| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
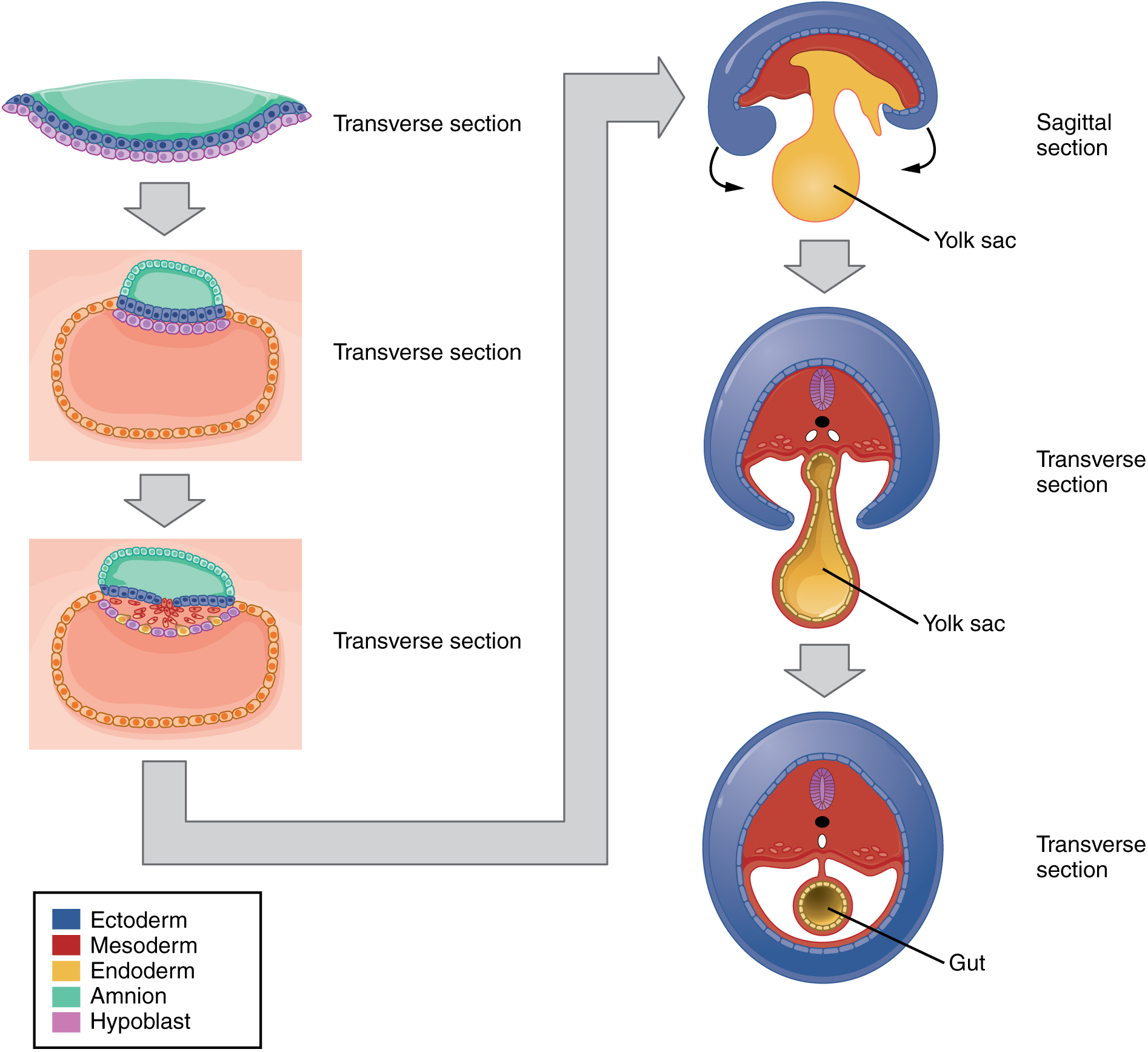
Within the first 8 weeks of gestation, a developing embryo establishes the rudimentary structures of all of its organs and tissues from the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. This process is called organogenesis .
Like the central nervous system, the heart also begins its development in the embryo as a tube-like structure, connected via capillaries to the chorionic villi. Cells of the primitive tube-shaped heart are capable of electrical conduction and contraction. The heart begins beating in the beginning of the fourth week, although it does not actually pump embryonic blood until a week later, when the oversized liver has begun producing red blood cells. (This is a temporary responsibility of the embryonic liver that the bone marrow will assume during fetal development.) During weeks 4–5, the eye pits form, limb buds become apparent, and the rudiments of the pulmonary system are formed.
