| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
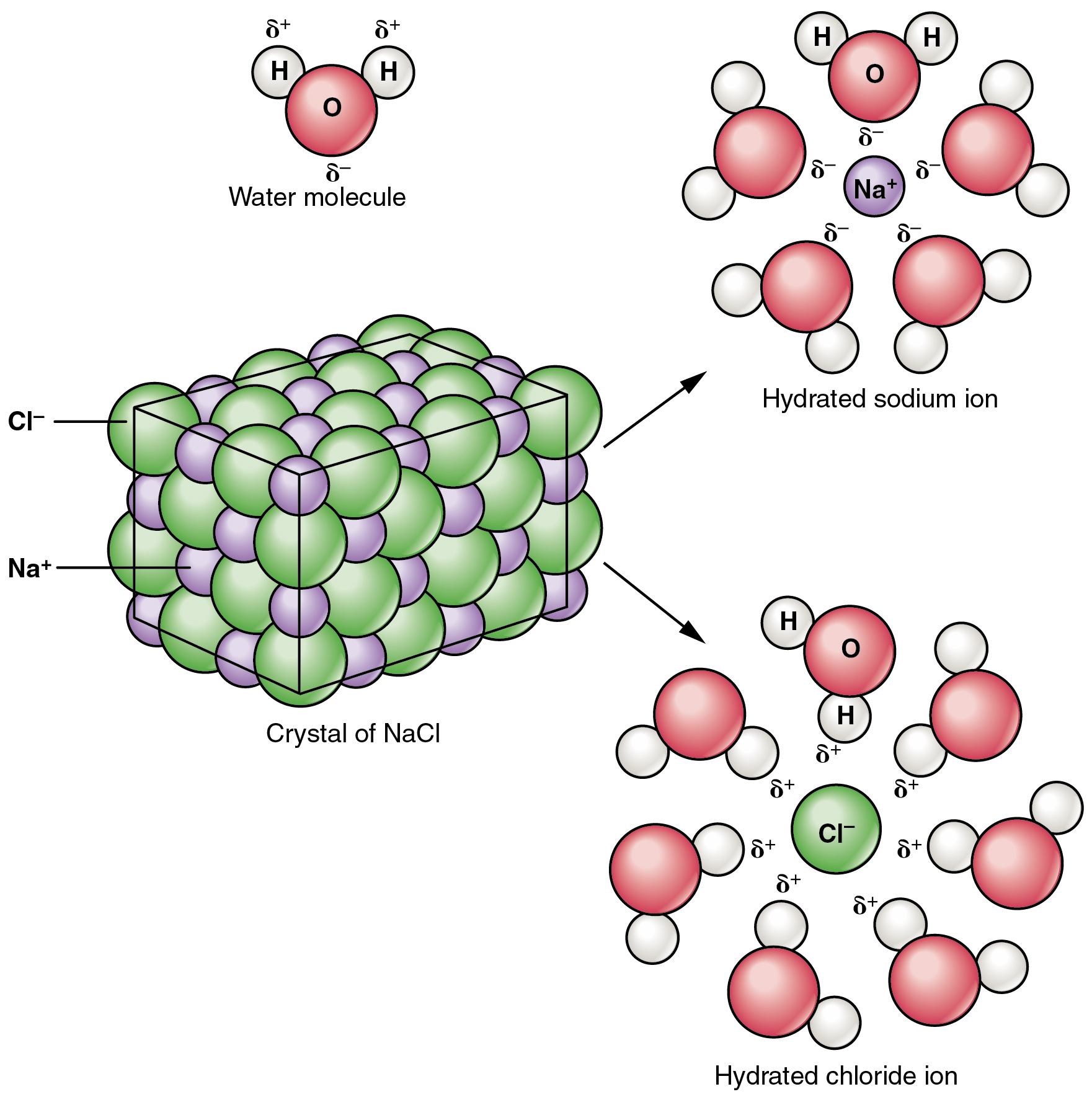
Many other salts are important in the body. For example, bile salts produced by the liver help break apart dietary fats, and calcium phosphate salts form the mineral portion of teeth and bones.
Acids and bases, like salts, dissociate in water into electrolytes. Acids and bases can very much change the properties of the solutions in which they are dissolved.
An acid is a substance that releases hydrogen ions (H + ) in solution ( [link] a ). Because an atom of hydrogen has just one proton and one electron, a positively charged hydrogen ion is simply a proton. This solitary proton is highly likely to participate in chemical reactions. Strong acids are compounds that release all of their H + in solution; that is, they ionize completely. Hydrochloric acid (HCl), which is released from cells in the lining of the stomach, is a strong acid because it releases all of its H + in the stomach’s watery environment. This strong acid aids in digestion and kills ingested microbes. Weak acids do not ionize completely; that is, some of their hydrogen ions remain bonded within a compound in solution. An example of a weak acid is vinegar, or acetic acid; it is called acetate after it gives up a proton.
