| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As saprobes, fungi help maintain a sustainable ecosystem for the animals and plants that share the same habitat. In addition to replenishing the environment with nutrients, fungi interact directly with other organisms in beneficial, and sometimes damaging, ways ( [link] ).

Symbiosis is the ecological interaction between two organisms that live together. The definition does not describe the quality of the interaction. When both members of the association benefit, the symbiotic relationship is called mutualistic. Fungi form mutualistic associations with many types of organisms, including cyanobacteria, algae, plants, and animals.
One of the most remarkable associations between fungi and plants is the establishment of mycorrhizae. Mycorrhiza , which comes from the Greek words myco meaning fungus and rhizo meaning root, refers to the association between vascular plant roots and their symbiotic fungi. Somewhere between 80 and 90 percent of all plant species have mycorrhizal partners. In a mycorrhizal association, the fungal mycelia use their extensive network of hyphae and large surface area in contact with the soil to channel water and minerals from the soil into the plant. In exchange, the plant supplies the products of photosynthesis to fuel the metabolism of the fungus.
There are a number of types of mycorrhizae. Ectomycorrhizae (“outside” mycorrhiza) depend on fungi enveloping the roots in a sheath (called a mantle) and a Hartig net of hyphae that extends into the roots between cells ( [link] ). The fungal partner can belong to the Ascomycota, Basidiomycota or Zygomycota. In a second type, the Glomeromycete fungi form vesicular–arbuscular interactions with arbuscular mycorrhiza (sometimes called endomycorrhizae). In these mycorrhiza, the fungi form arbuscules that penetrate root cells and are the site of the metabolic exchanges between the fungus and the host plant ( [link] and [link] ). The arbuscules (from the Latin for little trees) have a shrub-like appearance. Orchids rely on a third type of mycorrhiza. Orchids are epiphytes that form small seeds without much storage to sustain germination and growth. Their seeds will not germinate without a mycorrhizal partner (usually a Basidiomycete). After nutrients in the seed are depleted, fungal symbionts support the growth of the orchid by providing necessary carbohydrates and minerals. Some orchids continue to be mycorrhizal throughout their lifecycle.
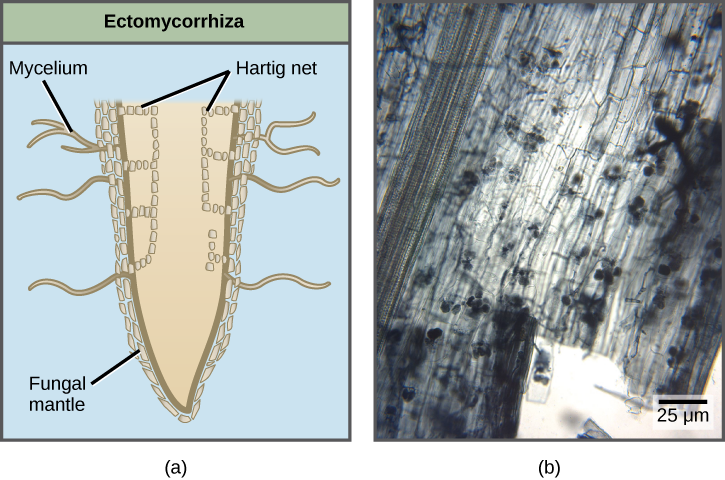
If symbiotic fungi are absent from the soil, what impact do you think this would have on plant growth?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?