| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
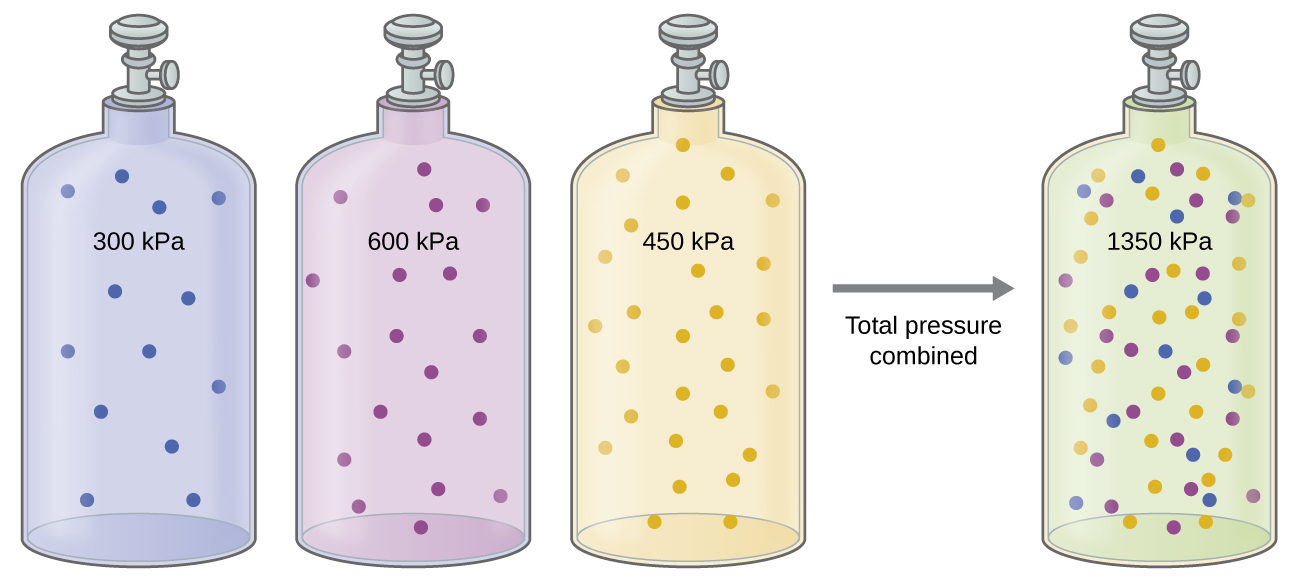
Unless they chemically react with each other, the individual gases in a mixture of gases do not affect each other’s pressure. Each individual gas in a mixture exerts the same pressure that it would exert if it were present alone in the container ( [link] ). The pressure exerted by each individual gas in a mixture is called its partial pressure . This observation is summarized by Dalton’s law of partial pressures : The total pressure of a mixture of ideal gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the component gases :
In the equation P Total is the total pressure of a mixture of gases, P A is the partial pressure of gas A; P B is the partial pressure of gas B; P C is the partial pressure of gas C; and so on.
The partial pressure of gas A is related to the total pressure of the gas mixture via its mole fraction ( X ) , a unit of concentration defined as the number of moles of a component of a solution divided by the total number of moles of all components:
where P A , X A , and n A are the partial pressure, mole fraction, and number of moles of gas A, respectively, and n Total is the number of moles of all components in the mixture.
(a) What are the partial pressures of each of the gases?
(b) What is the total pressure in atmospheres?
The total pressure is given by the sum of the partial pressures:
1.137 atm
Here is another example of this concept, but dealing with mole fraction calculations.
(a) What are the mole fractions of O 2 and N 2 O?
(b) What are the partial pressures of O 2 and N 2 O?
For O 2 ,
and
For N
2 O,
and
1.87 atm

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?