| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The learners must be able to:
1. identify and solve problems and make decisions using critical and creative thinking;
2. work effectively with others as members of a team, group, organisation and community;
3. organise and manage themselves and their activities responsibly and effectively;
4. collect, analyse, organise and critically evaluate information;
5. communicate effectively using visual, symbolic and/or language skills in various modes;
6. use science and technology effectively and critically, showing responsibility towards the environment and the health of others;
6. demonstrate an understanding of the world as a set of related systems by recognising that problem-solving contexts do not exist in isolation;
7. reflect on and explore a variety of strategies to learn more effectively;
8. participate as responsible citizens in the life of local, national, and global communities;
9. be culturally and aesthetically sensitive across a range of social contexts;
10. explore education and career opportunities; and
develop entrepreneurial opportunities.
Integration of Themes:
1 lunch box with 4 sandwiches
1 ℓ of cool drink
3 apples
2 chocolates
1 lunch box with 6 sandwiches
2 ℓ of cool drink
1 apple
2 chocolates
Answer these questions .
1. ________________________ (name) lunch box has the greater mass. Why?
2. ________________________ (name) lunch box has the smaller mass. Why?
3. One litre bottle can fill 4 mugs.
4. Tom will drink ______________________ mugs of cool drink.
5. Des will drink ______________________ mugs of cool drink.
6. Tom eats one quarter of an apple a day. He will eat a quarter of an apple for ______________________ days.
7. Des eats one half of an apple a day. He will eat half an apple for ______________________ days.
8. The chocolate has 8 squares. They eat 4 squares a day. They each have 4 squares for ______________________ days.
| LO 1.4 | LO 4.7 |
1. Tom and Des walked 5 km in one day. They will walk:
10 km in ______________________ days.
25 km in ______________________ days.
50 km in ______________________ days.
2. The camp is 15 km from Tom’s house and 12 km from Des’ house. Tom’s house is______________________ km further.
3. Tom can hit the ball 35 m far.
Des can hit the ball 4 m further.
He can hit the ball ______________________ m.
