| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Nitrogen pentaoxide, N 2 O 5 , and NO 2 react with water to form nitric acid, HNO 3 . Alchemists, as early as the eighth century, knew nitric acid (shown in [link] ) as aqua fortis (meaning "strong water"). The acid was useful in the separation of gold from silver because it dissolves silver but not gold. Traces of nitric acid occur in the atmosphere after thunderstorms, and its salts are widely distributed in nature. There are tremendous deposits of Chile saltpeter, NaNO 3 , in the desert region near the boundary of Chile and Peru. Bengal saltpeter, KNO 3 , occurs in India and in other countries of the Far East.
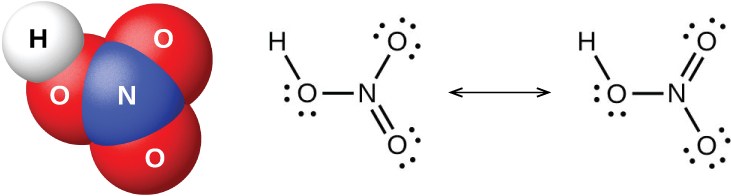
In the laboratory, it is possible to produce nitric acid by heating a nitrate salt (such as sodium or potassium nitrate) with concentrated sulfuric acid:
The Ostwald process is the commercial method for producing nitric acid. This process involves the oxidation of ammonia to nitric oxide, NO; oxidation of nitric oxide to nitrogen dioxide, NO 2 ; and further oxidation and hydration of nitrogen dioxide to form nitric acid:
Or
Pure nitric acid is a colorless liquid. However, it is often yellow or brown in color because NO 2 forms as the acid decomposes. Nitric acid is stable in aqueous solution; solutions containing 68% of the acid are commercially available concentrated nitric acid. It is both a strong oxidizing agent and a strong acid.
The action of nitric acid on a metal rarely produces H 2 (by reduction of H + ) in more than small amounts. Instead, the reduction of nitrogen occurs. The products formed depend on the concentration of the acid, the activity of the metal, and the temperature. Normally, a mixture of nitrates, nitrogen oxides, and various reduction products form. Less active metals such as copper, silver, and lead reduce concentrated nitric acid primarily to nitrogen dioxide. The reaction of dilute nitric acid with copper produces NO. In each case, the nitrate salts of the metals crystallize upon evaporation of the resultant solutions.
Nonmetallic elements, such as sulfur, carbon, iodine, and phosphorus, undergo oxidation by concentrated nitric acid to their oxides or oxyacids, with the formation of NO 2 :
Nitric acid oxidizes many compounds; for example, concentrated nitric acid readily oxidizes hydrochloric acid to chlorine and chlorine dioxide. A mixture of one part concentrated nitric acid and three parts concentrated hydrochloric acid (called aqua regia , which means royal water) reacts vigorously with metals. This mixture is particularly useful in dissolving gold, platinum, and other metals that are more difficult to oxidize than hydrogen. A simplified equation to represent the action of aqua regia on gold is:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?