| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
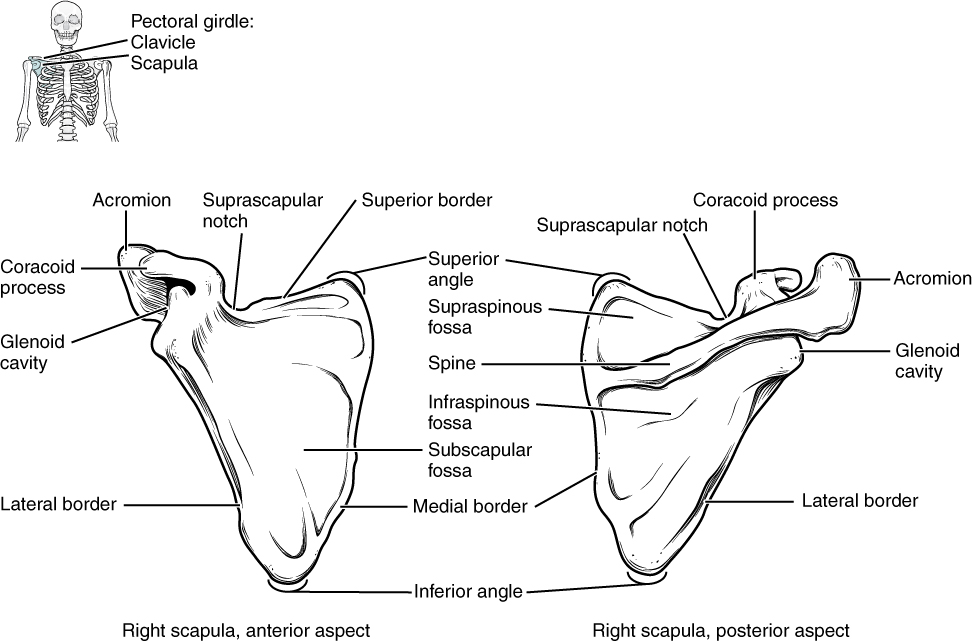
The scapula also has two prominent projections. Toward the lateral end of the superior border, between the suprascapular notch and glenoid cavity, is the hook-like coracoid process (coracoid = “shaped like a crow’s beak”). This process projects anteriorly and curves laterally. At the shoulder, the coracoid process is located inferior to the lateral end of the clavicle. It is anchored to the clavicle by a strong ligament, and serves as the attachment site for muscles of the anterior chest and arm. On the posterior aspect, the spine of the scapula is a long and prominent ridge that runs across its upper portion. Extending laterally from the spine is a flattened and expanded region called the acromion or acromial process . The acromion forms the bony tip of the superior shoulder region and articulates with the lateral end of the clavicle, forming the acromioclavicular joint (see [link] ). Together, the clavicle, acromion, and spine of the scapula form a V-shaped bony line that provides for the attachment of neck and back muscles that act on the shoulder, as well as muscles that pass across the shoulder joint to act on the arm.
The scapula has three depressions, each of which is called a fossa (plural = fossae). Two of these are found on the posterior scapula, above and below the scapular spine. Superior to the spine is the narrow supraspinous fossa , and inferior to the spine is the broad infraspinous fossa . The anterior (deep) surface of the scapula forms the broad subscapular fossa . All of these fossae provide large surface areas for the attachment of muscles that cross the shoulder joint to act on the humerus.
The acromioclavicular joint transmits forces from the upper limb to the clavicle. The ligaments around this joint are relatively weak. A hard fall onto the elbow or outstretched hand can stretch or tear the acromioclavicular ligaments, resulting in a moderate injury to the joint. However, the primary support for the acromioclavicular joint comes from a very strong ligament called the coracoclavicular ligament (see [link] ). This connective tissue band anchors the coracoid process of the scapula to the inferior surface of the acromial end of the clavicle and thus provides important indirect support for the acromioclavicular joint. Following a strong blow to the lateral shoulder, such as when a hockey player is driven into the boards, a complete dislocation of the acromioclavicular joint can result. In this case, the acromion is thrust under the acromial end of the clavicle, resulting in ruptures of both the acromioclavicular and coracoclavicular ligaments. The scapula then separates from the clavicle, with the weight of the upper limb pulling the shoulder downward. This dislocation injury of the acromioclavicular joint is known as a “shoulder separation” and is common in contact sports such as hockey, football, or martial arts.
The pectoral girdle, consisting of the clavicle and the scapula, attaches each upper limb to the axial skeleton. The clavicle is an anterior bone whose sternal end articulates with the manubrium of the sternum at the sternoclavicular joint. The sternal end is also anchored to the first rib by the costoclavicular ligament. The acromial end of the clavicle articulates with the acromion of the scapula at the acromioclavicular joint. This end is also anchored to the coracoid process of the scapula by the coracoclavicular ligament, which provides indirect support for the acromioclavicular joint. The clavicle supports the scapula, transmits the weight and forces from the upper limb to the body trunk, and protects the underlying nerves and blood vessels.
The scapula lies on the posterior aspect of the pectoral girdle. It mediates the attachment of the upper limb to the clavicle, and contributes to the formation of the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint. This triangular bone has three sides called the medial, lateral, and superior borders. The suprascapular notch is located on the superior border. The scapula also has three corners, two of which are the superior and inferior angles. The third corner is occupied by the glenoid cavity. Posteriorly, the spine separates the supraspinous and infraspinous fossae, and then extends laterally as the acromion. The subscapular fossa is located on the anterior surface of the scapula. The coracoid process projects anteriorly, passing inferior to the lateral end of the clavicle.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?