| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
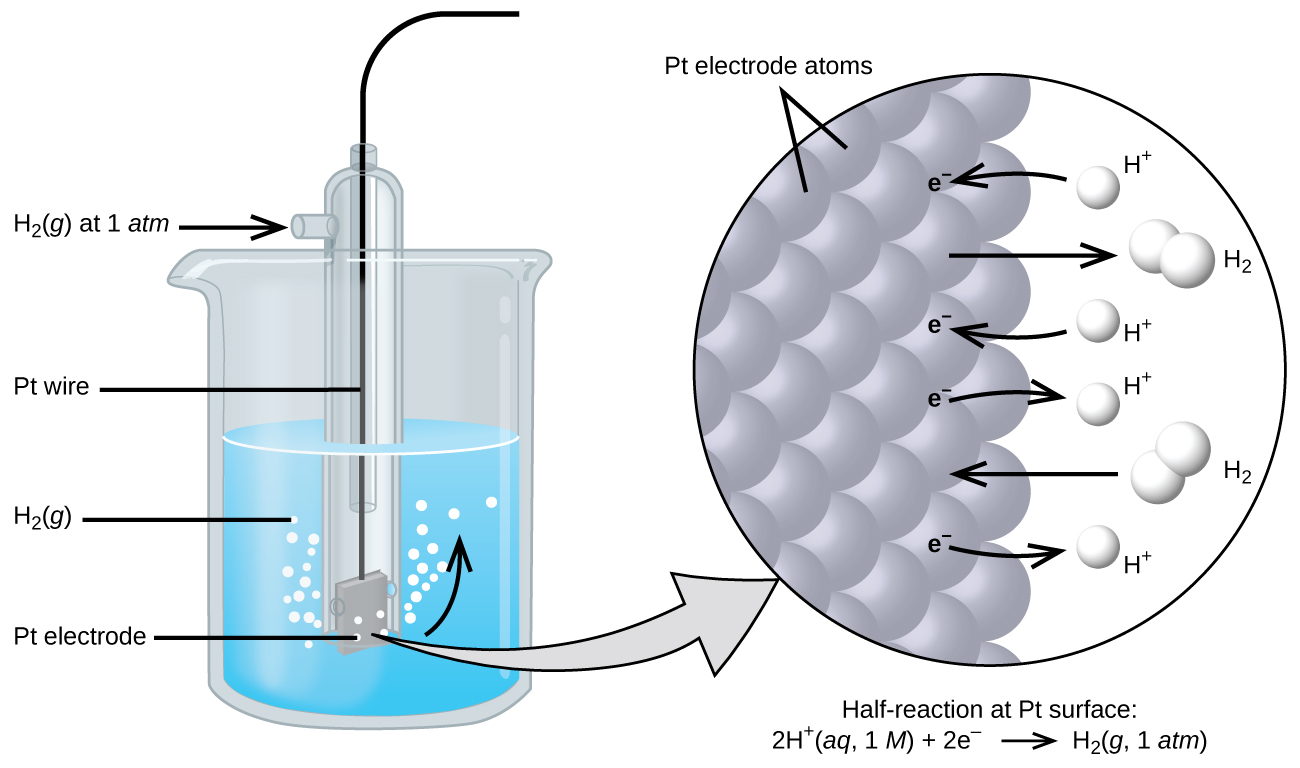
The cell potential in [link] (+0.46 V) results from the difference in the electrical potentials for each electrode. While it is impossible to determine the electrical potential of a single electrode, we can assign an electrode the value of zero and then use it as a reference. The electrode chosen as the zero is shown in [link] and is called the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) . The SHE consists of 1 atm of hydrogen gas bubbled through a 1 M HCl solution, usually at room temperature. Platinum, which is chemically inert, is used as the electrode. The reduction half-reaction chosen as the reference is
E ° is the standard reduction potential. The superscript “°” on the E denotes standard conditions (1 bar or 1 atm for gases, 1 M for solutes). The voltage is defined as zero for all temperatures.
