| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
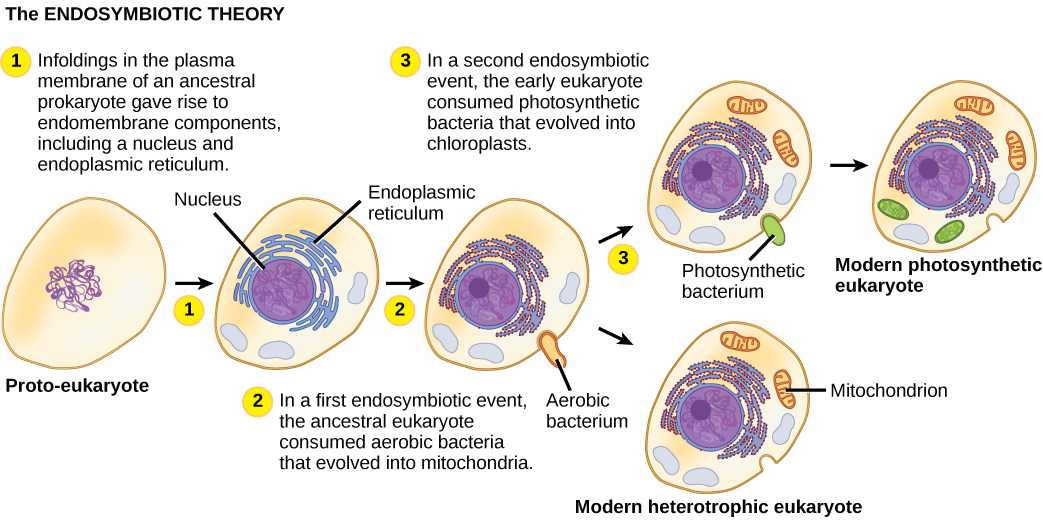
What evidence is there that mitochondria were incorporated into the ancestral eukaryotic cell before chloroplasts?
This leads to the question of the possibility of a cell containing an endosymbiont to itself become engulfed, resulting in a secondary endosymbiosis. Molecular and morphological evidence suggest that the chlorarachniophyte protists are derived from a secondary endosymbiotic event. Chlorarachniophytes are rare algae indigenous to tropical seas and sand that can be classified into the rhizarian supergroup. Chlorarachniophytes extend thin cytoplasmic strands, interconnecting themselves with other chlorarachniophytes, in a cytoplasmic network. These protists are thought to have originated when a eukaryote engulfed a green alga, the latter of which had already established an endosymbiotic relationship with a photosynthetic cyanobacterium ( [link] ).
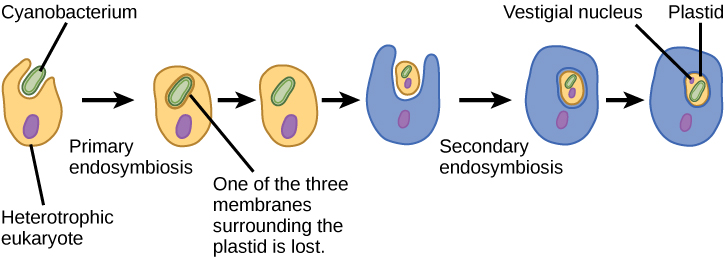
Several lines of evidence support that chlorarachniophytes evolved from secondary endosymbiosis. The chloroplasts contained within the green algal endosymbionts still are capable of photosynthesis, making chlorarachniophytes photosynthetic. The green algal endosymbiont also exhibits a stunted vestigial nucleus. In fact, it appears that chlorarachniophytes are the products of an evolutionarily recent secondary endosymbiotic event. The plastids of chlorarachniophytes are surrounded by four membranes: The first two correspond to the inner and outer membranes of the photosynthetic cyanobacterium, the third corresponds to the green alga, and the fourth corresponds to the vacuole that surrounded the green alga when it was engulfed by the chlorarachniophyte ancestor. In other lineages that involved secondary endosymbiosis, only three membranes can be identified around plastids. This is currently rectified as a sequential loss of a membrane during the course of evolution.
The process of secondary endosymbiosis is not unique to chlorarachniophytes. In fact, secondary endosymbiosis of green algae also led to euglenid protists, whereas secondary endosymbiosis of red algae led to the evolution of dinoflagellates, apicomplexans, and stramenopiles.
The oldest fossil evidence of eukaryotes is about 2 billion years old. Fossils older than this all appear to be prokaryotes. It is probable that today’s eukaryotes are descended from an ancestor that had a prokaryotic organization. The last common ancestor of today’s Eukarya had several characteristics, including cells with nuclei that divided mitotically and contained linear chromosomes where the DNA was associated with histones, a cytoskeleton and endomembrane system, and the ability to make cilia/flagella during at least part of its life cycle. It was aerobic because it had mitochondria that were the result of an aerobic alpha-proteobacterium that lived inside a host cell. Whether this host had a nucleus at the time of the initial symbiosis remains unknown. The last common ancestor may have had a cell wall for at least part of its life cycle, but more data are needed to confirm this hypothesis. Today’s eukaryotes are very diverse in their shapes, organization, life cycles, and number of cells per individual.
[link] What evidence is there that mitochondria were incorporated into the ancestral eukaryotic cell before chloroplasts?
[link] All eukaryotic cells have mitochondria, but not all eukaryotic cells have chloroplasts.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?