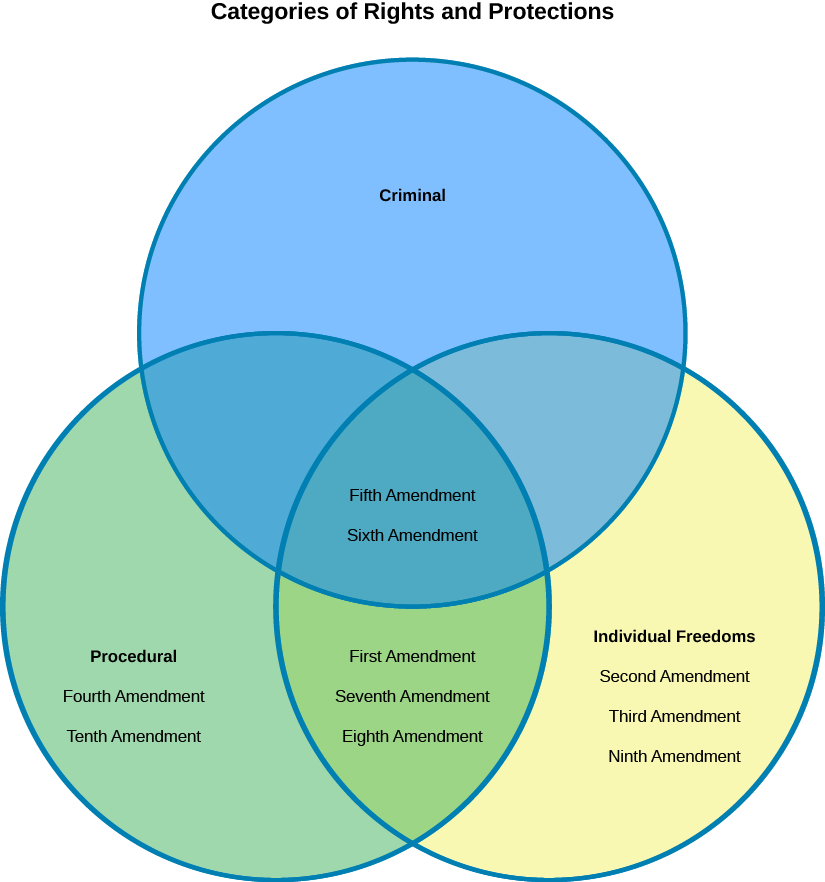
The First Amendment protects the right to freedom of religious conscience and practice and the right to free expression, particularly of political and social beliefs. The Second Amendment—perhaps the most controversial today—protects the right to defend yourself in your home or other property, as well as the collective right to protect the community as part of the militia. The Third Amendment prohibits the government from commandeering people’s homes to house soldiers, particularly in peacetime. Finally, the Fourth Amendment prevents the government from searching our persons or property or taking evidence without a warrant issued by a judge, with certain exceptions.
The First Amendment is perhaps the most famous provision of the Bill of Rights; it is arguably also the most extensive, because it guarantees both religious freedoms and the right to express your views in public. Specifically, the First Amendment says:
“Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof; or abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press; or the right of the people peaceably to assemble, and to petition the Government for a redress of grievances.”
Given the broad scope of this amendment, it is helpful to break it into its two major parts.
The first portion deals with religious freedom. However, it actually protects two related sorts of freedom: first, it protects people from having a set of religious beliefs imposed on them by the government, and second, it protects people from having their own religious beliefs restricted by government authorities.
The first of these two freedoms is known as the establishment clause . Congress is prohibited from creating or promoting a state-sponsored religion (this now includes the states too). When the United States was founded, most countries around the world had an established church or religion, an officially sponsored set of religious beliefs and values. In Europe, bitter wars were fought between and within states, often because the established church of one territory was in conflict with that of another; wars and civil strife were common, particularly between states with Protestant and Catholic churches that had differing interpretations of Christianity. Even today, the legacy of these wars remains, most notably in Ireland, which has been divided between a mostly Catholic south and a largely Protestant north for nearly a century.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'American government' conversation and receive update notifications?