| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
During the first several weeks of development, the cells of the endometrium—referred to as decidual cells—nourish the nascent embryo. During prenatal weeks 4–12, the developing placenta gradually takes over the role of feeding the embryo, and the decidual cells are no longer needed. The mature placenta is composed of tissues derived from the embryo, as well as maternal tissues of the endometrium. The placenta connects to the conceptus via the umbilical cord , which carries deoxygenated blood and wastes from the fetus through two umbilical arteries; nutrients and oxygen are carried from the mother to the fetus through the single umbilical vein. The umbilical cord is surrounded by the amnion, and the spaces within the cord around the blood vessels are filled with Wharton’s jelly, a mucous connective tissue.
The maternal portion of the placenta develops from the deepest layer of the endometrium, the decidua basalis. To form the embryonic portion of the placenta, the syncytiotrophoblast and the underlying cells of the trophoblast (cytotrophoblast cells) begin to proliferate along with a layer of extraembryonic mesoderm cells. These form the chorionic membrane , which envelops the entire conceptus as the chorion. The chorionic membrane forms finger-like structures called chorionic villi that burrow into the endometrium like tree roots, making up the fetal portion of the placenta. The cytotrophoblast cells perforate the chorionic villi, burrow farther into the endometrium, and remodel maternal blood vessels to augment maternal blood flow surrounding the villi. Meanwhile, fetal mesenchymal cells derived from the mesoderm fill the villi and differentiate into blood vessels, including the three umbilical blood vessels that connect the embryo to the developing placenta ( [link] ).
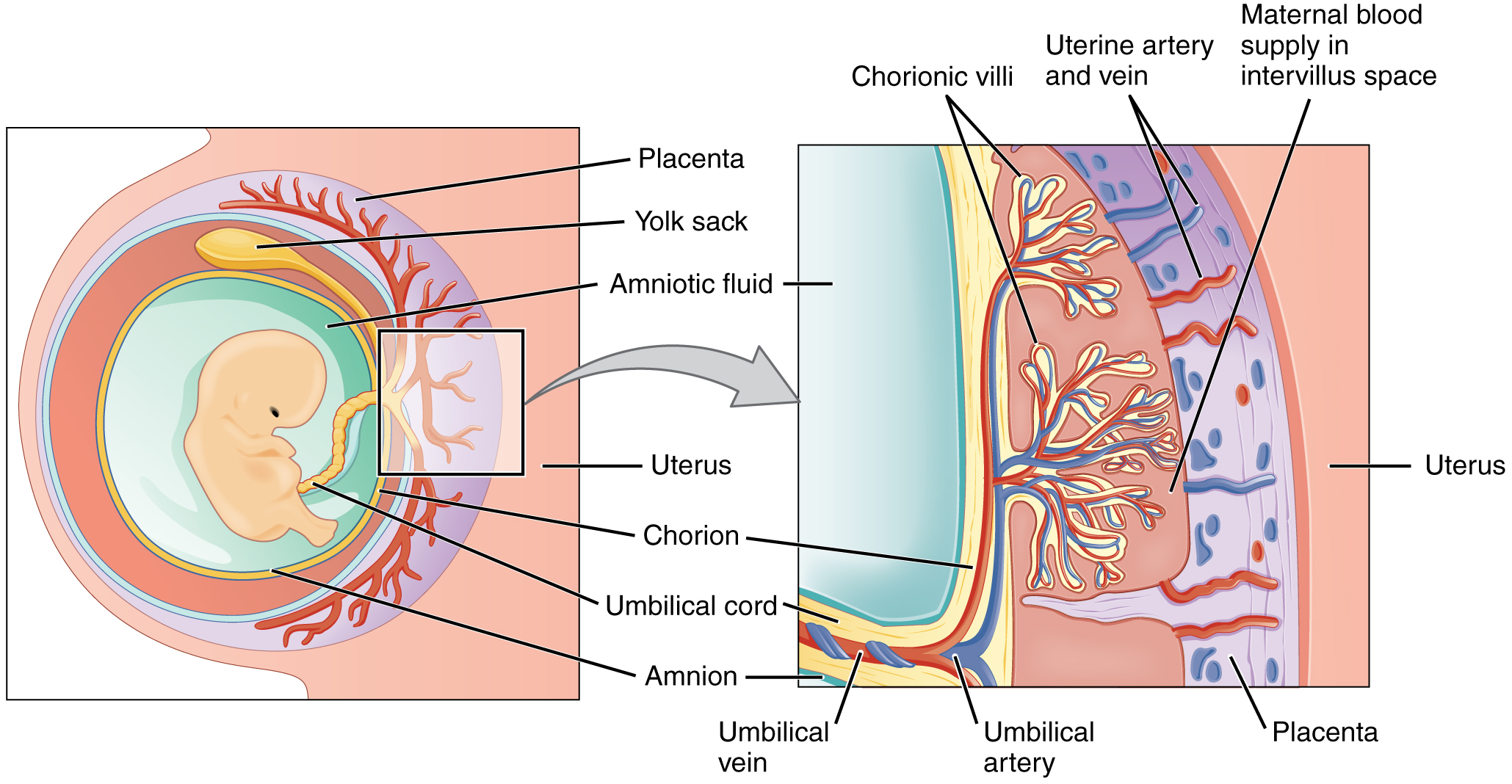
The placenta develops throughout the embryonic period and during the first several weeks of the fetal period; placentation is complete by weeks 14–16. As a fully developed organ, the placenta provides nutrition and excretion, respiration, and endocrine function ( [link] and [link] ). It receives blood from the fetus through the umbilical arteries. Capillaries in the chorionic villi filter fetal wastes out of the blood and return clean, oxygenated blood to the fetus through the umbilical vein. Nutrients and oxygen are transferred from maternal blood surrounding the villi through the capillaries and into the fetal bloodstream. Some substances move across the placenta by simple diffusion. Oxygen, carbon dioxide, and any other lipid-soluble substances take this route. Other substances move across by facilitated diffusion. This includes water-soluble glucose. The fetus has a high demand for amino acids and iron, and those substances are moved across the placenta by active transport.
Maternal and fetal blood does not commingle because blood cells cannot move across the placenta. This separation prevents the mother’s cytotoxic T cells from reaching and subsequently destroying the fetus, which bears “non-self” antigens. Further, it ensures the fetal red blood cells do not enter the mother’s circulation and trigger antibody development (if they carry “non-self” antigens)—at least until the final stages of pregnancy or birth. This is the reason that, even in the absence of preventive treatment, an Rh − mother doesn’t develop antibodies that could cause hemolytic disease in her first Rh + fetus.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?