| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
It is easy to measure the diameter of the Sun. Its angular diameter—that is, its apparent size on the sky—is about 1/2°. If we know the angle the Sun takes up in the sky and how far away it is, we can calculate its true (linear) diameter, which is 1.39 million kilometers, or about 109 times the diameter of Earth.
Unfortunately, the Sun is the only star whose angular diameter is easily measured. All the other stars are so far away that they look like pinpoints of light through even the largest ground-based telescopes. (They often seem to be bigger, but that is merely distortion introduced by turbulence in Earth’s atmosphere.) Luckily, there are several techniques that astronomers can use to estimate the sizes of stars.
One technique, which gives very precise diameters but can be used for only a few stars, is to observe the dimming of light that occurs when the Moon passes in front of a star. What astronomers measure (with great precision) is the time required for the star’s brightness to drop to zero as the edge of the Moon moves across the star’s disk. Since we know how rapidly the Moon moves in its orbit around Earth, it is possible to calculate the angular diameter of the star. If the distance to the star is also known, we can calculate its diameter in kilometers. This method works only for fairly bright stars that happen to lie along the zodiac, where the Moon (or, much more rarely, a planet) can pass in front of them as seen from Earth.
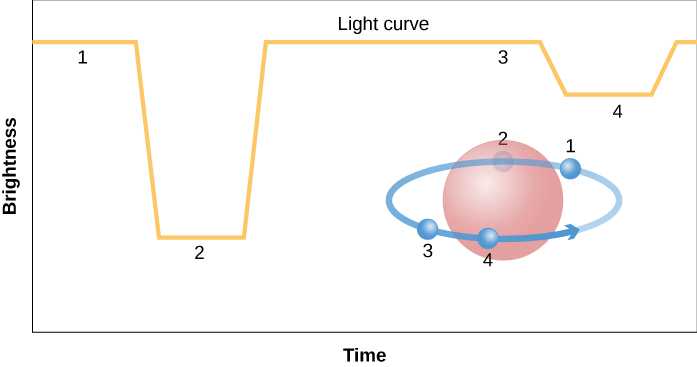
Accurate sizes for a large number of stars come from measurements of eclipsing binary star systems, and so we must make a brief detour from our main story to examine this type of star system. Some binary stars are lined up in such a way that, when viewed from Earth, each star passes in front of the other during every revolution ( [link] ). When one star blocks the light of the other, preventing it from reaching Earth, the luminosity of the system decreases, and astronomers say that an eclipse has occurred.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?