| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
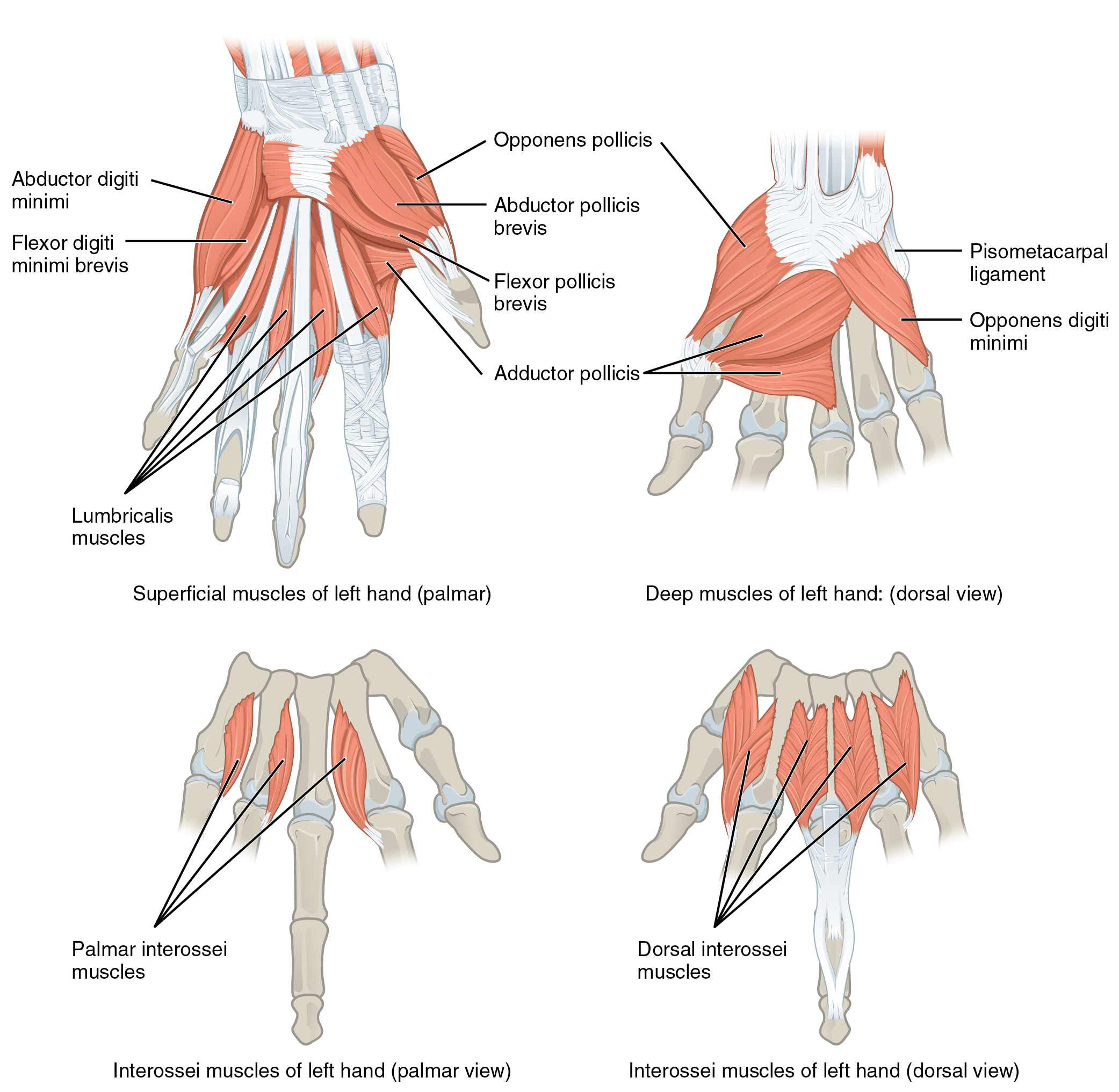
The hypothenar muscles include the abductor digiti minimi , flexor digiti minimi brevis , and the opponens digiti minimi . These muscles form the hypothenar eminence , the rounded contour of the little finger, and as such, they all act on the little finger. Finally, the intermediate muscles act on all the fingers and include the lumbrical , the palmar interossei , and the dorsal interossei .
| Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle | Movement | Target | Target motion direction | Prime mover | Origin | Insertion |
| Thenar muscles | Moves thumb toward body | Thumb | Abduction | Abductor pollicis brevis | Flexor retinaculum; and nearby carpals | Lateral base of proximal phalanx of thumb |
| Thenar muscles | Moves thumb across palm to touch other fingers | Thumb | Opposition | Opponens pollicis | Flexor retinaculum; trapezium | Anterior of first metacarpal |
| Thenar muscles | Flexes thumb | Thumb | Flexion | Flexor pollicis brevis | Flexor retinaculum; trapezium | Lateral base of proximal phalanx of thumb |
| Thenar muscles | Moves thumb away from body | Thumb | Adduction | Adductor pollicis | Capitate bone; bases of metacarpals 2–4; front of metacarpal 3 | Medial base of proximal phalanx of thumb |
| Hypothenar muscles | Moves little finger toward body | Little finger | Abduction | Abductor digiti minimi | Pisiform bone | Medial side of proximal phalanx of little finger |
| Hypothenar muscles | Flexes little finger | Little finger | Flexion | Flexor digiti minimi brevis | Hamate bone; flexor retinaculum | Medial side of proximal phalanx of little finger |
| Hypothenar muscles | Moves little finger across palm to touch thumb | Little finger | Opposition | Opponens digiti minimi | Hamate bone; flexor retinaculum | Medial side of fifth metacarpal |
| Intermediate muscles | Flexes each finger at metacarpo-phalangeal joints; extends each finger at interphalangeal joints | Fingers | Flexion | Lumbricals | Palm (lateral sides of tendons in flexor digitorum profundus) | Fingers 2–5 (lateral edges of extensional expansions on first phalanges) |
| Intermediate muscles | Adducts and flexes each finger at metacarpo-phalangeal joints; extends each finger at interphalangeal joints | Fingers | Adduction; flexion; extension | Palmar interossei | Side of each metacarpal that faces metacarpal 3 (absent from metacarpal 3) | Extensor expansion on first phalanx of each finger (except finger 3) on side facing finger 3 |
| Intermediate muscles | Abducts and flexes the three middle fingers at metacarpo-phalangeal joints; extends the three middle fingers at interphalangeal joints | Fingers | Abduction; flexion; extension | Dorsal interossei | Sides of metacarpals | Both sides of finger 3; for each other finger, extensor expansion over first phalanx on side opposite finger 3 |
The clavicle and scapula make up the pectoral girdle, which provides a stable origin for the muscles that move the humerus. The muscles that position and stabilize the pectoral girdle are located on the thorax. The anterior thoracic muscles are the subclavius, pectoralis minor, and the serratus anterior. The posterior thoracic muscles are the trapezius, levator scapulae, rhomboid major, and rhomboid minor. Nine muscles cross the shoulder joint to move the humerus. The ones that originate on the axial skeleton are the pectoralis major and the latissimus dorsi. The deltoid, subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres major, teres minor, and coracobrachialis originate on the scapula.
The forearm flexors include the biceps brachii, brachialis, and brachioradialis. The extensors are the triceps brachii and anconeus. The pronators are the pronator teres and the pronator quadratus. The supinator is the only one that turns the forearm anteriorly.
The extrinsic muscles of the hands originate along the forearm and insert into the hand in order to facilitate crude movements of the wrists, hands, and fingers. The superficial anterior compartment of the forearm produces flexion. These muscles are the flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor carpi ulnaris, and the flexor digitorum superficialis. The deep anterior compartment produces flexion as well. These are the flexor pollicis longus and the flexor digitorum profundus. The rest of the compartments produce extension. The extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi, and extensor carpi ulnaris are the muscles found in the superficial posterior compartment. The deep posterior compartment includes the abductor longus, extensor pollicis brevis, extensor pollicis longus, and the extensor indicis.
Finally, the intrinsic muscles of the hands allow our fingers to make precise movements, such as typing and writing. They both originate and insert within the hand. The thenar muscles, which are located on the lateral part of the palm, are the abductor pollicis brevis, opponens pollicis, flexor pollicis brevis, and adductor pollicis. The hypothenar muscles, which are located on the medial part of the palm, are the abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi brevis, and opponens digiti minimi. The intermediate muscles, located in the middle of the palm, are the lumbricals, palmar interossei, and dorsal interossei.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?