| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Having an orthonormal basis for the subspace of interest significantly simplifies the projection operator.
Lemma 1 Let , a Hilbert space, and let be a subspace of . If is an orthonormal basis for , then the closest point to is given by .
We begin by noting that
Now, since is the projection of onto , we must have that , and so for each basis element we must have . Additionally, since and is an orthonormal basis for , we must have that . Thus, we obtain
proving the lemma.
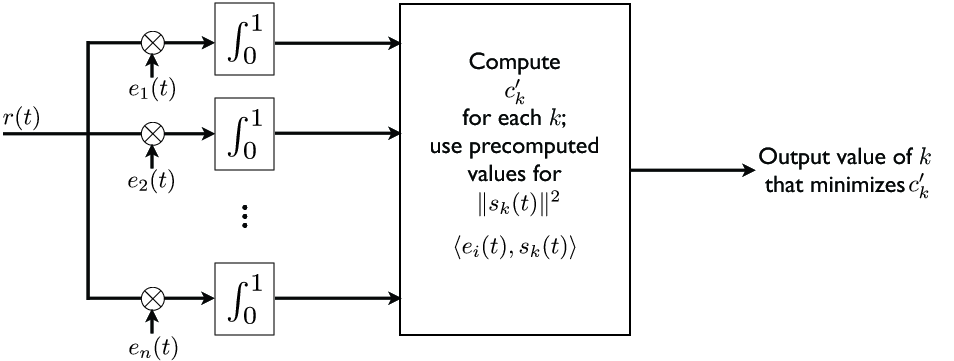
Consider the case of a communications receiver that records a continuous-time signal over , where is one of codeword signals , and is additive white Gaussian noise. The receiver must make the best possible decision on the observed codeword given the reading ; this usually involves removing as much of the noise as possible from .
We analyze this problem in the context of the Hilbert space . To remove as much of the noise as possible, we define the subspace . Anything that is not contained in this subspace is guaranteed to be part of the noise . Now, to obtain the projection into , we need to find an orthonormal basis for , which can be done for example by applying the Gram-Schmidt procedure on the vectors . The projection is then obtained according to the lemma as
where .
After the projection is obtained, an optimal receiver proceeds by finding the value of that minimizes the distance
note here that the first term does not depend on , so it suffices to find the value of that minimizes the “cost”
In practice, the codeword signals are designed so that their norms are all equal. This design choice reduces the problem above to finding the value of that maximizes the score
Thus, the receiver can be designed according to the diagram in [link] .
Let be elements of a Hilbert space and define the closed, finite-dimensional subspace of given by . We wish to find the best approximation of in terms of the vectors , that is, the linear combination with the smallest error . To measure the size of the error, we use the induced norm .
To solve this problem, we rely on the projection theorem: we are indeed looking for the closest point to in . The projection theorem tells us that the closest point must give , i.e., , which implies in turn that for all . The requirement can be rewritten as for each . These requirements can be collected and written in matrix form as

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Signal theory' conversation and receive update notifications?