| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Structures that produce photosynthates for the growing plant are referred to as sources . Sugars produced in sources, such as leaves, need to be delivered to growing parts of the plant via the phloem in a process called translocation . The points of sugar delivery, such as roots, young shoots, and developing seeds, are called sinks . Seeds, tubers, and bulbs can be either a source or a sink, depending on the plant’s stage of development and the season.
The products from the source are usually translocated to the nearest sink through the phloem. For example, the highest leaves will send photosynthates upward to the growing shoot tip, whereas lower leaves will direct photosynthates downward to the roots. Intermediate leaves will send products in both directions, unlike the flow in the xylem, which is always unidirectional (soil to leaf to atmosphere). The pattern of photosynthate flow changes as the plant grows and develops. Photosynthates are directed primarily to the roots early on, to shoots and leaves during vegetative growth, and to seeds and fruits during reproductive development. They are also directed to tubers for storage.
Photosynthates, such as sucrose, are produced in the mesophyll cells of photosynthesizing leaves. From there they are translocated through the phloem to where they are used or stored. Mesophyll cells are connected by cytoplasmic channels called plasmodesmata. Photosynthates move through these channels to reach phloem sieve-tube elements (STEs) in the vascular bundles. From the mesophyll cells, the photosynthates are loaded into the phloem STEs. The sucrose is actively transported against its concentration gradient (a process requiring ATP) into the phloem cells using the electrochemical potential of the proton gradient. This is coupled to the uptake of sucrose with a carrier protein called the sucrose-H + symporter.
Phloem STEs have reduced cytoplasmic contents, and are connected by a sieve plate with pores that allow for pressure-driven bulk flow, or translocation, of phloem sap. Companion cells are associated with STEs. They assist with metabolic activities and produce energy for the STEs ( [link] ).
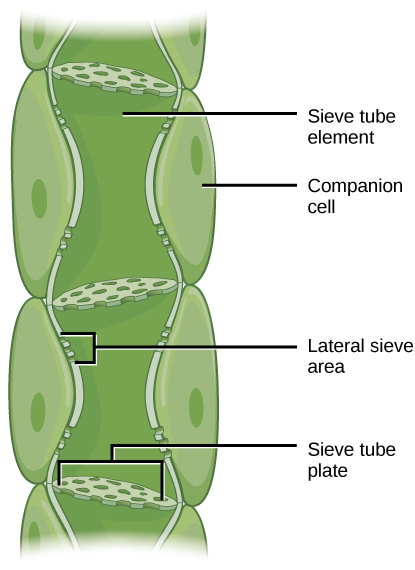
Once in the phloem, the photosynthates are translocated to the closest sink. Phloem sap is an aqueous solution that contains up to 30 percent sugar, minerals, amino acids, and plant growth regulators. The high percentage of sugar decreases Ψ s, which decreases the total water potential and causes water to move by osmosis from the adjacent xylem into the phloem tubes, thereby increasing pressure. This increase in total water potential causes the bulk flow of phloem from source to sink ( [link] ). Sucrose concentration in the sink cells is lower than in the phloem STEs because the sink sucrose has been metabolized for growth, or converted to starch for storage or other polymers, such as cellulose, for structural integrity. Unloading at the sink end of the phloem tube occurs by either diffusion or active transport of sucrose molecules from an area of high concentration to one of low concentration. Water diffuses from the phloem by osmosis and is then transpired or recycled via the xylem back into the phloem sap.
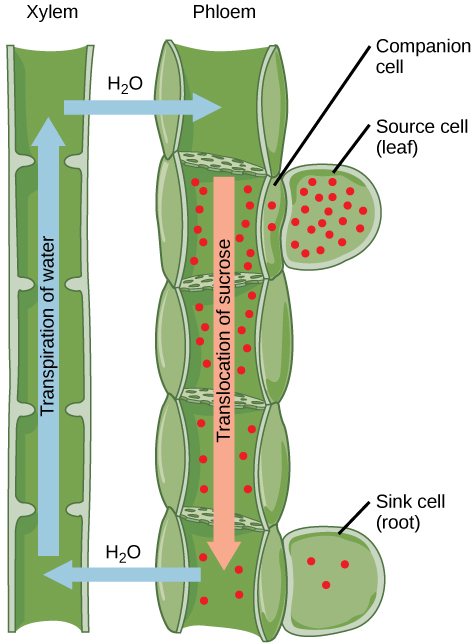
Water potential (Ψ) is a measure of the difference in potential energy between a water sample and pure water. The water potential in plant solutions is influenced by solute concentration, pressure, gravity, and matric potential. Water potential and transpiration influence how water is transported through the xylem in plants. These processes are regulated by stomatal opening and closing. Photosynthates (mainly sucrose) move from sources to sinks through the plant’s phloem. Sucrose is actively loaded into the sieve-tube elements of the phloem. The increased solute concentration causes water to move by osmosis from the xylem into the phloem. The positive pressure that is produced pushes water and solutes down the pressure gradient. The sucrose is unloaded into the sink, and the water returns to the xylem vessels.
[link] Positive water potential is placed on the left side of the tube by increasing Ψ p such that the water level rises on the right side. Could you equalize the water level on each side of the tube by adding solute, and if so, how?
[link] Yes, you can equalize the water level by adding the solute to the left side of the tube such that water moves toward the left until the water levels are equal.
[link] Which of the following statements is false?
[link] B.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?