| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Imagine a population of ten individuals, half with allele A and half with allele a (the individuals are haploid). In a stable population, the next generation will also have ten individuals. Choose that generation randomly by flipping a coin ten times and let heads be A and tails be a . It is unlikely that the next generation will have exactly half of each allele. There might be six of one and four of the other, or some different set of frequencies. Thus, the allele frequencies have changed and evolution has occurred. A coin will no longer work to choose the next generation (because the odds are no longer one half for each allele). The frequency in each generation will drift up and down on what is known as a random walk until at one point either all A or all a are chosen and that allele is fixed from that point on. This could take a very long time for a large population. This simplification is not very biological, but it can be shown that real populations behave this way. The effect of drift on frequencies is greater the smaller a population is. Its effect is also greater on an allele with a frequency far from one half. Drift will influence every allele, even those that are being naturally selected.
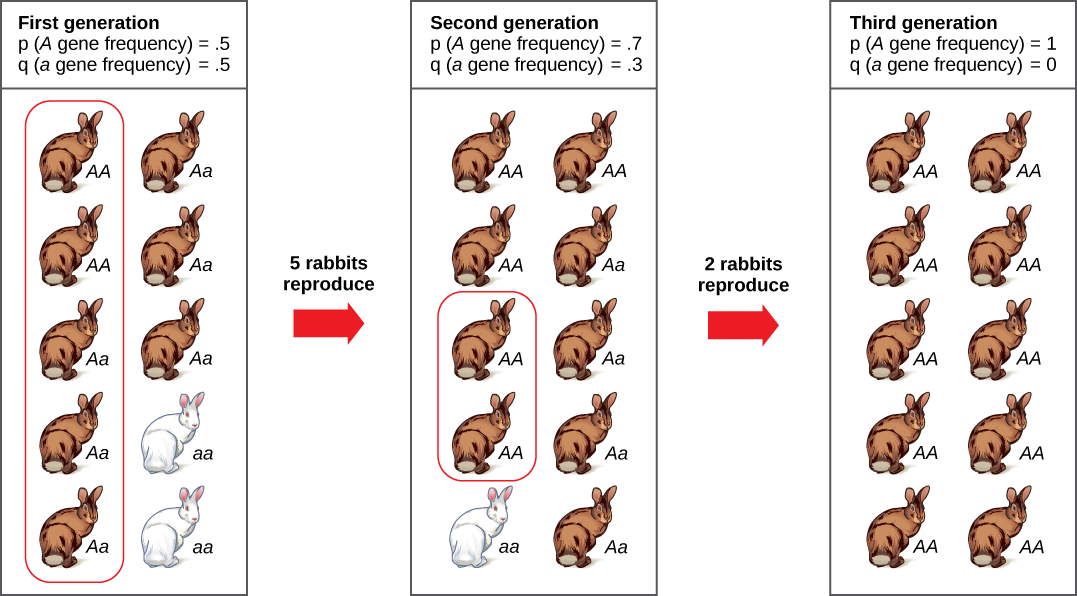
Do you think genetic drift would happen more quickly on an island or on the mainland?
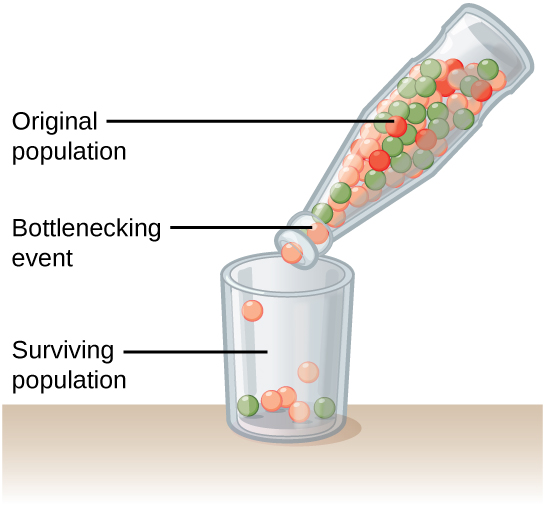
Genetic drift can also be magnified by natural or human-caused events, such as a disaster that randomly kills a large portion of the population, which is known as the bottleneck effect that results in a large portion of the genome suddenly being wiped out ( [link] ). In one fell swoop, the genetic structure of the survivors becomes the genetic structure of the entire population, which may be very different from the pre-disaster population. The disaster must be one that kills for reasons unrelated to the organism’s traits, such as a hurricane or lava flow. A mass killing caused by unusually cold temperatures at night, is likely to affect individuals differently depending on the alleles they possess that confer cold hardiness.
Another scenario in which populations might experience a strong influence of genetic drift is if some portion of the population leaves to start a new population in a new location, or if a population gets divided by a physical barrier of some kind. In this situation, those individuals are unlikely to be representative of the entire population which results in the founder effect . The founder effect occurs when the genetic structure matches that of the new population’s founding fathers and mothers. The founder effect is believed to have been a key factor in the genetic history of the Afrikaner population of Dutch settlers in South Africa, as evidenced by mutations that are common in Afrikaners but rare in most other populations. This is likely due to a higher-than-normal proportion of the founding colonists, which were a small sample of the original population, carried these mutations. As a result, the population expresses unusually high incidences of Huntington’s disease (HD) and Fanconi anemia (FA), a genetic disorder known to cause bone marrow and congenital abnormalities, and even cancer. A. J. Tipping et al., “Molecular and Genealogical Evidence for a Founder Effect in Fanconi Anemia Families of the Afrikaner Population of South Africa,” PNAS 98, no. 10 (2001): 5734-5739, doi: 10.1073/pnas.091402398.
Visit this site to learn more about genetic drift and to run simulations of allele changes caused by drift.
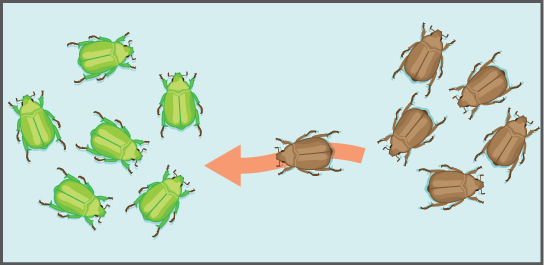
Another important evolutionary force is gene flow , or the flow of alleles in and out of a population resulting from the migration of individuals or gametes ( [link] ). While some populations are fairly stable, others experience more flux. Many plants, for example, send their seeds far and wide, by wind or in the guts of animals; these seeds may introduce alleles common in the source population to a new population in which they are rare.
There are four factors that can change the allele frequencies of a population. Natural selection works by selecting for alleles that confer beneficial traits or behaviors, while selecting against those for deleterious qualities. Mutations introduce new alleles into a population. Genetic drift stems from the chance occurrence that some individuals have more offspring than others and results in changes in allele frequencies that are random in direction. When individuals leave or join the population, allele frequencies can change as a result of gene flow.
[link] Do you think genetic drift would happen more quickly on an island or on the mainland?
[link] Genetic drift is likely to occur more rapidly on an island, where smaller populations are expected to occur.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?