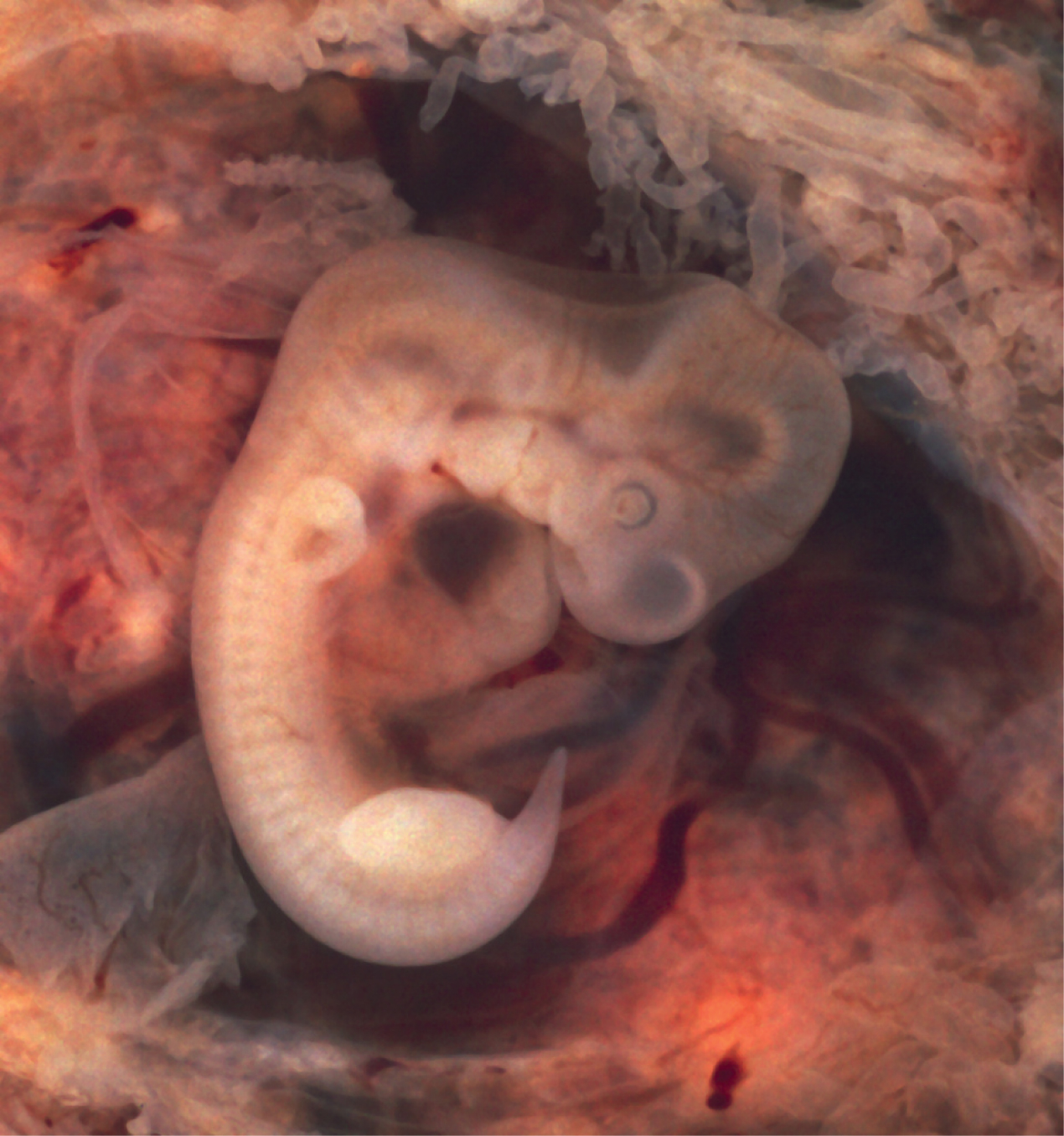
During the sixth week, uncontrolled fetal limb movements begin to occur. The gastrointestinal system develops too rapidly for the embryonic abdomen to accommodate it, and the intestines temporarily loop into the umbilical cord. Paddle-shaped hands and feet develop fingers and toes by the process of apoptosis (programmed cell death), which causes the tissues between the fingers to disintegrate. By week 7, the facial structure is more complex and includes nostrils, outer ears, and lenses ( [link] ). By the eighth week, the head is nearly as large as the rest of the embryo’s body, and all major brain structures are in place. The external genitalia are apparent, but at this point, male and female embryos are indistinguishable. Bone begins to replace cartilage in the embryonic skeleton through the process of ossification. By the end of the embryonic period, the embryo is approximately 3 cm (1.2 in) from crown to rump and weighs approximately 8 g (0.25 oz).
Use this interactive tool to view the process of embryogenesis from the perspective of the conceptus (left panel), as well as fetal development viewed from a maternal cross-section (right panel). Can you identify when neurulation occurs in the embryo?
As the zygote travels toward the uterus, it undergoes numerous cleavages in which the number of cells doubles (blastomeres). Upon reaching the uterus, the conceptus has become a tightly packed sphere of cells called the morula, which then forms into a blastocyst consisting of an inner cell mass within a fluid-filled cavity surrounded by trophoblasts. The blastocyst implants in the uterine wall, the trophoblasts fuse to form a syncytiotrophoblast, and the conceptus is enveloped by the endometrium. Four embryonic membranes form to support the growing embryo: the amnion, the yolk sac, the allantois, and the chorion. The chorionic villi of the chorion extend into the endometrium to form the fetal portion of the placenta. The placenta supplies the growing embryo with oxygen and nutrients; it also removes carbon dioxide and other metabolic wastes.
Following implantation, embryonic cells undergo gastrulation, in which they differentiate and separate into an embryonic disc and establish three primary germ layers (the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm). Through the process of embryonic folding, the fetus begins to take shape. Neurulation starts the process of the development of structures of the central nervous system and organogenesis establishes the basic plan for all organ systems.
View this time-lapse movie of a conceptus starting at day 3. What is the first structure you see? At what point in the movie does the blastocoel first appear? What event occurs at the end of the movie?
The first structure shown is the morula. The blastocoel appears at approximately 20 seconds. The movie ends with the hatching of the conceptus.
Use this interactive tool to view the process of embryogenesis from the perspective of the conceptus (left panel), as well as fetal development viewed from a maternal cross-section (right panel). Can you identify when neurulation occurs in the embryo?
Neurulation starts in week 4.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?