| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Produced by signaling cells and the subsequent binding to receptors in target cells, ligands act as chemical signals that travel to the target cells to coordinate responses. The types of molecules that serve as ligands are incredibly varied and range from small proteins to small ions like calcium (Ca 2+ ).
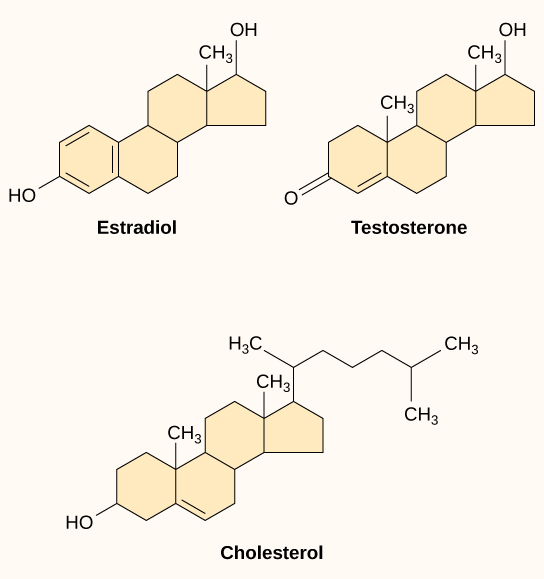
Small hydrophobic ligands can directly diffuse through the plasma membrane and interact with internal receptors. Important members of this class of ligands are the steroid hormones. Steroids are lipids that have a hydrocarbon skeleton with four fused rings; different steroids have different functional groups attached to the carbon skeleton. Steroid hormones include the female sex hormone, estradiol, which is a type of estrogen; the male sex hormone, testosterone; and cholesterol, which is an important structural component of biological membranes and a precursor of steriod hormones ( [link] ). Other hydrophobic hormones include thyroid hormones and vitamin D. In order to be soluble in blood, hydrophobic ligands must bind to carrier proteins while they are being transported through the bloodstream.
Water-soluble ligands are polar and therefore cannot pass through the plasma membrane unaided; sometimes, they are too large to pass through the membrane at all. Instead, most water-soluble ligands bind to the extracellular domain of cell-surface receptors. This group of ligands is quite diverse and includes small molecules, peptides, and proteins.
Nitric oxide (NO) is a gas that also acts as a ligand. It is able to diffuse directly across the plasma membrane, and one of its roles is to interact with receptors in smooth muscle and induce relaxation of the tissue. NO has a very short half-life and therefore only functions over short distances. Nitroglycerin, a treatment for heart disease, acts by triggering the release of NO, which causes blood vessels to dilate (expand), thus restoring blood flow to the heart. NO has become better known recently because the pathway that it affects is targeted by prescription medications for erectile dysfunction, such as Viagra (erection involves dilated blood vessels).
Cells communicate by both inter- and intracellular signaling. Signaling cells secrete ligands that bind to target cells and initiate a chain of events within the target cell. The four categories of signaling in multicellular organisms are paracrine signaling, endocrine signaling, autocrine signaling, and direct signaling across gap junctions. Paracrine signaling takes place over short distances. Endocrine signals are carried long distances through the bloodstream by hormones, and autocrine signals are received by the same cell that sent the signal or other nearby cells of the same kind. Gap junctions allow small molecules, including signaling molecules, to flow between neighboring cells.
Internal receptors are found in the cell cytoplasm. Here, they bind ligand molecules that cross the plasma membrane; these receptor-ligand complexes move to the nucleus and interact directly with cellular DNA. Cell-surface receptors transmit a signal from outside the cell to the cytoplasm. Ion channel-linked receptors, when bound to their ligands, form a pore through the plasma membrane through which certain ions can pass. G-protein-linked receptors interact with a G-protein on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane, promoting the exchange of bound GDP for GTP and interacting with other enzymes or ion channels to transmit a signal. Enzyme-linked receptors transmit a signal from outside the cell to an intracellular domain of a membrane-bound enzyme. Ligand binding causes activation of the enzyme. Small hydrophobic ligands (like steroids) are able to penetrate the plasma membrane and bind to internal receptors. Water-soluble hydrophilic ligands are unable to pass through the membrane; instead, they bind to cell-surface receptors, which transmit the signal to the inside of the cell.
[link] HER2 is a receptor tyrosine kinase. In 30 percent of human breast cancers, HER2 is permanently activated, resulting in unregulated cell division. Lapatinib, a drug used to treat breast cancer, inhibits HER2 receptor tyrosine kinase autophosphorylation (the process by which the receptor adds phosphates onto itself), thus reducing tumor growth by 50 percent. Besides autophosphorylation, which of the following steps would be inhibited by Lapatinib?
[link] C. The downstream cellular response would be inhibited.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?