| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
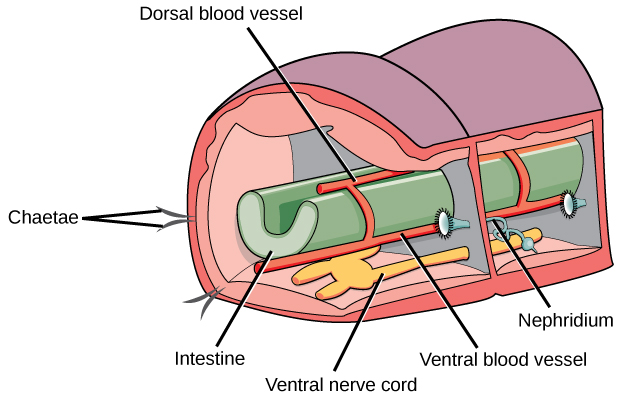
Annelids have a closed circulatory system with muscular pumping “hearts” in the anterior segments, dorsal and ventral blood vessels that run the length of the body with connections in each segment, and capillaries that service individual tissues. Gas exchange occurs across the moist body surface. Excretion is carried out by pairs of primitive “kidneys” called metanephridia that consist of a convoluted tubule and an open, ciliated funnel present in every segment. Annelids have a well-developed nervous system with two ventral nerve cords and a nerve ring of fused ganglia present around the pharynx.
Annelids may be either monoecious with permanent gonads (as in earthworms and leeches) or dioecious with temporary or seasonal gonads (as in polychaetes).
This video and animation provides a close-up look at annelid anatomy.
Phylum Annelida includes the classes Polychaeta and Clitellata ( [link] ); the latter contains subclasses Oligochaeta, Hirudinoidea, and Branchiobdellida.
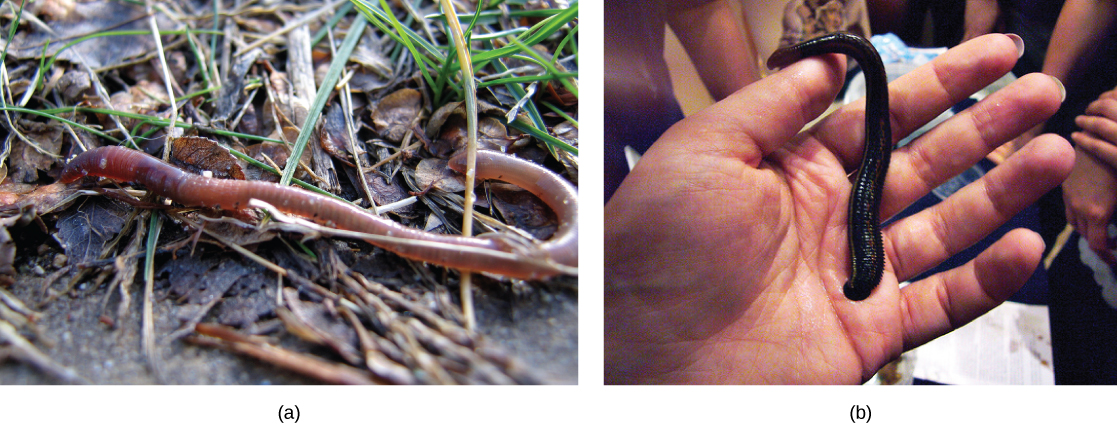
Earthworms are the most abundant members of the subclass Oligochaeta, distinguished by the presence of the clitellum , a ring structure in the skin that secretes mucus to bind mating individuals and forms a protective cocoon for the eggs. They also have a few, reduced chaetae (oligo- = “few”; -chaetae = “hairs”). The number and size of chaetae is greatly diminished in oligochaetes as compared to the polychaetes (poly- = “many”; -chaetae = “hairs”). The chaetae of polychaetes are also arranged within fleshy, flat, paired appendages on each segment called parapodia.
The subclass Hirudinoidea includes leeches. Significant differences between leeches and other annelids include the development of suckers at the anterior and posterior ends, and the absence of chaetae. Additionally, the segmentation of the body wall may not correspond to internal segmentation of the coelomic cavity. This adaptation may allow leeches to swell when ingesting blood from host vertebrates. The subclass Branchiobdellida includes about 150 species that show similarity to leeches as well as oligochaetes. All species are obligate symbionts, meaning that they can only survive associated with their host, mainly with freshwater crayfish. They feed on the algae that grows on the carapace of the crayfish.

The phylum Mollusca is a large, mainly marine group of invertebrates. Mollusks show a variety of morphologies. Many mollusks secrete a calcareous shell for protection, but in other species, the shell is reduced or absent. Mollusks are protostomes. The dorsal epidermis in mollusks is modified to form the mantle, which encloses the mantle cavity and visceral organs. This cavity is distinct from the coelomic cavity, which the adult animal retains, surrounding the heart. Respiration is facilitated by gills known as ctenidia. A chitinous scraper called the radula is present in most mollusks. Mollusks are mostly dioecious and are divided into seven classes.
The phylum Annelida includes worm-like, segmented animals. Segmentation is both external and internal, which is called metamerism. Annelids are protostomes. The presence of chitinous hairs called chaetae is characteristic of most members. These animals have well-developed nervous and digestive systems. Polychaete annelids have parapodia that participate in locomotion and respiration. Suckers are seen in the order Hirudinea. Breeding systems include separate sexes and hermaphroditism.
[link] Which of the following statements about the anatomy of a mollusk is false?
[link] D

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?