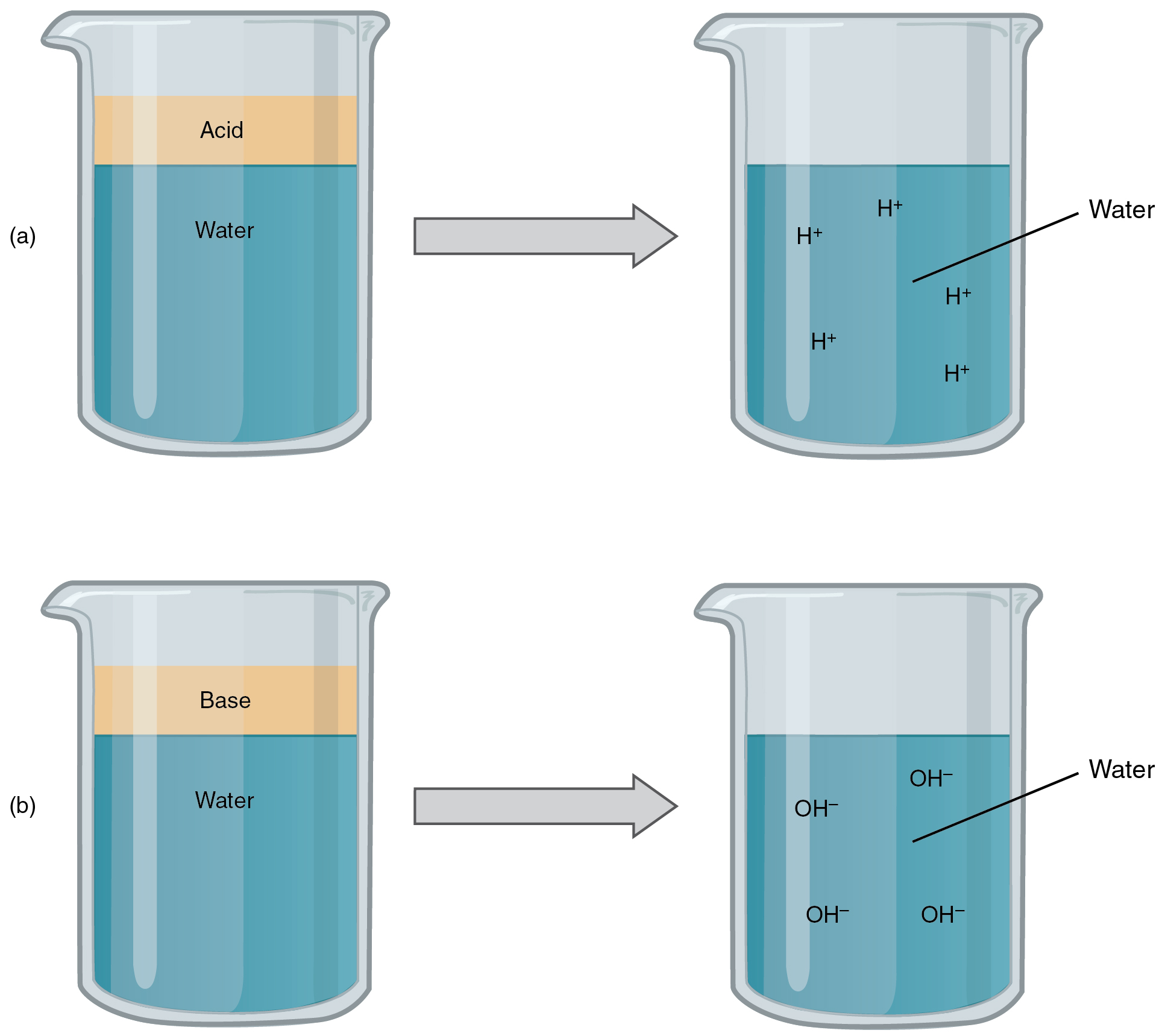
A base is a substance that releases hydroxyl ions (OH – ) in solution, or one that accepts H + already present in solution (see [link] b ). The hydroxyl ions (also known as hydroxide ions) or other basic substances combine with H + present to form a water molecule, thereby removing H + and reducing the solution’s acidity. Strong bases release most or all of their hydroxyl ions; weak bases release only some hydroxyl ions or absorb only a few H + . Food mixed with hydrochloric acid from the stomach would burn the small intestine, the next portion of the digestive tract after the stomach, if it were not for the release of bicarbonate (HCO 3 – ), a weak base that attracts H + . Bicarbonate accepts some of the H + protons, thereby reducing the acidity of the solution.
The relative acidity or alkalinity of a solution can be indicated by its pH. A solution’s pH is the negative, base-10 logarithm of the hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration of the solution. As an example, a pH 4 solution has an H + concentration that is ten times greater than that of a pH 5 solution. That is, a solution with a pH of 4 is ten times more acidic than a solution with a pH of 5. The concept of pH will begin to make more sense when you study the pH scale, like that shown in [link] . The scale consists of a series of increments ranging from 0 to 14. A solution with a pH of 7 is considered neutral—neither acidic nor basic. Pure water has a pH of 7. The lower the number below 7, the more acidic the solution, or the greater the concentration of H + . The concentration of hydrogen ions at each pH value is 10 times different than the next pH. For instance, a pH value of 4 corresponds to a proton concentration of 10 –4 M, or 0.0001M, while a pH value of 5 corresponds to a proton concentration of 10 –5 M, or 0.00001M. The higher the number above 7, the more basic (alkaline) the solution, or the lower the concentration of H + . Human urine, for example, is ten times more acidic than pure water, and HCl is 10,000,000 times more acidic than water.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?