4. Tom counted 28 birds.
Des counted 5 less.
Des counted ______________________ birds.
5. They left the house at 8 o’clock in the morning. The first day they came to the campsite at 3 o’clock in the afternoon. They walked for ______________________ hours.
| LO 1.8 | LO 4.3 | LO 4.7 |
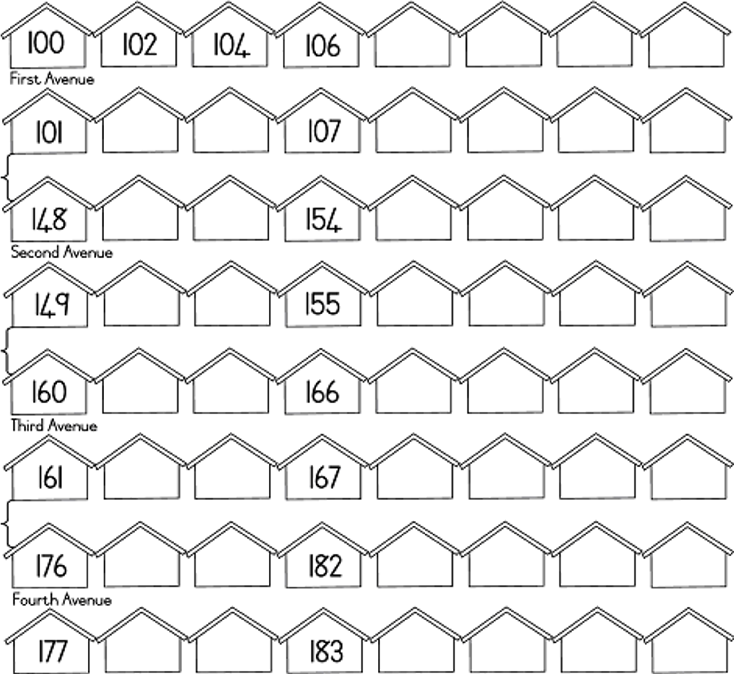
| LO 1.3 | LO 1.4 | LO 2.2 |
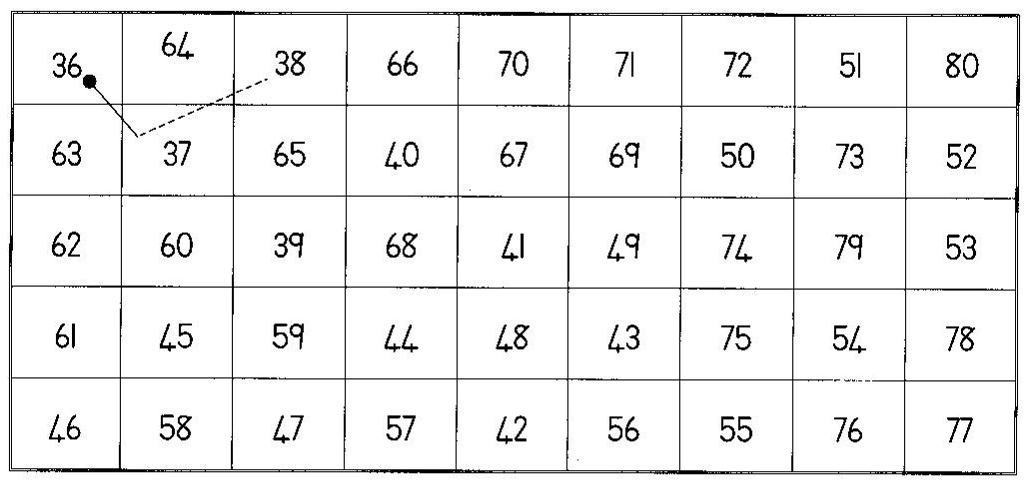
1 1 _______________ 22 _______________ 34 _______________
17 _______________ 29 _______________ 33 _______________
27 _______________ 41 _______________ 21 _______________
36 _______________ 26 _______________ 46 _______________
| LO 1.2 | LO 2.2 | LO 1.10 |
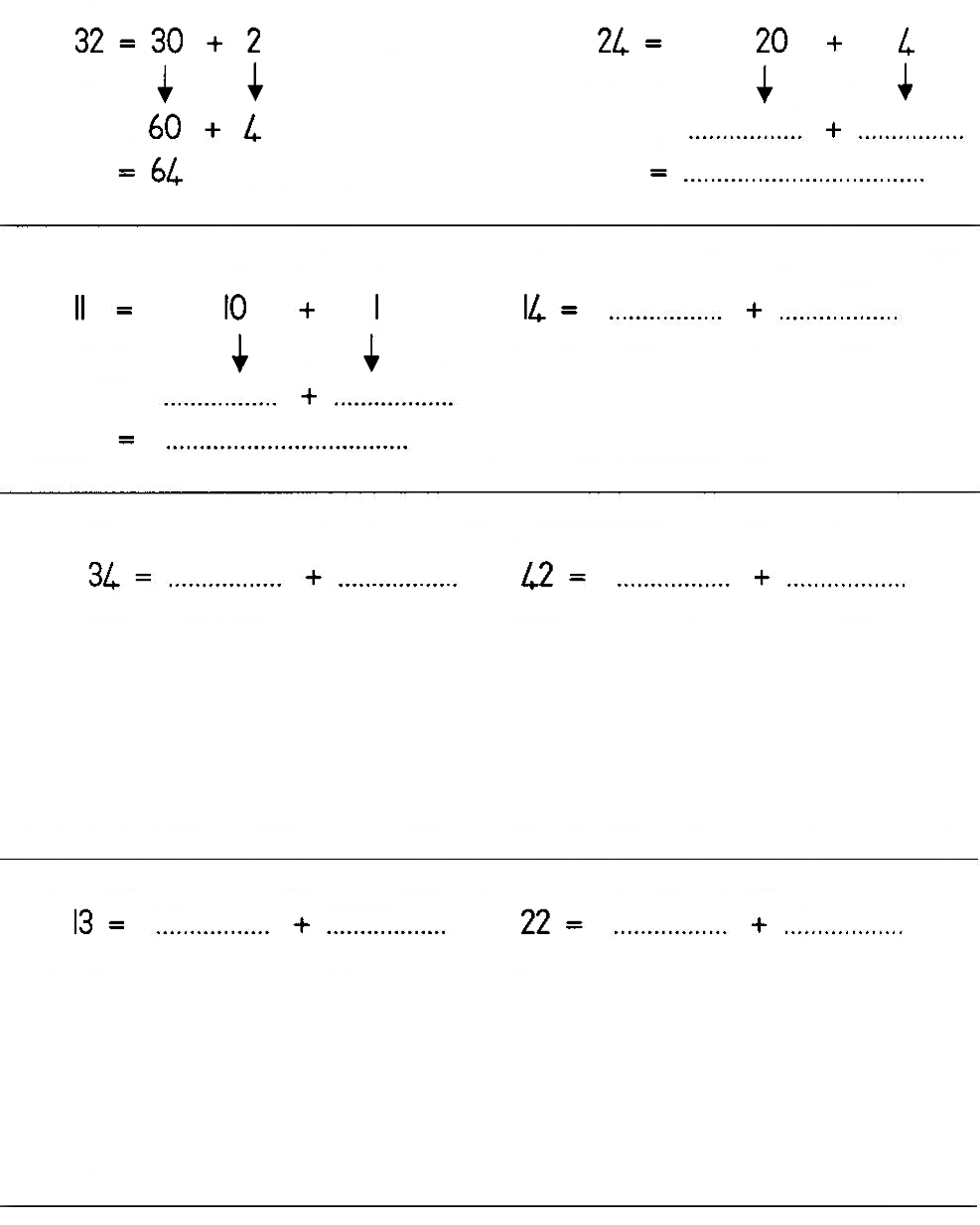
| LO 1.8 | LO 1.10 |
Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent numbers and their relationships, and to count, estimate, calculate and check with competence and confidence in solving problems.
Assessment Standard 1.2: We know this when the learner counts forwards and backwards;
Assessment Standard 1.3: We know this when the learner knows and reads number symbols from 1 to at least 200 and writes number names from 1 to at least 100;
Assessment Standard 1.4: We know this when the learner orders, describes and compares numbers;
Assessment Standard 1.8: We know this when the learner can perform calculations, using appropriate symbols, to solve problems;
Assessment Standard 1.10: We know this when the learner uses the following techniques:
1.10.1 building up and breaking down numbers;
1.10.2 doubling and halving;
1.10.3 using concrete apparatus (e.g. counters);
1.10.4 number-lines.
Learning Outcome 2: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent patterns and relationships, as well as to solve problems using algebraic language and skills.
Assessment Standard 2.2: We know this when the learner copies and extends simple number sequences to at least 200.
Learning Outcome 4: The learner will be able to use appropriate measuring units, instruments and formulae in a variety of contexts.
Assessment Standard 4.3: We know this when the learner calculates elapsed time;
Assessment Standard 4.7: We know this when the learner estimates, measures, compares and orders objects using standard measures.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 2' conversation and receive update notifications?