| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Light microscopes commonly used in the undergraduate college laboratory magnify up to approximately 400 times. Two parameters that are important in microscopy are magnification and resolving power. Magnification is the process of enlarging an object in appearance. Resolving power is the ability of a microscope to distinguish two adjacent structures as separate: the higher the resolution, the better the clarity and detail of the image. When oil immersion lenses are used for the study of small objects, magnification is usually increased to 1,000 times. In order to gain a better understanding of cellular structure and function, scientists typically use electron microscopes.
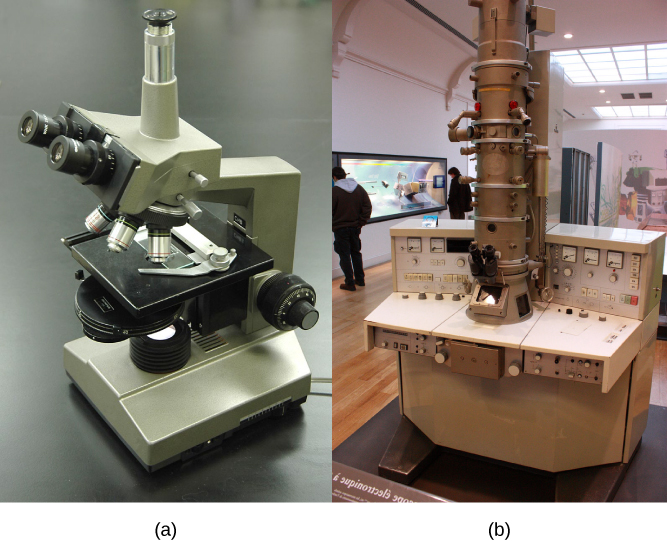
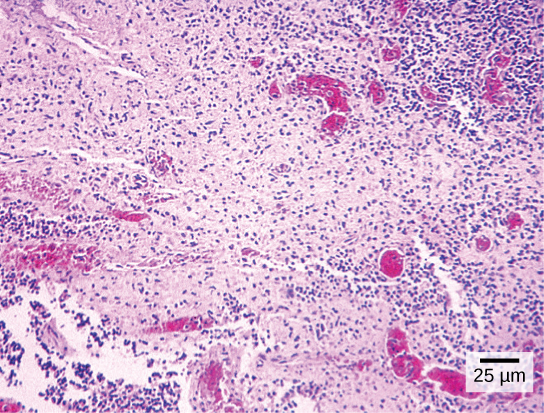
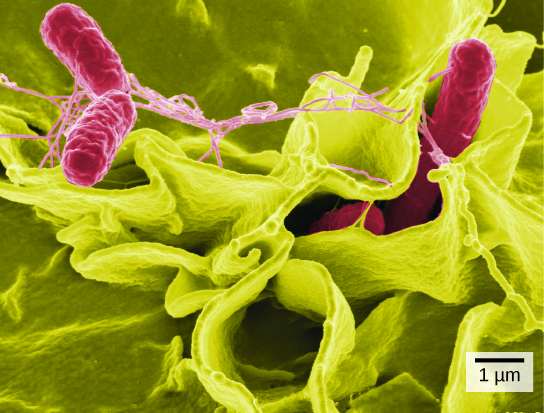
In contrast to light microscopes, electron microscopes ( [link] b ) use a beam of electrons instead of a beam of light. Not only does this allow for higher magnification and, thus, more detail ( [link] ), it also provides higher resolving power. The method used to prepare the specimen for viewing with an electron microscope kills the specimen. Electrons have short wavelengths (shorter than photons) that move best in a vacuum, so living cells cannot be viewed with an electron microscope.
In a scanning electron microscope, a beam of electrons moves back and forth across a cell’s surface, creating details of cell surface characteristics. In a transmission electron microscope, the electron beam penetrates the cell and provides details of a cell’s internal structures. As you might imagine, electron microscopes are significantly more bulky and expensive than light microscopes.
For another perspective on cell size, try the HowBig interactive at this site .
The microscopes we use today are far more complex than those used in the 1600s by Antony van Leeuwenhoek, a Dutch shopkeeper who had great skill in crafting lenses. Despite the limitations of his now-ancient lenses, van Leeuwenhoek observed the movements of protista (a type of single-celled organism) and sperm, which he collectively termed “animalcules.”
In a 1665 publication called Micrographia , experimental scientist Robert Hooke coined the term “cell” for the box-like structures he observed when viewing cork tissue through a lens. In the 1670s, van Leeuwenhoek discovered bacteria and protozoa. Later advances in lenses, microscope construction, and staining techniques enabled other scientists to see some components inside cells.
By the late 1830s, botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann were studying tissues and proposed the unified cell theory , which states that all living things are composed of one or more cells, the cell is the basic unit of life, and new cells arise from existing cells. Rudolf Virchow later made important contributions to this theory.
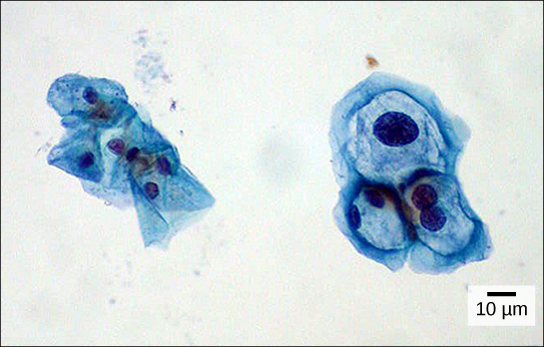
Cytotechnologists (cyto- = “cell”) are professionals who study cells via microscopic examinations and other laboratory tests. They are trained to determine which cellular changes are within normal limits and which are abnormal. Their focus is not limited to cervical cells; they study cellular specimens that come from all organs. When they notice abnormalities, they consult a pathologist, who is a medical doctor who can make a clinical diagnosis.
Cytotechnologists play a vital role in saving people’s lives. When abnormalities are discovered early, a patient’s treatment can begin sooner, which usually increases the chances of a successful outcome.
A cell is the smallest unit of life. Most cells are so tiny that they cannot be seen with the naked eye. Therefore, scientists use microscopes to study cells. Electron microscopes provide higher magnification, higher resolution, and more detail than light microscopes. The unified cell theory states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, the cell is the basic unit of life, and new cells arise from existing cells.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?