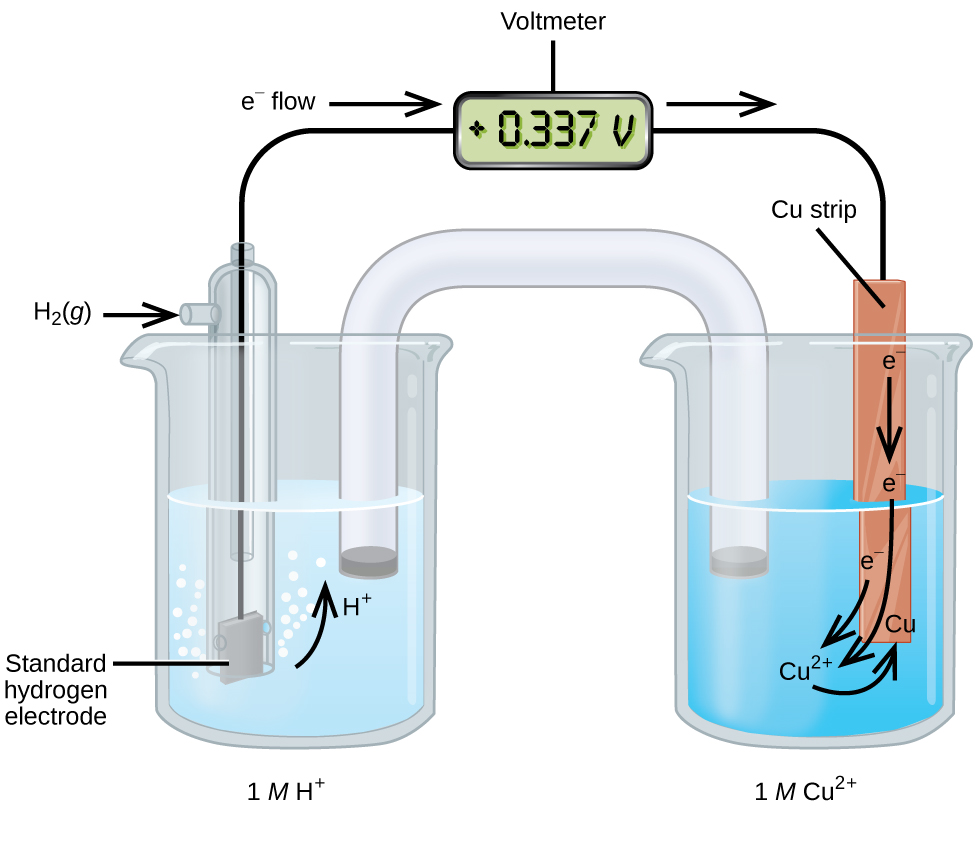
A galvanic cell consisting of a SHE and Cu 2+ /Cu half-cell can be used to determine the standard reduction potential for Cu 2+ ( [link] ). In cell notation, the reaction is
Electrons flow from the anode to the cathode. The reactions, which are reversible, are
The standard reduction potential can be determined by subtracting the standard reduction potential for the reaction occurring at the anode from the standard reduction potential for the reaction occurring at the cathode. The minus sign is necessary because oxidation is the reverse of reduction.
Using the SHE as a reference, other standard reduction potentials can be determined. Consider the cell shown in [link] , where
Electrons flow from left to right, and the reactions are
The standard reduction potential can be determined by subtracting the standard reduction potential for the reaction occurring at the anode from the standard reduction potential for the reaction occurring at the cathode. The minus sign is needed because oxidation is the reverse of reduction.
It is important to note that the potential is not doubled for the cathode reaction.
The SHE is rather dangerous and rarely used in the laboratory. Its main significance is that it established the zero for standard reduction potentials. Once determined, standard reduction potentials can be used to determine the standard cell potential , for any cell. For example, for the cell shown in [link] ,

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?