| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
This means that, along the demand curve between point B and A, if the price changes by 1%, the quantity demanded will change by 0.45%. A change in the price will result in a smaller percentage change in the quantity demanded. For example, a 10% increase in the price will result in only a 4.5% decrease in quantity demanded. A 10% decrease in the price will result in only a 4.5% increase in the quantity demanded. Price elasticities of demand are negative numbers indicating that the demand curve is downward sloping, but are read as absolute values. The following Work It Out feature will walk you through calculating the price elasticity of demand.
Calculate the price elasticity of demand using the data in [link] for an increase in price from G to H. Has the elasticity increased or decreased?
Step 1. We know that:
Step 2. From the Midpoint Formula we know that:
Step 3. So we can use the values provided in the figure in each equation:
Step 4. Then, those values can be used to determine the price elasticity of demand:
Therefore, the elasticity of demand from G to H 1.47. The magnitude of the elasticity has increased (in absolute value) as we moved up along the demand curve from points A to B. Recall that the elasticity between these two points was 0.45. Demand was inelastic between points A and B and elastic between points G and H. This shows us that price elasticity of demand changes at different points along a straight-line demand curve .
Assume that an apartment rents for $650 per month and at that price 10,000 units are rented as shown in [link] . When the price increases to $700 per month, 13,000 units are supplied into the market. By what percentage does apartment supply increase? What is the price sensitivity?
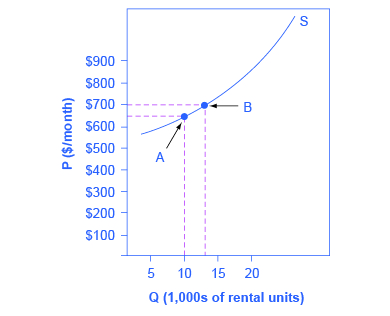
Using the Midpoint Method ,
Again, as with the elasticity of demand, the elasticity of supply is not followed by any units. Elasticity is a ratio of one percentage change to another percentage change—nothing more—and is read as an absolute value. In this case, a 1% rise in price causes an increase in quantity supplied of 3.5%. The greater than one elasticity of supply means that the percentage change in quantity supplied will be greater than a one percent price change. If you're starting to wonder if the concept of slope fits into this calculation, read the following Clear It Up box.
It is a common mistake to confuse the slope of either the supply or demand curve with its elasticity. The slope is the rate of change in units along the curve, or the rise/run (change in y over the change in x). For example, in [link] , each point shown on the demand curve, price drops by $10 and the number of units demanded increases by 200. So the slope is –10/200 along the entire demand curve and does not change. The price elasticity, however, changes along the curve. Elasticity between points A and B was 0.45 and increased to 1.47 between points G and H. Elasticity is the percentage change, which is a different calculation from the slope and has a different meaning.
When we are at the upper end of a demand curve, where price is high and the quantity demanded is low, a small change in the quantity demanded, even in, say, one unit, is pretty big in percentage terms. A change in price of, say, a dollar, is going to be much less important in percentage terms than it would have been at the bottom of the demand curve. Likewise, at the bottom of the demand curve, that one unit change when the quantity demanded is high will be small as a percentage.
So, at one end of the demand curve, where we have a large percentage change in quantity demanded over a small percentage change in price, the elasticity value would be high, or demand would be relatively elastic. Even with the same change in the price and the same change in the quantity demanded, at the other end of the demand curve the quantity is much higher, and the price is much lower, so the percentage change in quantity demanded is smaller and the percentage change in price is much higher. That means at the bottom of the curve we'd have a small numerator over a large denominator, so the elasticity measure would be much lower, or inelastic.
As we move along the demand curve, the values for quantity and price go up or down, depending on which way we are moving, so the percentages for, say, a $1 difference in price or a one unit difference in quantity, will change as well, which means the ratios of those percentages will change.
Price elasticity measures the responsiveness of the quantity demanded or supplied of a good to a change in its price. It is computed as the percentage change in quantity demanded (or supplied) divided by the percentage change in price. Elasticity can be described as elastic (or very responsive), unit elastic, or inelastic (not very responsive). Elastic demand or supply curves indicate that quantity demanded or supplied respond to price changes in a greater than proportional manner. An inelastic demand or supply curve is one where a given percentage change in price will cause a smaller percentage change in quantity demanded or supplied. A unitary elasticity means that a given percentage change in price leads to an equal percentage change in quantity demanded or supplied.
The equation for a demand curve is P = 48 – 3Q. What is the elasticity in moving from a quantity of 5 to a quantity of 6?
The equation for a demand curve is P = 2/Q. What is the elasticity of demand as price falls from 5 to 4? What is the elasticity of demand as the price falls from 9 to 8? Would you expect these answers to be the same?
The equation for a supply curve is 4P = Q. What is the elasticity of supply as price rises from 3 to 4? What is the elasticity of supply as the price rises from 7 to 8? Would you expect these answers to be the same?
The equation for a supply curve is P = 3Q – 8. What is the elasticity in moving from a price of 4 to a price of 7?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?