| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
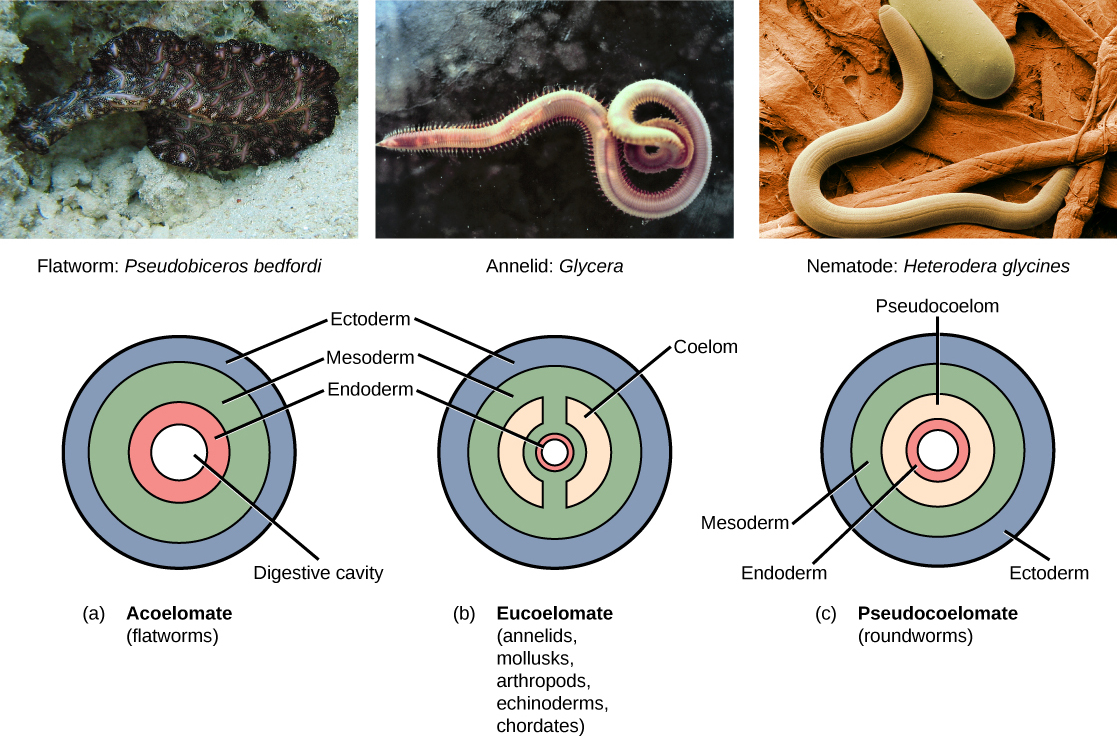
Triploblasts that do not develop a coelom are called acoelomates , and their mesoderm region is completely filled with tissue, although they do still have a gut cavity. Examples of acoelomates include animals in the phylum Platyhelminthes, also known as flatworms. Animals with a true coelom are called eucoelomates (or coelomates) ( [link] ). A true coelom arises entirely within the mesoderm germ layer and is lined by an epithelial membrane. This membrane also lines the organs within the coelom, connecting and holding them in position while allowing them some free motion. Annelids, mollusks, arthropods, echinoderms, and chordates are all eucoelomates. A third group of triploblasts has a slightly different coelom derived partly from mesoderm and partly from endoderm, which is found between the two layers. Although still functional, these are considered false coeloms, and those animals are called pseudocoelomates . The phylum Nematoda (roundworms) is an example of a pseudocoelomate. True coelomates can be further characterized based on certain features of their early embryological development.
Bilaterally symmetrical, tribloblastic eucoelomates can be further divided into two groups based on differences in their early embryonic development. Protostomes include arthropods, mollusks, and annelids. Deuterostomes include more complex animals such as chordates but also some simple animals such as echinoderms. These two groups are separated based on which opening of the digestive cavity develops first: mouth or anus. The word protostome comes from the Greek word meaning “mouth first,” and deuterostome originates from the word meaning “mouth second” (in this case, the anus develops first). The mouth or anus develops from a structure called the blastopore ( [link] ). The blastopore is the indentation formed during the initial stages of gastrulation. In later stages, a second opening forms, and these two openings will eventually give rise to the mouth and anus ( [link] ). It has long been believed that the blastopore develops into the mouth of protostomes, with the second opening developing into the anus; the opposite is true for deuterostomes. Recent evidence has challenged this view of the development of the blastopore of protostomes, however, and the theory remains under debate.
Another distinction between protostomes and deuterostomes is the method of coelom formation, beginning from the gastrula stage. The coelom of most protostomes is formed through a process called schizocoely , meaning that during development, a solid mass of the mesoderm splits apart and forms the hollow opening of the coelom. Deuterostomes differ in that their coelom forms through a process called enterocoely . Here, the mesoderm develops as pouches that are pinched off from the endoderm tissue. These pouches eventually fuse to form the mesoderm, which then gives rise to the coelom.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?