| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Carboxylic acids are a typical example of a discrete oligomeric species that are held together by intermolecular hydrogen bonds ( [link] a). A wide range of structurally analogous compounds also form head-to-tail hydrogen bonded dimers (e.g., [link] ). In a polymeric hydrogen bonded species every molecule hydrogen bonds but in a random form. As an example, liquid primary alcohols form extended hydrogen networks ( [link] b). Such an arrangement is labile and as such it is difficult to determine definitive speciation. Liquids that form this type of hydrogen-bonded network are known as associated liquids . In the solid state the networks generally adopt a more ordered structure. For example as is seen in the structure of ice.
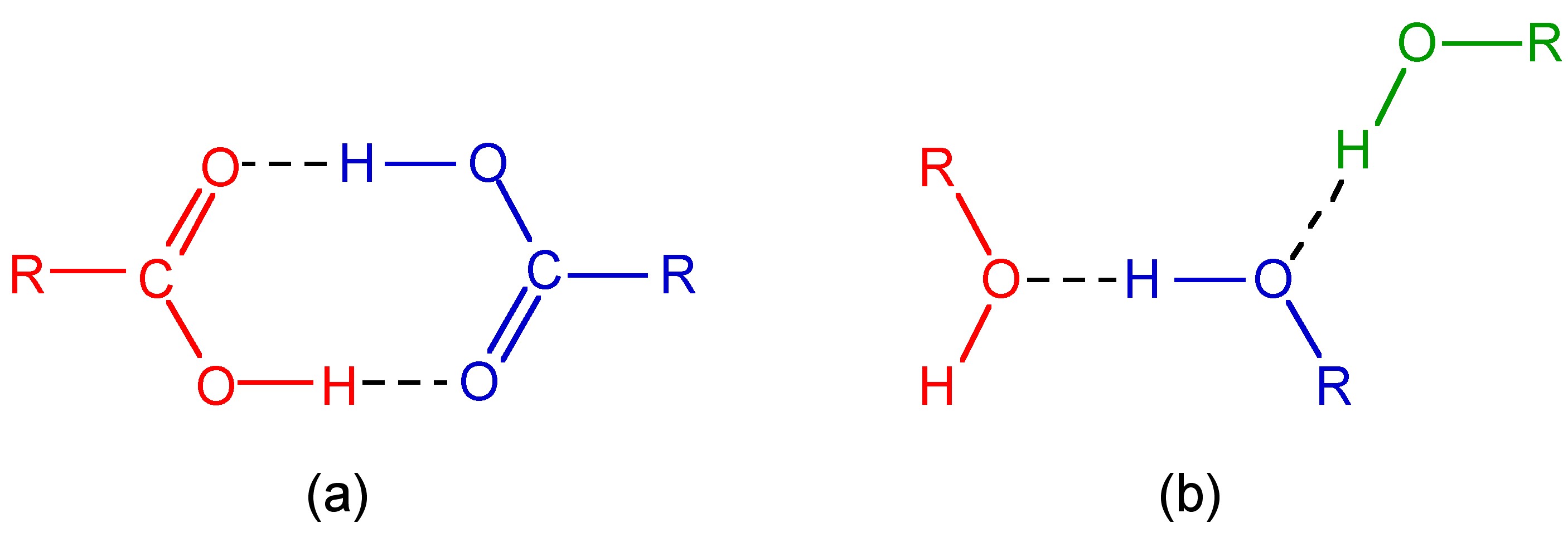
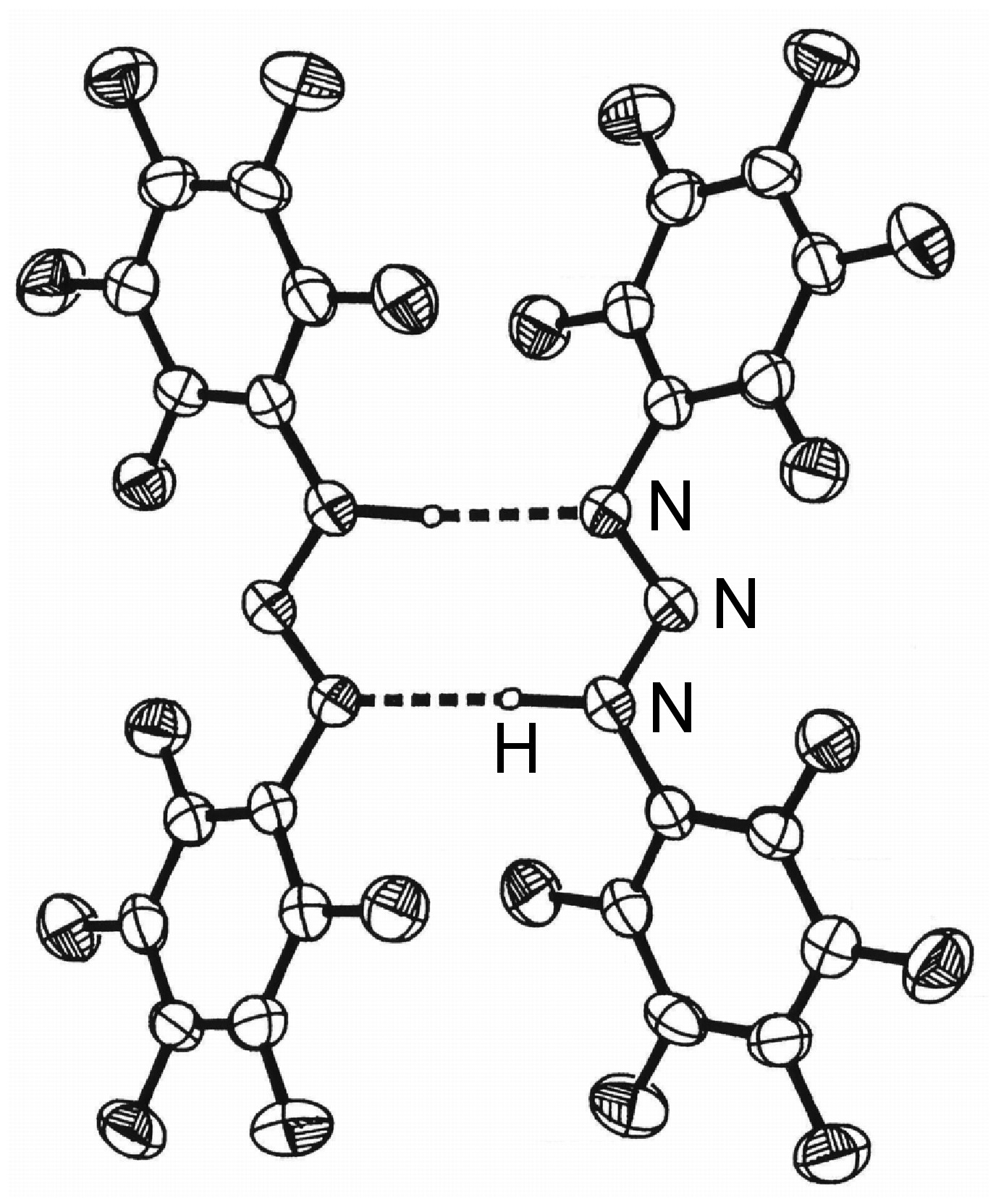
The study of the structure arising from hydrogen bonding and the properties exhibited due to the presence of hydrogen bonds is very important.
X-ray diffraction of single crystals is the most common structural method employed to determine the presence, effect, and strength of a hydrogen bond. Unfortunately, in order for the location of the hydrogen to be determined with some degree of accuracy, diffraction data of a high quality is needed and/or low temperature (e.g., -196 °C) data collection is required. Neutron scattering can be used where very accurate data is required because hydrogen atoms scatter neutrons better than they do X-rays. [link] summarizes the key parameters that are obtained from X-ray (and neutron) diffraction experiments.
