| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The equilibrium occurs where national income is equal to aggregate expenditure, which is shown on the graph as the point where the aggregate expenditure schedule crosses the 45-degree line. In this example, the equilibrium occurs at 6,000. This equilibrium can also be read off the table under the figure; it is the level of national income where aggregate expenditure is equal to national income.
With the aggregate expenditure line in place, the next step is to relate it to the two other elements of the Keynesian cross diagram. Thus, the first subsection interprets the intersection of the aggregate expenditure function and the 45-degree line, while the next subsection relates this point of intersection to the potential GDP line.
Where Equilibrium Occurs
The point where the aggregate expenditure line that is constructed from C + I + G + X – M crosses the 45-degree line will be the equilibrium for the economy. It is the only point on the aggregate expenditure line where the total amount being spent on aggregate demand equals the total level of production. In [link] , this point of equilibrium (E 0 ) happens at 6,000, which can also be read off [link] .
The meaning of “equilibrium” remains the same; that is, equilibrium is a point of balance where no incentive exists to shift away from that outcome. To understand why the point of intersection between the aggregate expenditure function and the 45-degree line is a macroeconomic equilibrium, consider what would happen if an economy found itself to the right of the equilibrium point E, say point H in [link] , where output is higher than the equilibrium. At point H, the level of aggregate expenditure is below the 45-degree line, so that the level of aggregate expenditure in the economy is less than the level of output. As a result, at point H, output is piling up unsold—not a sustainable state of affairs.
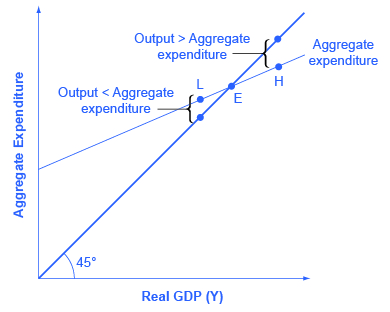
Conversely, consider the situation where the level of output is at point L—where real output is lower than the equilibrium. In that case, the level of aggregate demand in the economy is above the 45-degree line, indicating that the level of aggregate expenditure in the economy is greater than the level of output. When the level of aggregate demand has emptied the store shelves, it cannot be sustained, either. Firms will respond by increasing their level of production. Thus, the equilibrium must be the point where the amount produced and the amount spent are in balance, at the intersection of the aggregate expenditure function and the 45-degree line.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?