| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Differential rotation would appear to explain why so much of the material in the disk of the Milky Way is concentrated into elongated features that resemble spiral arms . No matter what the original distribution of the material might be, the differential rotation of the Galaxy can stretch it out into spiral features. [link] shows the development of spiral arms from two irregular blobs of interstellar matter. Notice that as the portions of the blobs closest to the galactic center move faster, those farther out trail behind.
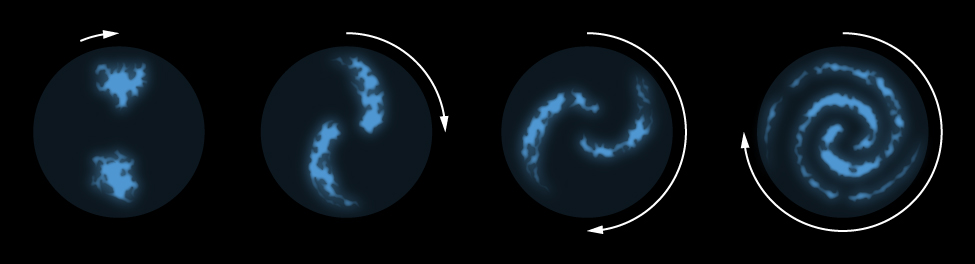
But this picture of spiral arms presents astronomers with an immediate problem. If that’s all there were to the story, differential rotation—over the roughly 13-billion-year history of the Galaxy—would have wound the Galaxy’s arms tighter and tighter until all semblance of spiral structure had disappeared. But did the Milky Way actually have spiral arms when it formed 13 billion years ago? And do spiral arms, once formed, last for that long a time?
With the advent of the Hubble Space Telescope, it has become possible to observe the structure of very distant galaxies and to see what they were like shortly after they began to form more than 13 billion years ago. What the observations show is that galaxies in their infancy had bright, clumpy star-forming regions, but no regular spiral structure.
Over the next few billion years, the galaxies began to “settle down.” The galaxies that were to become spirals lost their massive clumps and developed a central bulge. The turbulence in these galaxies decreased, rotation began to dominate the motions of the stars and gas, and stars began to form in a much quieter disk. Smaller star-forming clumps began to form fuzzy, not-very-distinct spiral arms. Bright, well-defined spiral arms began to appear only when the galaxies were about 3.6 billion years old. Initially, there were two well-defined arms. Multi-armed structures in galaxies like we see in the Milky Way appeared only when the universe was about 8 billion years old.
We will discuss the history of galaxies in more detail in The Evolution and Distribution of Galaxies . But, even from our brief discussion, you can get the sense that the spiral structures we now observe in mature galaxies have come along later in the full story of how things develop in the universe.
Scientists have used supercomputer calculations to model the formation and evolution of the arms. These calculations follow the motions of up to 100 million “star particles” to see whether gravitational forces can cause them to form spiral structure. What these calculations show is that giant molecular clouds (which we discussed in Between the Stars: Gas and Dust in Space ) have enough gravitational influence over their surroundings to initiate the formation of structures that look like spiral arms. These arms then become self-perpetuating and can survive for at least several billion years. The arms may change their brightness over time as star formation comes and goes, but they are not temporary features. The concentration of matter in the arms exerts sufficient gravitational force to keep the arms together over long periods of time.
The gaseous distribution in the Galaxy’s disk has two main spiral arms that emerge from the ends of the central bar, along with several fainter arms and short spurs; the Sun is located in one of those spurs. Measurements show that the Galaxy does not rotate as a solid body, but instead its stars and gas follow differential rotation, such that the material closer to the galactic center completes its orbit more quickly. Observations show that galaxies like the Milky Way take several billion years after they began to form to develop spiral structure.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?