| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A simple way to collect gases that do not react with water is to capture them in a bottle that has been filled with water and inverted into a dish filled with water. The pressure of the gas inside the bottle can be made equal to the air pressure outside by raising or lowering the bottle. When the water level is the same both inside and outside the bottle ( [link] ), the pressure of the gas is equal to the atmospheric pressure, which can be measured with a barometer.
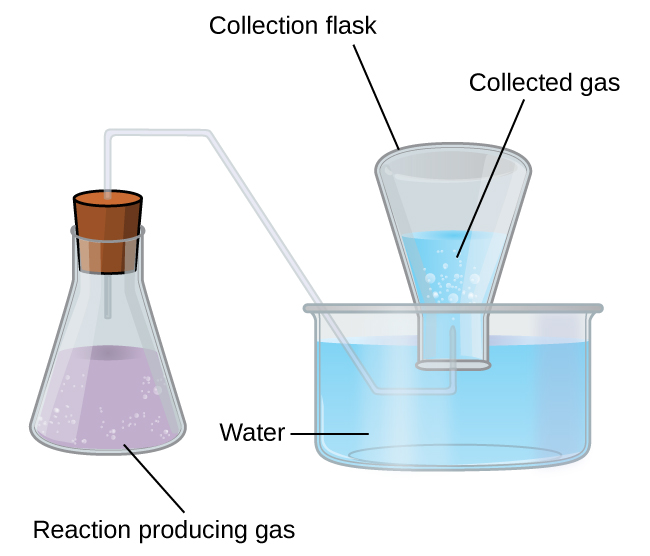
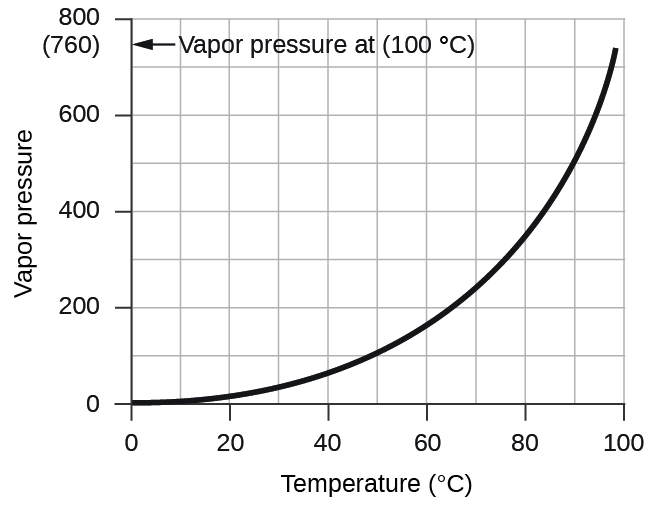
However, there is another factor we must consider when we measure the pressure of the gas by this method. Water evaporates and there is always gaseous water (water vapor) above a sample of liquid water. As a gas is collected over water, it becomes saturated with water vapor and the total pressure of the mixture equals the partial pressure of the gas plus the partial pressure of the water vapor. The pressure of the pure gas is therefore equal to the total pressure minus the pressure of the water vapor—this is referred to as the “dry” gas pressure, that is, the pressure of the gas only, without water vapor. The vapor pressure of water , which is the pressure exerted by water vapor in equilibrium with liquid water in a closed container, depends on the temperature ( [link] ); more detailed information on the temperature dependence of water vapor can be found in [link] , and vapor pressure will be discussed in more detail in the next chapter on liquids.
| Vapor Pressure of Ice and Water in Various Temperatures at Sea Level | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | Pressure (torr) | Temperature (°C) | Pressure (torr) | Temperature (°C) | Pressure (torr) | ||
| –10 | 1.95 | 18 | 15.5 | 30 | 31.8 | ||
| –5 | 3.0 | 19 | 16.5 | 35 | 42.2 | ||
| –2 | 3.9 | 20 | 17.5 | 40 | 55.3 | ||
| 0 | 4.6 | 21 | 18.7 | 50 | 92.5 | ||
| 2 | 5.3 | 22 | 19.8 | 60 | 149.4 | ||
| 4 | 6.1 | 23 | 21.1 | 70 | 233.7 | ||
| 6 | 7.0 | 24 | 22.4 | 80 | 355.1 | ||
| 8 | 8.0 | 25 | 23.8 | 90 | 525.8 | ||
| 10 | 9.2 | 26 | 25.2 | 95 | 633.9 | ||
| 12 | 10.5 | 27 | 26.7 | 99 | 733.2 | ||
| 14 | 12.0 | 28 | 28.3 | 100.0 | 760.0 | ||
| 16 | 13.6 | 29 | 30.0 | 101.0 | 787.6 |
Rearranging this equation to solve for the pressure of argon gives:
The pressure of water vapor above a sample of liquid water at 26 °C is 25.2 torr ( Appendix E ), so:
0.583 L

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?