| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
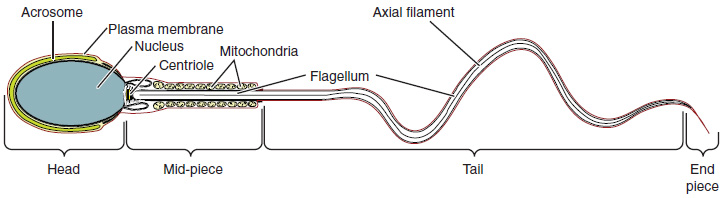
Sperm are smaller than most cells in the body; in fact, the volume of a sperm cell is 85,000 times less than that of the female gamete. Approximately 100 to 300 million sperm are produced each day, whereas women typically ovulate only one oocyte per month as is true for most cells in the body, the structure of sperm cells speaks to their function. Sperm have a distinctive head, mid-piece, and tail region ( [link] ). The head of the sperm contains the extremely compact haploid nucleus with very little cytoplasm. These qualities contribute to the overall small size of the sperm (the head is only 5 μ m long). A structure called the acrosome covers most of the head of the sperm cell as a “cap” that is filled with lysosomal enzymes important for preparing sperm to participate in fertilization. Tightly packed mitochondria fill the mid-piece of the sperm. ATP produced by these mitochondria will power the flagellum, which extends from the neck and the mid-piece through the tail of the sperm, enabling it to move the entire sperm cell. The central strand of the flagellum, the axial filament, is formed from one centriole inside the maturing sperm cell during the final stages of spermatogenesis.
To fertilize an egg, sperm must be moved from the seminiferous tubules in the testes, through the epididymis, and—later during ejaculation—along the length of the penis and out into the female reproductive tract.
From the lumen of the seminiferous tubules, the immotile sperm are surrounded by testicular fluid and moved to the epididymis (plural = epididymides), a coiled tube attached to the testis where newly formed sperm continue to mature (see [link] ). Though the epididymis does not take up much room in its tightly coiled state, it would be approximately 6 m (20 feet) long if straightened. It takes an average of 12 days for sperm to move through the coils of the epididymis, with the shortest recorded transit time in humans being one day. Sperm enter the head of the epididymis and are moved along predominantly by the contraction of smooth muscles lining the epididymal tubes. As they are moved along the length of the epididymis, the sperm further mature and acquire the ability to move under their own power. Once inside the female reproductive tract, they will use this ability to move independently toward the unfertilized egg. The more mature sperm are then stored in the tail of the epididymis (the final section) until ejaculation occurs.
During ejaculation, sperm exit the tail of the epididymis and are pushed by smooth muscle contraction to the ductus deferens (also called the vas deferens). The ductus deferens is a thick, muscular tube that is bundled together inside the scrotum with connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves into a structure called the spermatic cord (see [link] and [link] ). Because the ductus deferens is physically accessible within the scrotum, surgical sterilization to interrupt sperm delivery can be performed by cutting and sealing a small section of the ductus (vas) deferens. This procedure is called a vasectomy, and it is an effective form of male birth control. Although it may be possible to reverse a vasectomy, clinicians consider the procedure permanent, and advise men to undergo it only if they are certain they no longer wish to father children.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?