| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Similarly, if is a factor of then the remainder of the Division Algorithm is 0. This tells us that is a zero.
This pair of implications is the Factor Theorem. As we will soon see, a polynomial of degree in the complex number system will have zeros. We can use the Factor Theorem to completely factor a polynomial into the product of factors. Once the polynomial has been completely factored, we can easily determine the zeros of the polynomial.
According to the Factor Theorem , is a zero of if and only if is a factor of
Given a factor and a third-degree polynomial, use the Factor Theorem to factor the polynomial.
Show that is a factor of Find the remaining factors. Use the factors to determine the zeros of the polynomial .
We can use synthetic division to show that
is a factor of the polynomial.
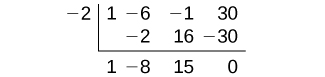
The remainder is zero, so is a factor of the polynomial. We can use the Division Algorithm to write the polynomial as the product of the divisor and the quotient:
We can factor the quadratic factor to write the polynomial as
By the Factor Theorem, the zeros of are –2, 3, and 5.
Use the Factor Theorem to find the zeros of given that is a factor of the polynomial.
The zeros are 2, –2, and –4.
Another use for the Remainder Theorem is to test whether a rational number is a zero for a given polynomial. But first we need a pool of rational numbers to test. The Rational Zero Theorem helps us to narrow down the number of possible rational zeros using the ratio of the factors of the constant term and factors of the leading coefficient of the polynomial
Consider a quadratic function with two zeros, and By the Factor Theorem, these zeros have factors associated with them. Let us set each factor equal to 0, and then construct the original quadratic function absent its stretching factor.

Notice that two of the factors of the constant term, 6, are the two numerators from the original rational roots: 2 and 3. Similarly, two of the factors from the leading coefficient, 20, are the two denominators from the original rational roots: 5 and 4.
We can infer that the numerators of the rational roots will always be factors of the constant term and the denominators will be factors of the leading coefficient. This is the essence of the Rational Zero Theorem; it is a means to give us a pool of possible rational zeros.
The Rational Zero Theorem states that, if the polynomial has integer coefficients, then every rational zero of has the form where is a factor of the constant term and is a factor of the leading coefficient
When the leading coefficient is 1, the possible rational zeros are the factors of the constant term.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?