| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The requirement of continuity is that there should not be abrupt change in function value when there is small change in independent variable. We can enforce this requirement if we can determine x-values in its immediate neighborhood in the domain of function for smallest change in the function values. Mathematically, we say that a function is continuous at a point x=a, if there is small change in function such that , then independent variable “x” varies in its immediate neighborhood such that , where δ and ∈are arbitrarily chosen small positive numbers.
Condition of continuity is expressed in terms of definition of various limits. Note that limit approaches a value when independent variable comes very close to a point where continuity is being checked. If limit approaches very close to the function value at a point, then it is guaranteed that there exists a value of independent variable in its immediate neighborhood. This fulfills the requirement of continuity as explained in previous paragraph.
For the sake of understanding the requirement of continuity, let us consider identity function, which is known to be continuous in its domain.
Identity function
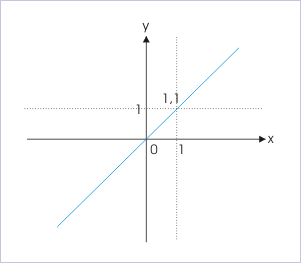
Let us consider a test point, x=1. Here, both left and right limit exist and is equal to 1. As such limit of function exists and is equal to 1, which is equal to the function value. As a matter of fact, these observations underline the requirement of continuity at a point. The conditions for continuity at a point in the domain of function are :
1: Limit of function exits at the point.
2: Limit of function is equal to function value at that point.
Mathematically,
One important aspect of the requirement is that we test continuity at a finite real value of x, having finite function value. Hence, it is implicitly implied that limit of function should evaluate to a finite function value.
A function is continuous from left at x=a when left limit exists at x=a and is equal to function value at that point.
A function is continuous from right at x=a when right limit exists at x=a and is equal to function value at that point.
The condition of continuity given above appears to be same as that of limit, which is defined as :
However, there is one differentiating aspect. The limit need not evaluate to function value as required for continuity. It means continuity of function has stricter requirement than that of the existence of limit. To understand this point, we consider a variant of modulus function as given here,
| x ; x>0
f(x) = | 1 ; x=0| -x ; x<0
Graph of function
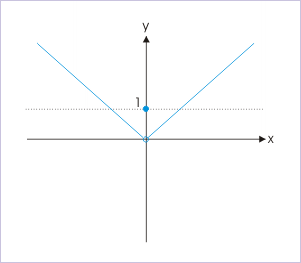
Clearly, limit exists and is equal to zero, but function value is 1 at x=0. Thus, limit is finite, but not equal to function value. As such, given function is not continuous at x=0. The important point to note is that existence of limit or function value at a point is a necessary condition, but not a sufficient condition for continuity. Both the conditions as enumerated should be fulfilled. The concept of continuity, therefore, is a stricter property of a function with respect to limit.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Functions' conversation and receive update notifications?