| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Now we know what happens when the frequency of the sin and cos terms in Figure 6 match the frequency of sine and cosine components in the target time series. Another important question is, what do sine and cosine components in thetarget time series with frequencies different from the cos and sin terms in Figure 6 contribute to the output?
The answer is not very much. Referring once more to the functional forms produced by multiplying sine and cosine functions (repeated in Figure 13 for convenience) , we see that for any values of a and b , where a is not equal to b , the function produced by multiplying two sinusoids will be the sum of two othersinusoids. The sum of the values for any sinusoid computed over an even number of cycles of the sinusoid will always be zero, and these sinusoids are noexception to that rule.
| Figure 13. Products of sine and cosine functions. |
|---|
1. f(n) = sin(a*n)*sin(b*n) =
(1/2)*(cos((a-b)*n)-cos((a+b)*n))2. f(n) = cos(a*n)*cos(b*n) =
(1/2)*(cos((a-b)*n)+cos((a+b)*n))3. f(n) = sin(a*n)*cos(b*n)
=(1/2)*(sin((a+b)*n)+sin((a-b)*n)) |
For any pair of arbitrary values for a and b , the frequencies of the sinusoids in the resulting functions will be given by a+b and a-b .
(These are often referred to as the sum and difference frequencies. Note that as a approaches b , the difference frequency approaches zero. This is what produces the constant values of 1/2in Figure 9 and the positive bias on the black curve in Figures 10 and 11.)
As a practical matter, if those resulting sum and difference frequencies are not multiples of one another, it will not be possible to perform the summationover an even number of cycles of both sinusoids. Therefore, one or the other, or perhaps both, will contribute a small amount to the sum of products due toincluding a partial cycle in the summation. This is a form of measurement error that occurs when performing frequency spectrum analysis using Fourier transformmethods.
(The percentage contribution of this error to the average value decreases as the number of cycles included in the average increases.)
Consider the product of two sine functions at different frequencies as shown in Figure 14 . This is a plot of the function produced by multiplying sin(1.8x) by sin(2.2x).
| Figure 14. Plot of sin(1.8x)*sin(2.2x). |
|---|
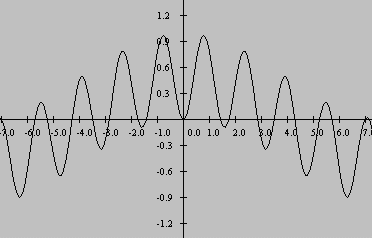 |
The high frequency component shown in Figure 14 is the component attributable to a+b . The long sweeping low frequency component is the component attributable to a-b .
Judging from the graph in Figure 14 , performing a summation of the product function from -7 to +7 would include almost exactly nine cycles of the highfrequency component. Thus, the high frequency component would contribute very little, if anything, to the summation.
However, the summation would include less than one complete cycle of the low frequency component. Therefore, the low frequency component would contributesome output to the summation in the form of a measurement error.
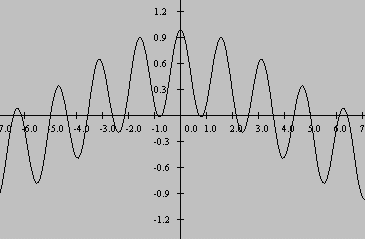
Similar results occur when multiplying a cosine function by a cosine function having a different frequency, or when multiplying a cosine function by a sinefunction having a different frequency. Graphical results for these two cases are shown in Figure 15 and Figure 16 .
| Figure 15. Plot of cos(1.8x)*cos(2.2x). |
|---|
 |
| Figure 16. Plot of sin(1.8x)*cos(2.2x). |
|---|
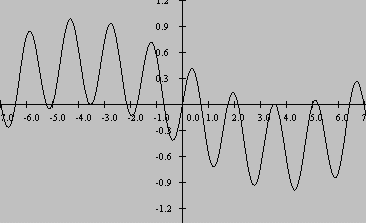 |
Once again, unless the summation interval includes an exact number of samples of both the sum frequency and the difference frequency, one of both of thesinusoids contained in the product function will contribute a measurement error to the result.
In this module, I have provided a quasi-theoretical basis for frequency spectrum analysis.
A pure theoretical basis for frequency spectrum analysis involves some rather complicated mathematics and is somewhat difficult to understand. However, from apractical viewpoint, it is not too difficult to understand how the complex mathematics produce the results that they produce.
Hopefully the quasi-theoretical explanations provided in this module will help you to understand what makes spectrum analysis work.
The next module in this series will reduce much of what I have discussed in this module to practice. I will present and explain a program that implements aDFT algorithm for performing frequency spectrum analysis. In addition, I will present the results of several interesting experiments in frequency spectrumanalysis using that algorithm.
A subsequent module will explain some of the signal processing concepts that made it possible for the inventors of the FFT algorithm to design acomputational algorithm that is much faster than the DFT algorithm. As is often the case, however, the FFT algorithm trades off speed for generality.
This section contains a variety of miscellaneous information.
Baldwin explains how the Fourier transform can be used to determine the spectral content of a signal in the time domain.
Financial : Although the Connexions site makes it possible for you to download a PDF file for thismodule at no charge, and also makes it possible for you to purchase a pre-printed version of the PDF file, you should beaware that some of the HTML elements in this module may not translate well into PDF.
I also want you to know that, I receive no financial compensation from the Connexions website even if you purchase the PDF version of the module.
In the past, unknown individuals have copied my modules from cnx.org, converted them to Kindle books, and placed them for sale on Amazon.com showing me as the author. Ineither receive compensation for those sales nor do I know who does receive compensation. If you purchase such a book, please beaware that it is a copy of a module that is freely available on cnx.org and that it was made and published withoutmy prior knowledge.
Affiliation : I am a professor of Computer Information Technology at Austin Community College in Austin, TX.
-end-

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Digital signal processing - dsp' conversation and receive update notifications?