| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Negative inotropic agents include hypoxia, acidosis, hyperkalemia, and a variety of synthetic drugs. These include numerous beta blockers and calcium channel blockers. Early beta blocker drugs include propranolol and pronethalol, and are credited with revolutionizing treatment of cardiac patients experiencing angina pectoris. There is also a large class of dihydropyridine, phenylalkylamine, and benzothiazepine calcium channel blockers that may be administered decreasing the strength of contraction and SV.
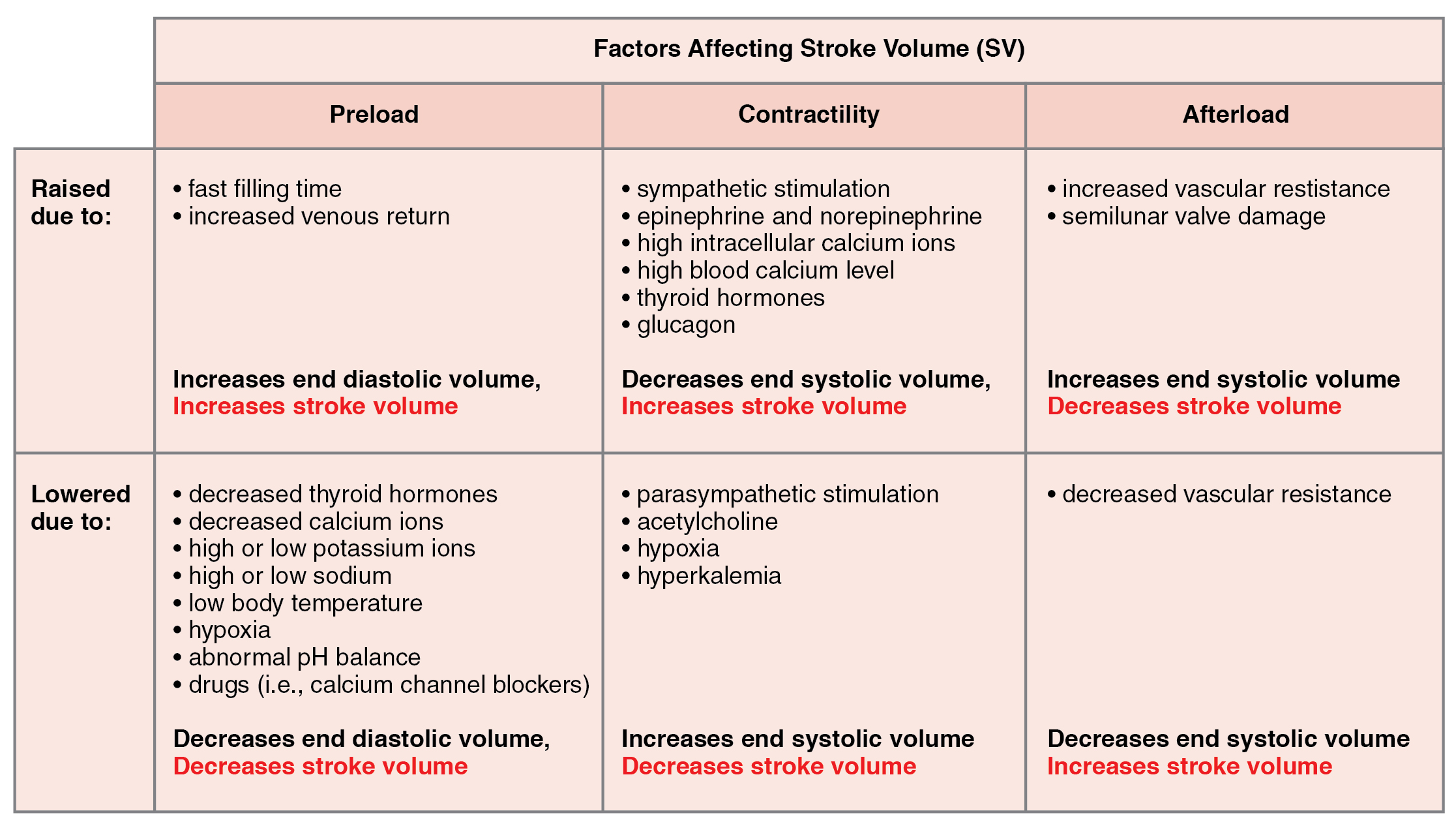
Afterload refers to the tension that the ventricles must develop to pump blood effectively against the resistance in the vascular system. Any condition that increases resistance requires a greater afterload to force open the semilunar valves and pump the blood. Damage to the valves, such as stenosis, which makes them harder to open will also increase afterload. Any decrease in resistance decreases the afterload. [link] summarizes the major factors influencing SV, [link] summarizes the major factors influencing CO, and [link] and [link] summarize cardiac responses to increased and decreased blood flow and pressure in order to restore homeostasis.

| Cardiac Response to Decreasing Blood Flow and Pressure Due to Decreasing Cardiac Output | ||
|---|---|---|
| Baroreceptors (aorta, carotid arteries, venae cavae, and atria) | Chemoreceptors (both central nervous system and in proximity to baroreceptors) | |
| Sensitive to | Decreasing stretch | Decreasing O 2 and increasing CO 2 , H + , and lactic acid |
| Target | Parasympathetic stimulation suppressed | Sympathetic stimulation increased |
| Response of heart | Increasing heart rate and increasing stroke volume | Increasing heart rate and increasing stroke volume |
| Overall effect | Increasing blood flow and pressure due to increasing cardiac output; hemostasis restored | Increasing blood flow and pressure due to increasing cardiac output; hemostasis restored |
| Cardiac Response to Increasing Blood Flow and Pressure Due to Increasing Cardiac Output | ||
|---|---|---|
| Baroreceptors (aorta, carotid arteries, venae cavae, and atria) | Chemoreceptors (both central nervous system and in proximity to baroreceptors) | |
| Sensitive to | Increasing stretch | Increasing O 2 and decreasing CO 2 , H + , and lactic acid |
| Target | Parasympathetic stimulation increased | Sympathetic stimulation suppressed |
| Response of heart | Decreasing heart rate and decreasing stroke volume | Decreasing heart rate and decreasing stroke volume |
| Overall effect | Decreasing blood flow and pressure due to decreasing cardiac output; hemostasis restored | Decreasing blood flow and pressure due to decreasing cardiac output; hemostasis restored |
Many factors affect HR and SV, and together, they contribute to cardiac function. HR is largely determined and regulated by autonomic stimulation and hormones. There are several feedback loops that contribute to maintaining homeostasis dependent upon activity levels, such as the atrial reflex, which is determined by venous return.
SV is regulated by autonomic innervation and hormones, but also by filling time and venous return. Venous return is determined by activity of the skeletal muscles, blood volume, and changes in peripheral circulation. Venous return determines preload and the atrial reflex. Filling time directly related to HR also determines preload. Preload then impacts both EDV and ESV. Autonomic innervation and hormones largely regulate contractility. Contractility impacts EDV as does afterload. CO is the product of HR multiplied by SV. SV is the difference between EDV and ESV.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the '101-321-va - vertebrate form and function ii' conversation and receive update notifications?