| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The vertical asymptotes of a rational function may be found by examining the factors of the denominator that are not common to the factors in the numerator. Vertical asymptotes occur at the zeros of such factors.
Given a rational function, identify any vertical asymptotes of its graph.
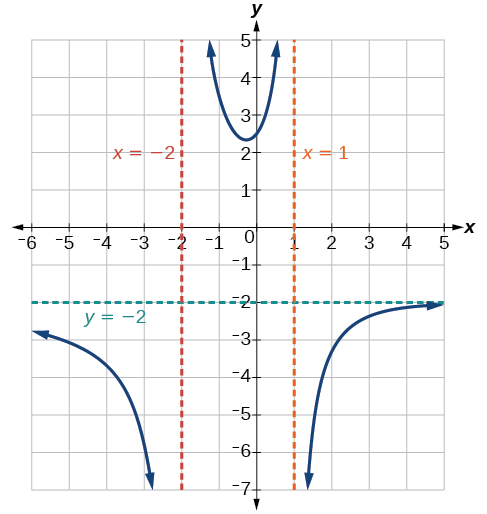
Find the vertical asymptotes of the graph of
First, factor the numerator and denominator.
To find the vertical asymptotes, we determine where this function will be undefined by setting the denominator equal to zero:
Neither nor are zeros of the numerator, so the two values indicate two vertical asymptotes. The graph in [link] confirms the location of the two vertical asymptotes.
Occasionally, a graph will contain a hole: a single point where the graph is not defined, indicated by an open circle. We call such a hole a removable discontinuity .
For example, the function may be re-written by factoring the numerator and the denominator.
Notice that is a common factor to the numerator and the denominator. The zero of this factor, is the location of the removable discontinuity. Notice also that is not a factor in both the numerator and denominator. The zero of this factor, is the vertical asymptote. See [link] . [Note that removable discontinuities may not be visible when we use a graphing calculator, depending upon the window selected.]
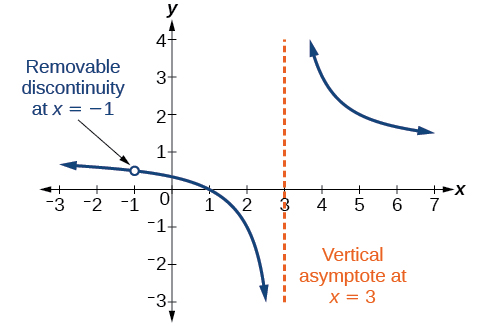
A removable discontinuity occurs in the graph of a rational function at if is a zero for a factor in the denominator that is common with a factor in the numerator. We factor the numerator and denominator and check for common factors. If we find any, we set the common factor equal to 0 and solve. This is the location of the removable discontinuity. This is true if the multiplicity of this factor is greater than or equal to that in the denominator. If the multiplicity of this factor is greater in the denominator, then there is still an asymptote at that value.
Find the vertical asymptotes and removable discontinuities of the graph of
Factor the numerator and the denominator.
Notice that there is a common factor in the numerator and the denominator, The zero for this factor is This is the location of the removable discontinuity.
Notice that there is a factor in the denominator that is not in the numerator, The zero for this factor is The vertical asymptote is See [link] .
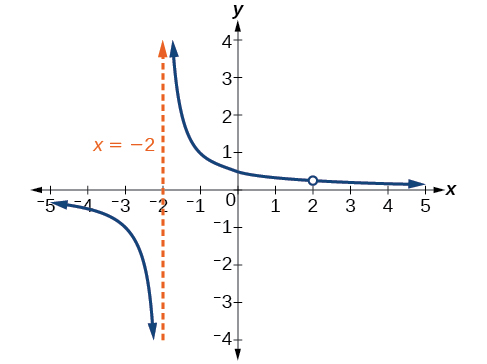
The graph of this function will have the vertical asymptote at but at the graph will have a hole.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?