| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Find the vertical and horizontal asymptotes of the function:
Vertical asymptotes at and horizontal asymptote at
A rational function will have a y -intercept at , if the function is defined at zero. A rational function will not have a y -intercept if the function is not defined at zero.
Likewise, a rational function will have x -intercepts at the inputs that cause the output to be zero. Since a fraction is only equal to zero when the numerator is zero, x -intercepts can only occur when the numerator of the rational function is equal to zero.
Find the intercepts of
We can find the y -intercept by evaluating the function at zero
The x -intercepts will occur when the function is equal to zero:
The y -intercept is the x -intercepts are and See [link] .
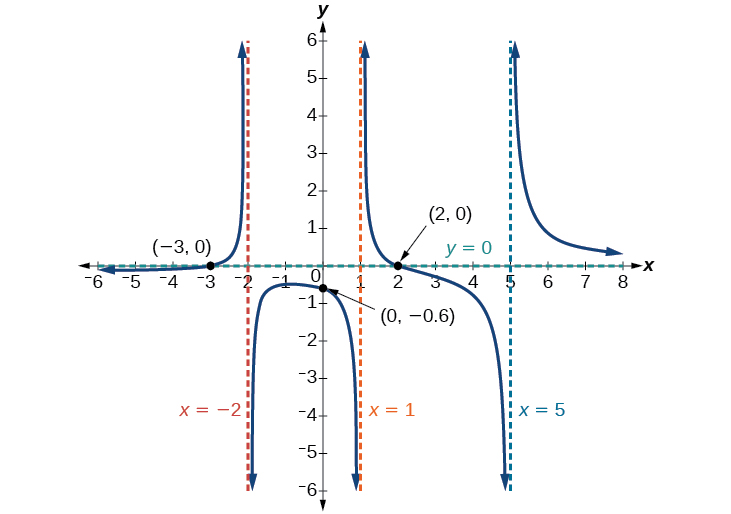
Given the reciprocal squared function that is shifted right 3 units and down 4 units, write this as a rational function. Then, find the x - and y -intercepts and the horizontal and vertical asymptotes.
For the transformed reciprocal squared function, we find the rational form.
Because the numerator is the same degree as the denominator we know that as is the horizontal asymptote. Next, we set the denominator equal to zero, and find that the vertical asymptote is because as We then set the numerator equal to 0 and find the x -intercepts are at and Finally, we evaluate the function at 0 and find the y -intercept to be at
In [link] , we see that the numerator of a rational function reveals the x -intercepts of the graph, whereas the denominator reveals the vertical asymptotes of the graph. As with polynomials, factors of the numerator may have integer powers greater than one. Fortunately, the effect on the shape of the graph at those intercepts is the same as we saw with polynomials.
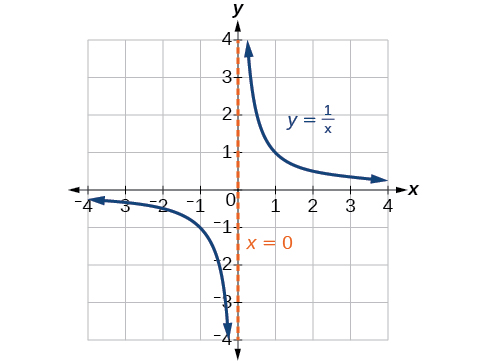
The vertical asymptotes associated with the factors of the denominator will mirror one of the two toolkit reciprocal functions. When the degree of the factor in the denominator is odd, the distinguishing characteristic is that on one side of the vertical asymptote the graph heads towards positive infinity, and on the other side the graph heads towards negative infinity. See [link] .
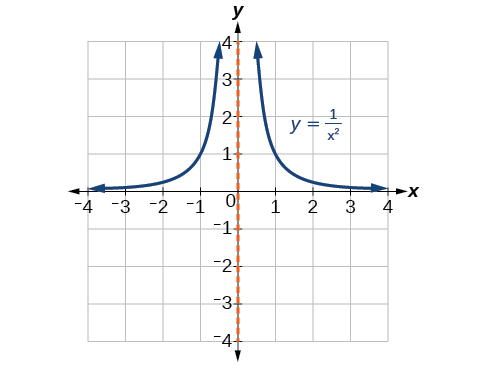
When the degree of the factor in the denominator is even, the distinguishing characteristic is that the graph either heads toward positive infinity on both sides of the vertical asymptote or heads toward negative infinity on both sides. See [link] .
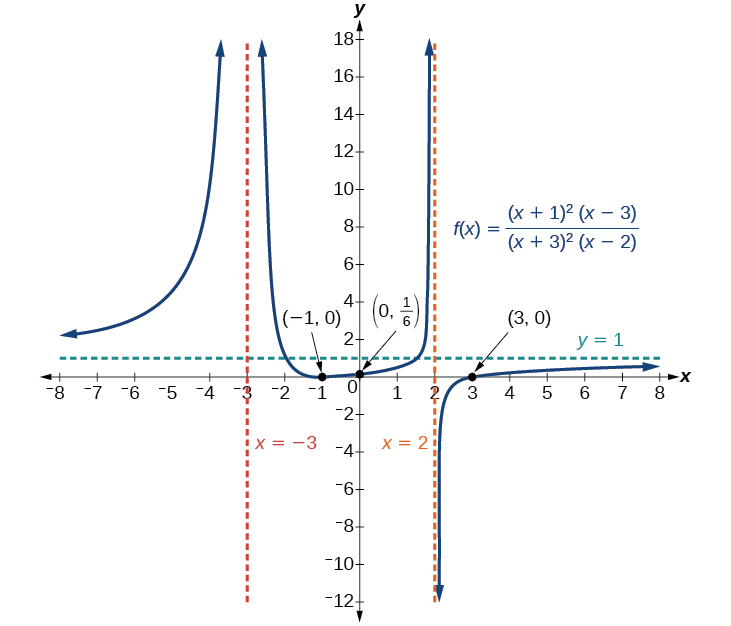
For example, the graph of is shown in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?