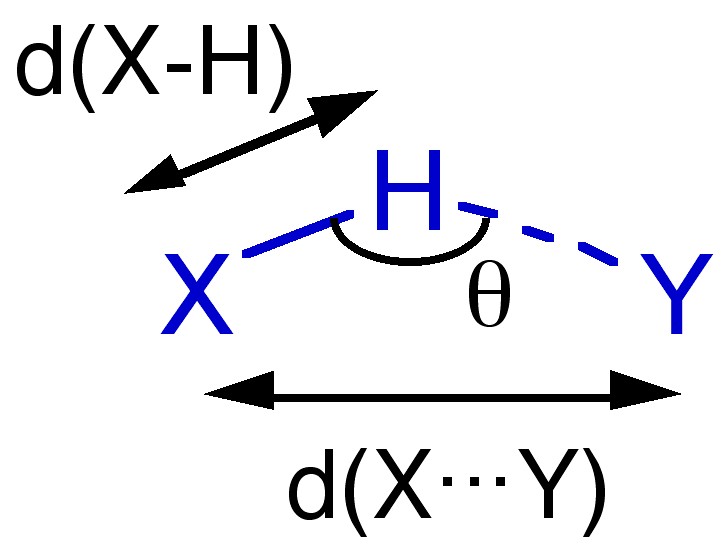
Given the electrostatic nature of a hydrogen bond between a polar X-H bond and a Lewis base it is reasonable that the X-H ... Y angle (θ) is roughly linear (i.e., 180°). However, it is not always so and non-linear interactions are known where steric or conformational restrictions limit the orientation of the X-H bond with respect to Y.
The distance between X and Y, d(X ... Y), is less than the sum of the van der Waal radii of X and Y ( [link] ). This is in line with the relative strength of these interactions. As would be expected the shorter the X ... Y distance the stronger the hydrogen bond.
| X | Y | Sum of van der Waal radii (Å) | Typical X ... Y distance (Å) |
| O | O | 2.8 | 2.50 – 2.69 |
| O | N | 2.9 | 2.75 - 2.85 |
| N | N | 3.0 | 2.69 – 2.98 |
The bond distance to hydrogen, d(X-H), is often longer in hydrogen bonded species. For example the O-H distance for an alcohol in the absence of hydrogen bonding is typically 0.97 Å. In contrast, the value typically seen for a hydrogen-bonded analog is 1.05 Å.
Spectroscopy is a simple method of comparing hydrogen-bonded systems in particular in the solution or liquid phase.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry of the main group elements' conversation and receive update notifications?