| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
If the pathogen is never encountered again during the individual’s lifetime, B and T memory cells will circulate for a few years or even several decades and will gradually die off, having never functioned as effector cells. However, if the host is re-exposed to the same pathogen type, circulating memory cells will immediately differentiate into plasma cells and CTLs without input from APCs or T H cells. One reason the adaptive immune response is delayed is because it takes time for naïve B and T cells with the appropriate antigen specificities to be identified and activated. Upon reinfection, this step is skipped, and the result is a more rapid production of immune defenses. Memory B cells that differentiate into plasma cells output tens to hundreds-fold greater antibody amounts than were secreted during the primary response, as the graph in [link] illustrates. This rapid and dramatic antibody response may stop the infection before it can even become established, and the individual may not realize they had been exposed.
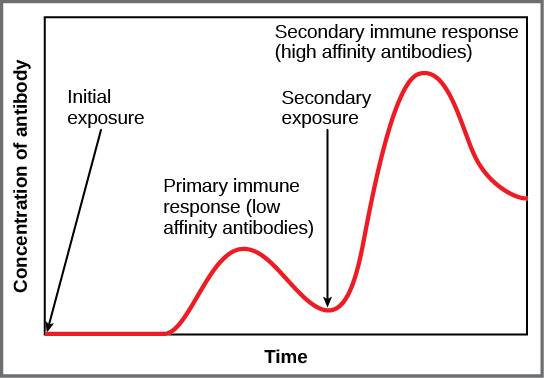
Vaccination is based on the knowledge that exposure to noninfectious antigens, derived from known pathogens, generates a mild primary immune response. The immune response to vaccination may not be perceived by the host as illness but still confers immune memory. When exposed to the corresponding pathogen to which an individual was vaccinated, the reaction is similar to a secondary exposure. Because each reinfection generates more memory cells and increased resistance to the pathogen, and because some memory cells die, certain vaccine courses involve one or more booster vaccinations to mimic repeat exposures: for instance, tetanus boosters are necessary every ten years because the memory cells only live that long.
A subset of T and B cells of the mucosal immune system differentiates into memory cells just as in the systemic immune system. Upon reinvasion of the same pathogen type, a pronounced immune response occurs at the mucosal site where the original pathogen deposited, but a collective defense is also organized within interconnected or adjacent mucosal tissue. For instance, the immune memory of an infection in the oral cavity would also elicit a response in the pharynx if the oral cavity was exposed to the same pathogen.
Vaccinologists are involved in the process of vaccine development from the initial idea to the availability of the completed vaccine. This process can take decades, can cost millions of dollars, and can involve many obstacles along the way. For instance, injected vaccines stimulate the systemic immune system, eliciting humoral and cell-mediated immunity, but have little effect on the mucosal response, which presents a challenge because many pathogens are deposited and replicate in mucosal compartments, and the injection does not provide the most efficient immune memory for these disease agents. For this reason, vaccinologists are actively involved in developing new vaccines that are applied via intranasal, aerosol, oral, or transcutaneous (absorbed through the skin) delivery methods. Importantly, mucosal-administered vaccines elicit both mucosal and systemic immunity and produce the same level of disease resistance as injected vaccines.
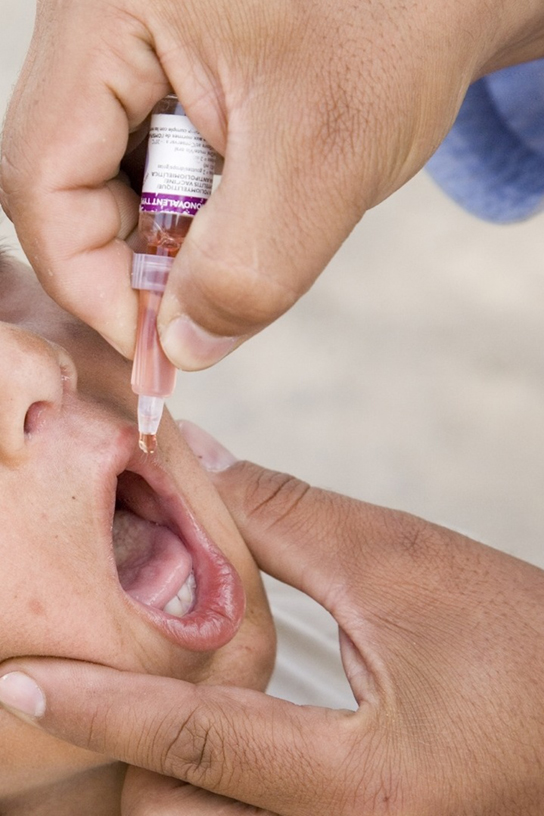
Currently, a version of intranasal influenza vaccine is available, and the polio and typhoid vaccines can be administered orally, as shown in [link] . Similarly, the measles and rubella vaccines are being adapted to aerosol delivery using inhalation devices. Eventually, transgenic plants may be engineered to produce vaccine antigens that can be eaten to confer disease resistance. Other vaccines may be adapted to rectal or vaginal application to elicit immune responses in rectal, genitourinary, or reproductive mucosa. Finally, vaccine antigens may be adapted to transdermal application in which the skin is lightly scraped and microneedles are used to pierce the outermost layer. In addition to mobilizing the mucosal immune response, this new generation of vaccines may end the anxiety associated with injections and, in turn, improve patient participation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?