| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In order to get the necessary constant reinforcement, the container has to be the perfect size (length) for a certain wavelength, so that waves bouncing back or being produced at each end reinforce each other, instead of interfering with each other and cancelling each other out. And it really helps to keep the container very narrow, so that you don't have to worry about waves bouncing off the sides and complicating things. So you have a bunch of regularly-spaced waves that are trapped, bouncing back and forth in a container that fits their wavelength perfectly. If you could watch these waves, it would not even look as if they are traveling back and forth. Instead, waves would seem to be appearing and disappearing regularly at exactly the same spots, so these trapped waves are called standing waves .
For any narrow "container" of a particular length, there are plenty of possible standing waves that don't fit. But there are also many standing waves that do fit. The longest wave that fits it is called the fundamental . It is also called the first harmonic . The next longest wave that fits is the second harmonic , or the first overtone . The next longest wave is the third harmonic , or second overtone , and so on.
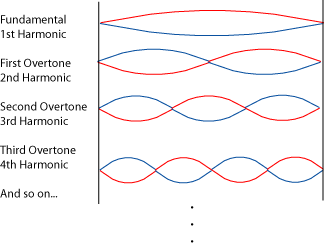
Notice that it doesn't matter what the length of the fundamental is; the waves in the second harmonic must be half the length of the first harmonic; that's the only way they'll both "fit". The waves of the third harmonic must be a third the length of the first harmonic, and so on. This has a direct effect on the frequency and pitch of harmonics, and so it affects the basics of music tremendously. To find out more about these subjects, please see Frequency, Wavelength, and Pitch , Harmonic Series , or Musical Intervals, Frequency, and Ratio .
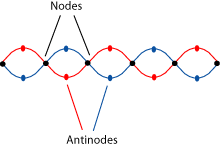
You may have noticed an interesting thing in the animation of standing waves: there are spots where the "water" goes up and down a great deal, and other spots where the "water level" doesn't seem to move at all. All standing waves have places, called nodes , where there is no wave motion, and antinodes , where the wave is largest. It is the placement of the nodes that determines which wavelengths "fit" into a musical instrument "container".

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Sound, physics and music' conversation and receive update notifications?