| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
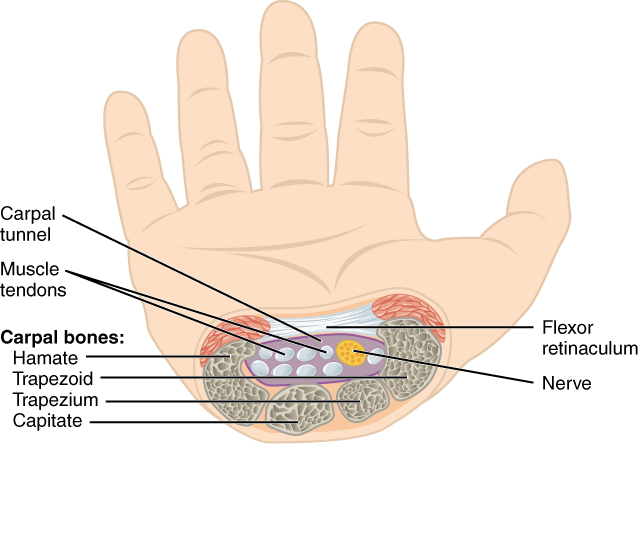
In the articulated hand, the carpal bones form a U-shaped grouping. A strong ligament called the flexor retinaculum spans the top of this U-shaped area to maintain this grouping of the carpal bones. The flexor retinaculum is attached laterally to the trapezium and scaphoid bones, and medially to the hamate and pisiform bones. Together, the carpal bones and the flexor retinaculum form a passageway called the carpal tunnel , with the carpal bones forming the walls and floor, and the flexor retinaculum forming the roof of this space ( [link] ). The tendons of nine muscles of the anterior forearm and an important nerve pass through this narrow tunnel to enter the hand. Overuse of the muscle tendons or wrist injury can produce inflammation and swelling within this space. This produces compression of the nerve, resulting in carpal tunnel syndrome, which is characterized by pain or numbness, and muscle weakness in those areas of the hand supplied by this nerve.
The palm of the hand contains five elongated metacarpal bones. These bones lie between the carpal bones of the wrist and the bones of the fingers and thumb (see [link] ). The proximal end of each metacarpal bone articulates with one of the distal carpal bones. Each of these articulations is a carpometacarpal joint (see [link] ). The expanded distal end of each metacarpal bone articulates at the metacarpophalangeal joint with the proximal phalanx bone of the thumb or one of the fingers. The distal end also forms the knuckles of the hand, at the base of the fingers. The metacarpal bones are numbered 1–5, beginning at the thumb.
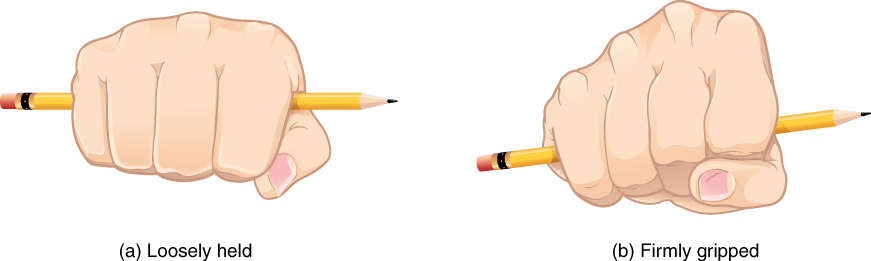
The first metacarpal bone, at the base of the thumb, is separated from the other metacarpal bones. This allows it a freedom of motion that is independent of the other metacarpal bones, which is very important for thumb mobility. The remaining metacarpal bones are united together to form the palm of the hand. The second and third metacarpal bones are firmly anchored in place and are immobile. However, the fourth and fifth metacarpal bones have limited anterior-posterior mobility, a motion that is greater for the fifth bone. This mobility is important during power gripping with the hand ( [link] ). The anterior movement of these bones, particularly the fifth metacarpal bone, increases the strength of contact for the medial hand during gripping actions.
The fingers and thumb contain 14 bones, each of which is called a phalanx bone (plural = phalanges), named after the ancient Greek phalanx (a rectangular block of soldiers). The thumb ( pollex ) is digit number 1 and has two phalanges, a proximal phalanx, and a distal phalanx bone (see [link] ). Digits 2 (index finger) through 5 (little finger) have three phalanges each, called the proximal, middle, and distal phalanx bones. An interphalangeal joint is one of the articulations between adjacent phalanges of the digits (see [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?