| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The order of a covalent bond is a guide to its strength; a bond between two given atoms becomes stronger as the bond order increases ( [link] ). If the distribution of electrons in the molecular orbitals between two atoms is such that the resulting bond would have a bond order of zero, a stable bond does not form. We next look at some specific examples of MO diagrams and bond orders.
A dihydrogen molecule (H 2 ) forms from two hydrogen atoms. When the atomic orbitals of the two atoms combine, the electrons occupy the molecular orbital of lowest energy, the σ 1 s bonding orbital. A dihydrogen molecule, H 2 , readily forms because the energy of a H 2 molecule is lower than that of two H atoms. The σ 1 s orbital that contains both electrons is lower in energy than either of the two 1 s atomic orbitals.
A molecular orbital can hold two electrons, so both electrons in the H 2 molecule are in the σ 1 s bonding orbital; the electron configuration is We represent this configuration by a molecular orbital energy diagram ( [link] ) in which a single upward arrow indicates one electron in an orbital, and two (upward and downward) arrows indicate two electrons of opposite spin.
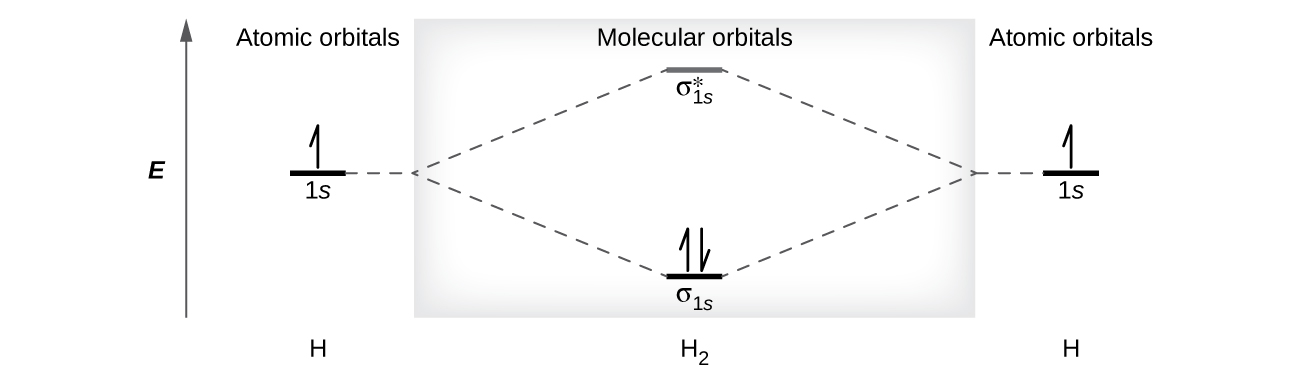
A dihydrogen molecule contains two bonding electrons and no antibonding electrons so we have
Because the bond order for the H–H bond is equal to 1, the bond is a single bond.
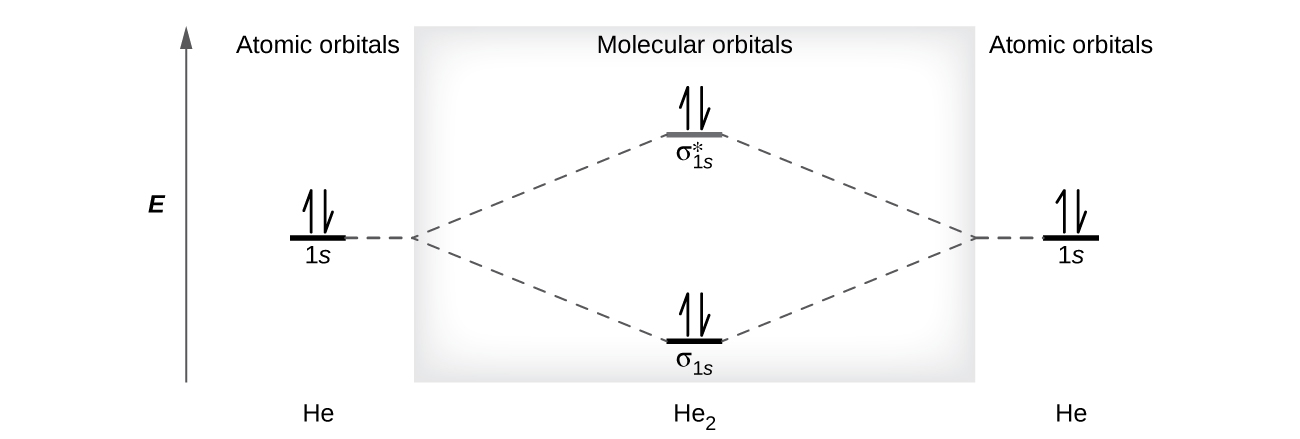
A helium atom has two electrons, both of which are in its 1 s orbital. Two helium atoms do not combine to form a dihelium molecule, He 2 , with four electrons, because the stabilizing effect of the two electrons in the lower-energy bonding orbital would be offset by the destabilizing effect of the two electrons in the higher-energy antibonding molecular orbital. We would write the hypothetical electron configuration of He 2 as as in [link] . The net energy change would be zero, so there is no driving force for helium atoms to form the diatomic molecule. In fact, helium exists as discrete atoms rather than as diatomic molecules. The bond order in a hypothetical dihelium molecule would be zero.
A bond order of zero indicates that no bond is formed between two atoms.
Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li 2 , Be 2 , B 2 , C 2 , N 2 , O 2 , F 2 , and Ne 2 . However, we can predict that the Be 2 molecule and the Ne 2 molecule would not be stable. We can see this by a consideration of the molecular electron configurations ( [link] ).
We predict valence molecular orbital electron configurations just as we predict electron configurations of atoms. Valence electrons are assigned to valence molecular orbitals with the lowest possible energies. Consistent with Hund’s rule, whenever there are two or more degenerate molecular orbitals, electrons fill each orbital of that type singly before any pairing of electrons takes place.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?