| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
While we await more discoveries and better understanding of other planetary systems, let us look again at the early history of our own solar system, after the dissipation of our dust disk. The era of giant impacts was probably confined to the first 100 million years of solar system history, ending by about 4.4 billion years ago. Shortly thereafter, the planets cooled and began to assume their present aspects. Up until about 4 billion years ago, they continued to acquire volatile materials, and their surfaces were heavily cratered from the remaining debris that hit them. However, as external influences declined, all the terrestrial planets as well as the moons of the outer planets began to follow their own evolutionary courses. The nature of this evolution depended on each object’s composition, mass, and distance from the Sun.
We have seen a wide range in the level of geological activity on the terrestrial planets and icy moons. Internal sources of such activity (as opposed to pummeling from above) require energy, either in the form of primordial heat left over from the formation of a planet or from the decay of radioactive elements in the interior. The larger the planet or moon, the more likely it is to retain its internal heat and the more slowly it cools—this is the “baked potato effect” mentioned in Other Worlds: An Introduction to the Solar System . Therefore, we are more likely to see evidence of continuing geological activity on the surface of larger (solid) worlds ( [link] ). Jupiter’s moon Io is an interesting exception to this rule; we saw that it has an unusual source of heat from the gravitational flexing of its interior by the tidal pull of Jupiter. Europa is probably also heated by jovian tides. Saturn may be having a similar effect on its moon Enceladus.
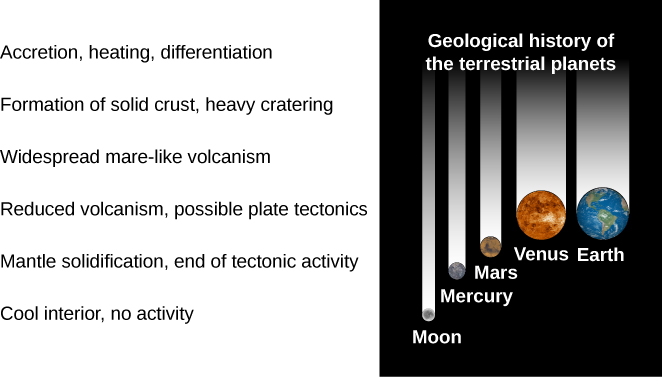
The Moon , the smallest of the terrestrial worlds, was internally active until about 3.3 billion years ago, when its major volcanism ceased. Since that time, its mantle has cooled and become solid, and today even internal seismic activity has declined to almost zero. The Moon is a geologically dead world. Although we know much less about Mercury, it seems likely that this planet, too, ceased most volcanic activity about the same time the Moon did.
Mars represents an intermediate case, and it has been much more active than the Moon. The southern hemisphere crust had formed by 4 billion years ago, and the northern hemisphere volcanic plains seem to be contemporary with the lunar maria. However, the Tharsis bulge formed somewhat later, and activity in the large Tharsis volcanoes has apparently continued on and off to the present era.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?