| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We have studied the general characteristics of functions, so now let’s examine some specific classes of functions. We begin by reviewing the basic properties of linear and quadratic functions, and then generalize to include higher-degree polynomials. By combining root functions with polynomials, we can define general algebraic functions and distinguish them from the transcendental functions we examine later in this chapter. We finish the section with examples of piecewise-defined functions and take a look at how to sketch the graph of a function that has been shifted, stretched, or reflected from its initial form.
The easiest type of function to consider is a linear function . Linear functions have the form where and are constants. In [link] , we see examples of linear functions when is positive, negative, and zero. Note that if the graph of the line rises as increases. In other words, is increasing on If the graph of the line falls as increases. In this case, is decreasing on If the line is horizontal.
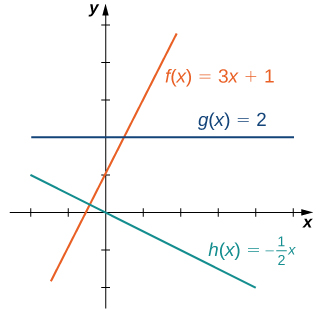
As suggested by [link] , the graph of any linear function is a line. One of the distinguishing features of a line is its slope. The slope is the change in for each unit change in The slope measures both the steepness and the direction of a line. If the slope is positive, the line points upward when moving from left to right. If the slope is negative, the line points downward when moving from left to right. If the slope is zero, the line is horizontal. To calculate the slope of a line, we need to determine the ratio of the change in versus the change in To do so, we choose any two points and on the line and calculate In [link] , we see this ratio is independent of the points chosen.
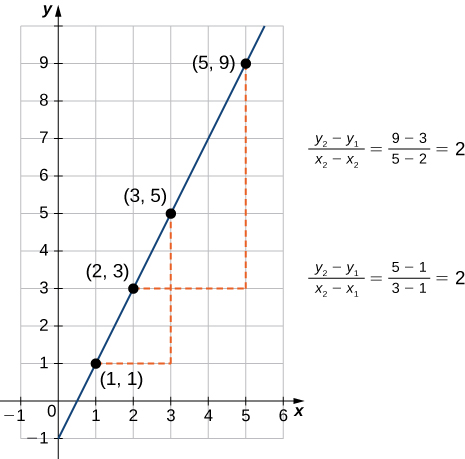
Consider line passing through points and Let and denote the changes in and respectively. The slope of the line is
We now examine the relationship between slope and the formula for a linear function. Consider the linear function given by the formula As discussed earlier, we know the graph of a linear function is given by a line. We can use our definition of slope to calculate the slope of this line. As shown, we can determine the slope by calculating for any points and on the line. Evaluating the function at we see that is a point on this line. Evaluating this function at we see that is also a point on this line. Therefore, the slope of this line is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?