| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
You might wonder why the next major step in nuclear fusion in stars involves three helium nuclei and not just two. Although it is a lot easier to get two helium nuclei to collide, the product of this collision is not stable and falls apart very quickly. It takes three helium nuclei coming together simultaneously to make a stable nuclear structure. Given that each helium nucleus has two positive protons and that such protons repel one another, you can begin to see the problem. It takes a temperature of 100 million K to slam three helium nuclei (six protons) together and make them stick. But when that happens, the star produces a carbon nucleus.
Stop reading for a moment and look at your little finger. It’s full of carbon atoms because carbon is a fundamental chemical building block for life on Earth. Each of those carbon atoms was once inside a red giant star and was fused from helium nuclei in the triple-alpha process. All the carbon on Earth—in you, in the charcoal you use for barbecuing, and in the diamonds you might exchange with a loved one—was “cooked up” by previous generations of stars. How the carbon atoms (and other elements) made their way from inside some of those stars to become part of Earth is something we will discuss in the next chapter. For now, we want to emphasize that our description of stellar evolution is, in a very real sense, the story of our own cosmic “roots”—the history of how our own atoms originated among the stars. We are made of “star-stuff.”
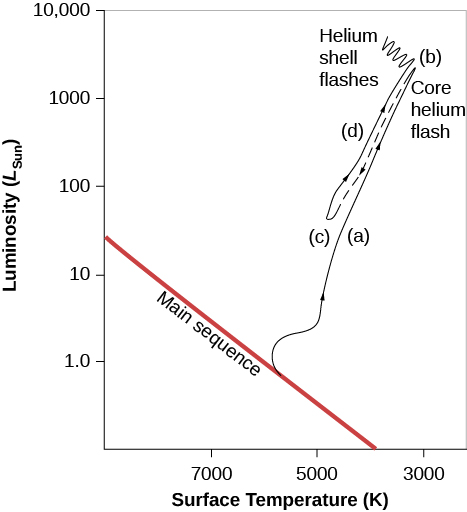
After the helium flash, the star, having survived the “energy crisis” that followed the end of the main-sequence stage and the exhaustion of the hydrogen fuel at its center, finds its balance again. As the star readjusts to the release of energy from the triple-alpha process in its core, its internal structure changes once more: its surface temperature increases and its overall luminosity decreases. The point that represents the star on the H–R diagram thus moves to a new position to the left of and somewhat below its place as a red giant ( [link] ). The star then continues to fuse the helium in its core for a while, returning to the kind of equilibrium between pressure and gravity that characterized the main-sequence stage. During this time, a newly formed carbon nucleus at the center of the star can sometimes be joined by another helium nucleus to produce a nucleus of oxygen—another building block of life.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?