| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
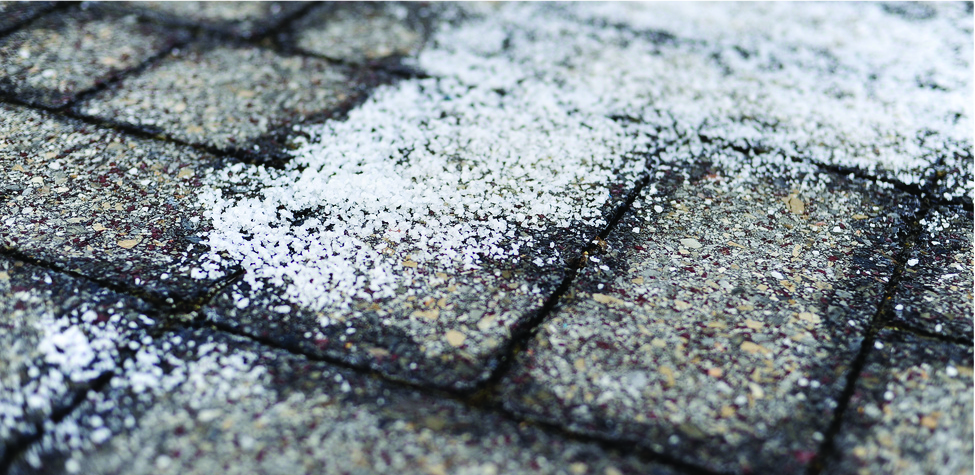
Solutions freeze at lower temperatures than pure liquids. This phenomenon is exploited in “de-icing” schemes that use salt ( [link] ), calcium chloride, or urea to melt ice on roads and sidewalks, and in the use of ethylene glycol as an “antifreeze” in automobile radiators. Seawater freezes at a lower temperature than fresh water, and so the Arctic and Antarctic oceans remain unfrozen even at temperatures below 0 °C (as do the body fluids of fish and other cold-blooded sea animals that live in these oceans).

The decrease in freezing point of a dilute solution compared to that of the pure solvent, Δ T f , is called the freezing point depression and is directly proportional to the molal concentration of the solute
where m is the molal concentration of the solute in the solvent and K f is called the freezing point depression constant (or cryoscopic constant ). Just as for boiling point elevation constants, these are characteristic properties whose values depend on the chemical identity of the solvent. Values of K f for several solvents are listed in [link] .

−9.3 °C
Sodium chloride and its group 2 analogs calcium and magnesium chloride are often used to de-ice roadways and sidewalks, due to the fact that a solution of any one of these salts will have a freezing point lower than 0 °C, the freezing point of pure water. The group 2 metal salts are frequently mixed with the cheaper and more readily available sodium chloride (“rock salt”) for use on roads, since they tend to be somewhat less corrosive than the NaCl, and they provide a larger depression of the freezing point, since they dissociate to yield three particles per formula unit, rather than two particles like the sodium chloride.
Because these ionic compounds tend to hasten the corrosion of metal, they would not be a wise choice to use in antifreeze for the radiator in your car or to de-ice a plane prior to takeoff. For these applications, covalent compounds, such as ethylene or propylene glycol, are often used. The glycols used in radiator fluid not only lower the freezing point of the liquid, but they elevate the boiling point, making the fluid useful in both winter and summer. Heated glycols are often sprayed onto the surface of airplanes prior to takeoff in inclement weather in the winter to remove ice that has already formed and prevent the formation of more ice, which would be particularly dangerous if formed on the control surfaces of the aircraft ( [link] ).


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?