| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
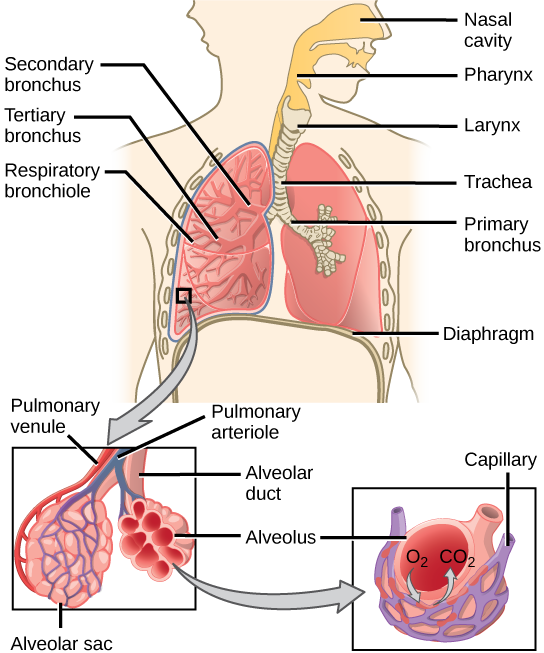
The end of the trachea divides into two bronchi that enter the right and left lung. Air enters the lungs through the primary bronchi . The primary bronchus divides, creating smaller and smaller diameter bronchi until the passages are under 1 mm (.03 in) in diameter when they are called bronchioles as they split and spread through the lung. Like the trachea, the bronchus and bronchioles are made of cartilage and smooth muscle. Bronchi are innervated by nerves of both the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems that control muscle contraction (parasympathetic) or relaxation (sympathetic) in the bronchi and bronchioles, depending on the nervous system’s cues. The final bronchioles are the respiratory bronchioles. Alveolar ducts are attached to the end of each respiratory bronchiole. At the end of each duct are alveolar sacs, each containing 20 to 30 alveoli . Gas exchange occurs only in the alveoli. The alveoli are thin-walled and look like tiny bubbles within the sacs. The alveoli are in direct contact with capillaries of the circulatory system. Such intimate contact ensures that oxygen will diffuse from the alveoli into the blood. In addition, carbon dioxide will diffuse from the blood into the alveoli to be exhaled. The anatomical arrangement of capillaries and alveoli emphasizes the structural and functional relationship of the respiratory and circulatory systems. Estimates for the surface area of alveoli in the lungs vary around 100 m 2 . This large area is about the area of half a tennis court. This large surface area, combined with the thin-walled nature of the alveolar cells, allows gases to easily diffuse across the cells.
Which of the following statements about the human respiratory system is false?
Watch this video for a review of the respiratory system.
The circulatory system is a network of vessels—the arteries, veins, and capillaries—and a pump, the heart. In all vertebrate organisms this is a closed-loop system, in which the blood is largely separated from the body’s other extracellular fluid compartment, the interstitial fluid, which is the fluid bathing the cells. Blood circulates inside blood vessels and circulates unidirectionally from the heart around one of two circulatory routes, then returns to the heart again; this is a closed circulatory system . Open circulatory systems are found in invertebrate animals in which the circulatory fluid bathes the internal organs directly even though it may be moved about with a pumping heart.
The heart is a complex muscle that consists of two pumps: one that pumps blood through pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the other that pumps blood through systemic circulation to the rest of the body’s tissues (and the heart itself).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?